"OKEXの先物取引のヘッジ戦略のC++バージョン"で 硬い定量戦略を紹介します
作者: リン・ハーン優しさ, 作成日:2019-08-29 16:05:07, 更新日:2025-01-15 22:07:49
ヘージング戦略について言えば,さまざまな市場には様々な種類,多様な組み合わせ,多様なアイデアがあります.我々は最も古典的な間間ヘージングからヘージング戦略のデザインアイデアと概念を探索します.今日,暗号通貨市場は最初よりもはるかに活発であり,また,仲介ヘージングの機会をたくさん提供する多くの先物契約取引所もあります.スポットクロスマーケット・アービタージ,キャッシュ・ヘージング・アービタージ,先物間間間間間間 arbitrage,先物間間市場 arbitrageなど,暗号定量取引戦略が一つずつ出現しています.C++で書かれた
戦略の原則
戦略はC++で書かれているため,戦略読み方が少し難しいため,なぜ戦略が少しハードコアなのか.しかし,読者がこの戦略のデザインとアイデアの本質を学ぶことを妨げない.戦略論理は比較的シンプルで,コード長さは中程度で,わずか500行です.市場データ取得の観点から,
戦略構造は合理的であり,コード結合度は非常に低く,拡張または最適化するのが便利である.論理は明確であり,そのようなデザインは理解しやすいだけでなく,教材としてこの戦略の設計を学ぶことも良い例である.この戦略の原則は比較的シンプルである.すなわち,先行契約と最近の契約のスプレッドが正または否定的であるか?基本的な原則は,商品先物間の時間間のヘッジと一致している.
- ポジティブ・スプレッド ショート・フォワード・コントラクトの販売 長期・最近のコントラクトの購入
- 負のスプレッドで 長期先行契約を買い 近年の契約を短売り
基本原理を理解した後,残りは,戦略がヘッジのオープニングポジションを起動する方法,ポジションを閉じる方法,ポジションを追加する方法,総ポジション制御方法,その他の戦略の詳細処理です.
ヘージング戦略は主に対象価格差 (スプレッド) の変動とその回帰に関わります.しかし,差はわずかに変動するか,急激に振動するか,または1つの方向に振舞う可能性があります.
これは,利益と損失のヘッジに関する不確実性をもたらしますが,リスクは一方的なトレンドよりもまだはるかに小さいです. インターテンポラル戦略のさまざまな最適化のために,ポジション制御レベルと開閉・閉じるトリガー条件からスタートすることを選択できます. 例えば,価格変動を決定するために,古典的な
戦略コードの分析
このコードは4つの部分に分かれています このコードは
値定義をリストし,いくつかの状態値を定義し,状態をマークするために使用する. urlエンコーディング機能,時間変換機能など,戦略に関連していないいくつかの機能は,データ処理のための戦略論理とは関係ありません.
K線データ生成器クラス:この戦略は,生成器クラスオブジェクトによって生成されるK線データによって動かす.
ヘージングクラス:このクラスのオブジェクトは,特定の取引論理,ヘージングオペレーション,戦略の処理詳細を実行することができます.
戦略の主な機能は,
main 関数である. 主な機能は戦略の入力機能である. 主なループはこの関数の内部で実行される. さらに,この機能は重要な操作も実行する.つまり,取引所のウェブソケットインターフェースにアクセスし,Kラインデータジェネレーターとしてプッシュされた生ティック市場データを取得する.
戦略コードの全体的な理解を通じて 戦略の様々な側面を徐々に学び 次に戦略のデザインやアイデアやスキルを研究することができます
- 列挙値の定義,他の機能機能
- 列挙されたタイプ
State声明
enum State { // Enum type defines some states
STATE_NA, // Abnormal state
STATE_IDLE, // idle
STATE_HOLD_LONG, // holding long positions
STATE_HOLD_SHORT, // holding short positions
};
この状態は,数値型で定義されます.State.
その姿を見てSTATE_NAコードに表示されるのは異常でSTATE_IDLE稼働していない状態,つまり 稼働状態がカバーできる状態です.STATE_HOLD_LONGポジティブなヘッジポジションが保持されている状態です.STATE_HOLD_SHORT負のヘッジポジションが保持されている状態です.
- この戦略では呼び出されていない文字列置き換えは,主に文字列を扱う代替ユーティリティ関数です.
string replace(string s, const string from, const string& to)
- ヘクサデシマル文字に変換する関数
toHex
inline unsigned char toHex(unsigned char x)
- urlコード関数を処理する
std::string urlencode(const std::string& str)
- 文字列形式の時間をタイムスタンプに変換する時間変換関数.
uint64_t _Time(string &s)
- K線データ生成器クラス
class BarFeeder { // K line data generator class
public:
BarFeeder(int period) : _period(period) { // constructor with argument "period" period, initialized in initialization list
_rs.Valid = true; // Initialize the "Valid" property of the K-line data in the constructor body.
}
void feed(double price, chart *c=nullptr, int chartIdx=0) { // input data, "nullptr" null pointer type, "chartIdx" index default parameter is 0
uint64_t epoch = uint64_t(Unix() / _period) * _period * 1000; // The second-level timestamp removes the incomplete time period (incomplete _period seconds) and is converted to a millisecond timestamp.
bool newBar = false; // mark the tag variable of the new K line Bar
if (_rs.size() == 0 || _rs[_rs.size()-1].Time < epoch) { // if the K line data is 0 in length. Or the last bar's timestamp is less than epoch (the last bar of the K line is more than the current most recent cycle timestamp)
record r; // declare a K line bar structure
r.Time = epoch; // construct the K line bar of the current cycle
r.Open = r.High = r.Low = r.close = price; // Initialize the property
_rs.push_back(r); // K line bar is pressed into the K line data structure
if (_rs.size() > 2000) { // if the K-line data structure length exceeds 2000, the oldest data is removed.
_rs.erase(_rs.begin());
}
newBar = true; // tag
} else { // In other cases, it is not the case of a new bar.
record &r = _rs[_rs.size() - 1]; // Reference the data of the last bar in the data.
r.High = max(r.High, price); // The highest price update operation for the referenced data.
r.Low = min(r.Low, price); // The lowest price update operation for the referenced data.
r.close = price; // Update the closing price of the referenced data.
}
auto bar = _rs[_rs.size()-1]; // Take the last column data and assign it to the bar variable
json point = {bar.Time, bar.Open, bar.High, bar.Low, bar.close}; // construct a json type data
if (c != nullptr) { // The chart object pointer is not equal to the null pointer, do the following.
if (newBar) { // judge if the new Bar appears
c->add(chartIdx, point); // call the chart object member function add to insert data into the chart object (new k line bar)
c->reset(1000); // retain only 1000 bar of data
} else {
c->add(chartIdx, point, -1); // Otherwise update (not new bar), this point (update this bar).
}
}
}
records & get() { // member function, method for getting K line data.
Return _rs; // Returns the object's private variable _rs . (ie generated K-line data)
}
private:
int _period;
records _rs;
};
このクラスは,主に,戦略ヘッジ論理を動かすために,取得されたティックデータを差K線に処理する責任があります.
ティックデータをなぜ使うのか?なぜK線データジェネレータをこのように構築するのか?K線データを直接使うのは良いことではないのか?この種の質問は3回の爆発で発行されています.いくつかのヘッジ戦略を書いたとき,私は騒ぎも起こしました.私は
2つの契約間の差のK線データは,一定の期間の差値変化統計である.したがって,単に2つの契約のそれぞれのK線データを引くために取り,各K線バー上の各データの差を計算することは不可能である.最も明らかな誤りは,例えば,必ずしも同時に2つの契約の最高価格と最低価格である.したがって,引いた値はあまり意味がない.
したがって,リアルタイムで差を計算し,リアルタイムで特定の期間の価格変化 (つまり,K線列の最高,最低,オープン,閉鎖価格) を計算するために,リアルタイムでティックデータを使用する必要があります.
- 負債の負債の負債
class Hedge { // Hedging class, the main logic of the strategy.
public:
Hedge() { // constructor
...
};
State getState(string &symbolA, depth &depthA, string &symbolB, depth &depthB) { // Get state, parameters: contract A name, contract A depth data, contract B name, contract B depth data
...
}
bool Loop(string &symbolA, depth &depthA, string &symbolB, depth &depthB, string extra="") { // Opening and closing position main logic
...
}
private:
vector<double> _addArr; // Hedging adding position list
string _state_desc[4] = {"NA", "IDLE", "LONG", "SHORT"}; // Status value Description
int _countOpen = 0; // number of opening positions
int _countcover = 0; // number of closing positions
int _lastcache = 0; //
int _hedgecount = 0; // number of hedging
int _loopcount = 0; // loop count (cycle count)
double _holdPrice = 0; // holding position price
BarFeeder _feederA = BarFeeder(DPeriod); // A contract Quote K line generator
BarFeeder _feederB = BarFeeder(DPeriod); // B contract Quote K line generator
State _st = STATE_NA; // Hedging type Object Hedging position status
string _cfgStr; // chart configuration string
double _holdAmount = 0; // holding position amount
bool _iscover = false; // the tag of whether to close the position
bool _needcheckOrder = true; // Set whether to check the order
chart _c = chart(""); // chart object and initialize
};
コードが比較的長いため,いくつかの部分は省略されています.これは主にこのヘッジクラスの構造を示しています.コンストラクターヘッジ関数は省略されています.主にオブジェクト初期化の目的です.次に,2つの主要な
getState を取得する
この機能は,主にオーダー検査,オーダーキャンセル,ポジション検出,ポジションバランスなどに対応する.ヘジング取引の過程で,単一のステップ (つまり,契約が実行され,もう1つは実行されない) を回避することは不可能であるため,配置オーダー論理で審査が行われ,その後再送信オーダー操作または閉じるポジション操作の処理は,戦略論理は混沌とします.
一歩のヘッジがあるかどうかに関わらず,デフォルトはヘッジが成功し,その後ポジションバランスが検出されます. 取引は,取引先で実行されます. 取引は,取引先で実行されます.getStateバランスの処理の論理は独立して処理されます.
ループ
戦略の取引ロジックは,この関数に収められています.getState差のK線データを生成するために,K線データ生成物 (K-line data generator object) が呼ばれ,開封,閉封,位置論理の追加判断が実行されます.また,チャートのためのいくつかのデータ更新操作があります.
- 戦略の主な機能
void main() {
...
string realSymbolA = exchange.SetcontractType(symbolA)["instrument"]; // Get the A contract (this_week / next_week / quarter ), the real contract ID corresponding to the week, next week, and quarter of the OKEX futures contract.
string realSymbolB = exchange.SetcontractType(symbolB)["instrument"]; // ...
string qs = urlencode(json({{"op", "subscribe"}, {"args", {"futures/depth5:" + realSymbolA, "futures/depth5:" + realSymbolB}}}).dump()) ; // jSON encoding, url encoding for the parameters to be passed on the ws interface
Log("try connect to websocket"); // Print the information of the connection WS interface.
auto ws = Dial("wss://real.okex.com:10442/ws/v3|compress=gzip_raw&mode=recv&reconnect=true&payload="+qs); // call the FMZ API "Dial" function to acess the WS interface of OKEX Futures
Log("connect to websocket sucess");
depth depthA, depthB; // Declare two variables of the depth data structure to store the depth data of the A contract and the B contract
auto filldepth = [](json &data, depth &d) { // construct the code for the depth data with the json data returned by the interface.
d.Valid = true;
d.Asks.clear();
d.Asks.push_back({atof(string(data["asks"][0][0]).c_str()), atof(string(data["asks"][0][1]).c_str( ))});
d.Bids.clear();
d.Bids.push_back({atof(string(data["bids"][0][0]).c_str()), atof(string(data["bids"][0][1]).c_str( ))});
};
string timeA; // time string A
string timeB; // time string B
while (true) {
auto buf = ws.read(); // Read the data pushed by the WS interface
...
}
ストラテジーが起動された後,メイン機能から実行される.メイン機能の初期化では,戦略はウェブソケットインターフェイスのティックマーケットにサブスクリプトする.メイン機能の主な仕事は,取引所のウェブソケットインターフェイスによって押し出されたティック・コートを継続的に受信し,その後ヘッジクラスオブジェクトのメンバー関数:ループ関数を呼び出すメインループを構築することです.ループ関数の取引論理は市場データによって動きます.
上記に言及したティックマーケットは,実際には各ファイルのオーダーブックデータであるサブスクリプションオーダー薄深度データインターフェースである.しかし,この戦略は最初のデータファイルのみを使用し,実際には,ティックマーケットデータとほぼ同じです.この戦略は他のファイルのデータを使用せず,最初のファイルのオーダー値を使用しません.
Webソケットインターフェースのデータへの戦略のサブスクリプションと設定方法について詳しく見てみましょう.
string qs = urlencode(json({{"op", "subscribe"}, {"args", {"futures/depth5:" + realSymbolA, "futures/depth5:" + realSymbolB}}}).dump());
Log("try connect to websocket");
auto ws = Dial("wss://real.okex.com:10442/ws/v3|compress=gzip_raw&mode=recv&reconnect=true&payload="+qs);
Log("connect to websocket sucess");
登録されたインターフェースが送った json パラメータの url コード,つまり,payloadFMZ Quant プラットフォームの API インターフェース関数を呼び出すことですDial機能Dial接続の自動再接続 (サブスクリプションメッセージは依然として値を使用します) を設定します.qs文字列payloadこの関数を達成するには,パラメータ文字列に設定を追加する必要があります.Dial function.
初期にDial機能パラメータは次のとおりです.
wss://real.okex.com:10442/ws/v3
これはアクセスする必要がある Webソケットインターフェースのアドレスで,
|Parameter name|description|
|-|-|
|compress|compress is compression mode, OKEX websocket interface uses gzip_raw this way, so it is set to gzip_raw|
|mode|Mode is mode, optional dual, send and recv three kind. Dual is bidirectional, sending compressed data and receiving compressed data. Send is to send compressed data. Recv receives the compressed data and decompresses it locally.|
|reconnect|Reconnect is set to reconnect, reconnect=true to enable reconnection, no default is not reconnected.|
|payload|The payload is a subscription message that needs to be sent when ws is reconnected.|
After this setting, even if the websocket connection is disconnected, FMZ Quant trading platform's underlying system of the docker system will automatically reconnect and get the latest market data in time.
Grab every price fluctuation and quickly capture the right hedge.
- Position control
Position control is controlled using a ratio of hedge positions similar to the “Fibonaci” series.
for (int i = 0; i < AddMax + 1; i++) { //は,ヘッジの数に対するボフィナック配列の比率に類似した,スケールアップの数を制御するデータ構造を構築します.
if (_addArr.size() < 2) { // 最初の2つの追加ポジションは,ヘッジの数を倍にするように変更されます.
_addArr.push_back (((i+1)*OpenAmount) );
{ \ pos (192,220) }
_addArr.push_back ((_addArr[_addArr.size()-1] + _addArr[_addArr.size()-2]); // 最後の2つの追加位置が加算され,現在の位置量は計算され,データ構造
It can be seen that the number of additional positions added each time is the sum of the last two positions.
Such position control can realize the larger the difference, the relative increase of the arbitrage hedge, and the dispersion of the position, so as to grasp the small position of the small price fluctuation, and the large price fluctuation position is appropriately increased.
- closing position: stop loss and take profit
Fixed stop loss spread and take profit spread.
When the position difference reaches the take profit position and the stop loss position, the take profit and stop loss are carried out.
- The designing of entering the market and leaving the market
The period of the parameter ```NPeriod``` control provides some dynamic control over the opening and closing position of the strategy.
- Strategy chart
The strategy automatically generates a spread K-line chart to mark relevant transaction information.
c++ strategy custom chart drawing operation is also very simple. You can see that in the constructor of the hedge class, we use the written chart configuration string ```_cfgStr``` to configure the chart object ```_c```, ```_c``` is the private component of the hedge class. When the private member is initialized, the ```chart``` object constructed by the FMZ Quant platform custom chart API interface function is called.
_cfgStr = R
呼び出し _c.update(_cfgStr); チャートオブジェクトに設定するには _cfgStr を使用します.
_c.reset() を呼び出す.チャートデータをリセットする.
When the strategy code needs to insert data into the chart, it also calls the member function of the ```_c``` object directly, or passes the reference of ```_c``` as a parameter, and then calls the object member function (method) of ```_c``` to update the chart data and insert operation.
E.g:
_c.add(chartIdx, {{
After placing the order, mark the K line chart.
As follows, when drawing a K line, a reference to the chart object ```_c``` is passed as a parameter when calling the member function ```feed``` of the ```BarFeeder``` class.
無効入力 (二重価格,チャート *c=nullptr,intチャートIdx=0)
That is, the formal parameter ```c``` of the ```feed``` function.
json point = {bar.Time, bar.Open, bar.High, bar.Low, bar.close}; // json型データを作成する
if (c!= nullptr) { // チャートオブジェクトポインタが nullポインタに等しくない場合は,次の操作を行います.
if (newBar) { // newBar が表示されるかどうかを判断する
c->add(chartIdx,点); //チャートオブジェクトメンバー関数
Insert a new K-line Bar data into the chart by calling the ```add``` member function of the chart object ```_c```.
c->追加 (図)
バックテスト
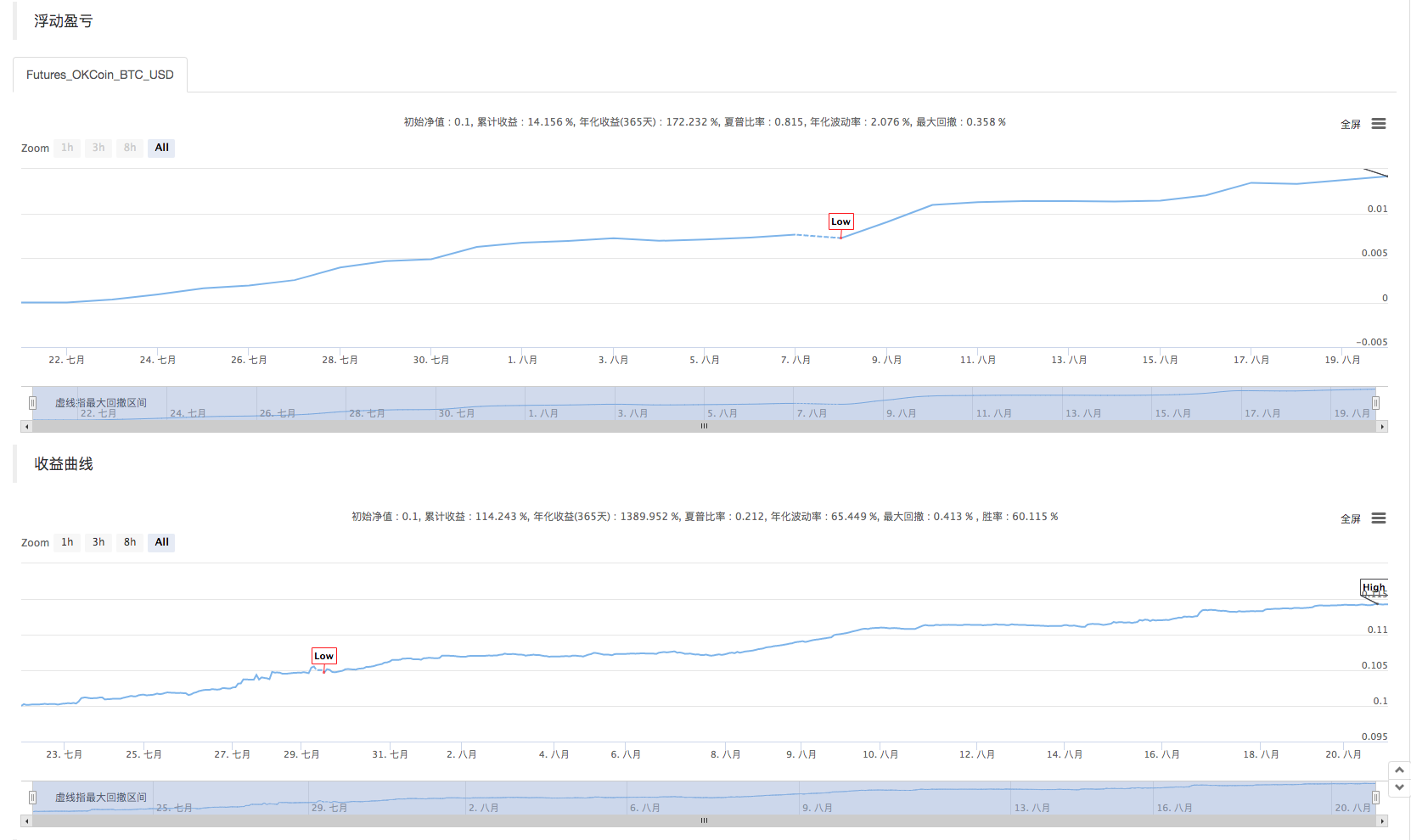
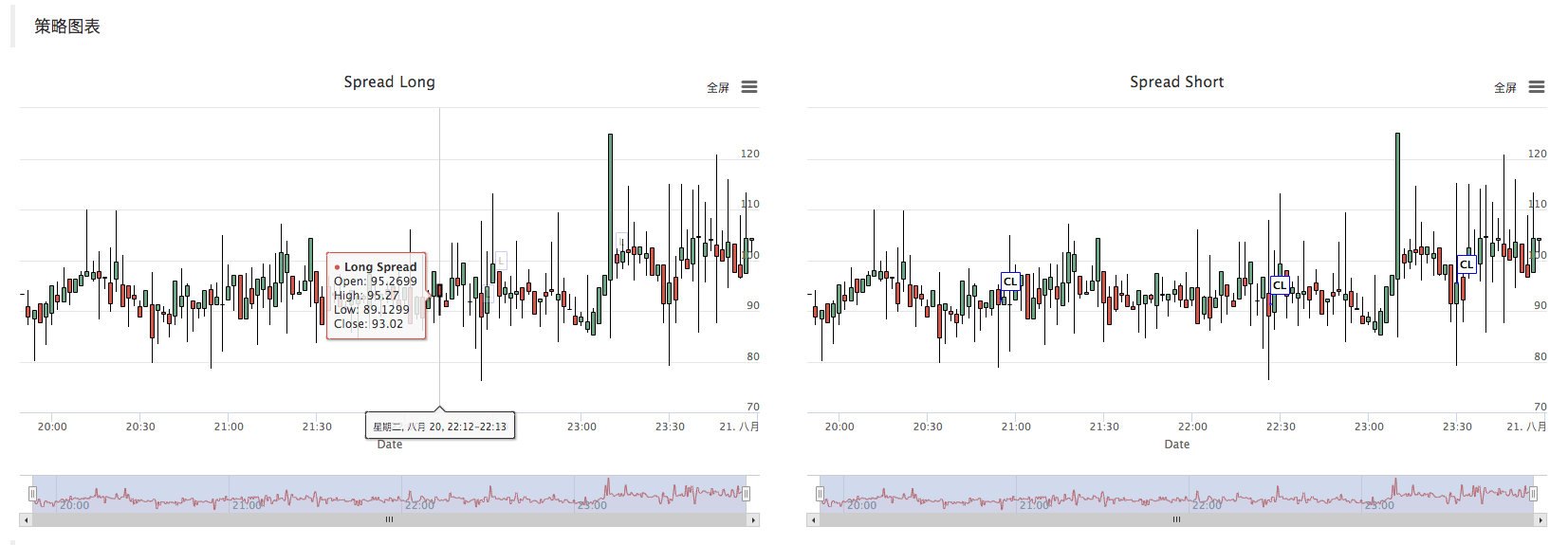

この戦略は,学習とコミュニケーションの目的のみです.実際の市場でそれを適用する場合は,市場の実際の状況に合わせて修正して最適化してください.
戦略アドレス:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/163447
FMZ Quantのプラットフォームに より興味深い戦略があります:https://www.fmz.com
- DEX取引所の定量実践 (2) -- ハイパーリキッドユーザーガイド
- DEX取引所の量化実践 (2) -- Hyperliquidの使用ガイド
- DEX取引所の定量実践 (1) -- dYdX v4 ユーザーガイド
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・レイグ・アービトラージへの導入 (3)
- DEX取引所の量化実践 ((1)-- dYdX v4 ユーザーガイド
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (3)
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (2)
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (2)
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する議論: 戦略におけるHttpサービス内蔵の信号受信のための完全なソリューション
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する探求:戦略内蔵Httpサービス信号受信の完全な方案
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (1)
- 商品先物取引と仮想通貨取引所の類似点と違い API
- ウェブソケットにシームレス接続する 古い戦略のインターフェースを教えます
- 多レベル 利得率戦略
- コモディティフューチャーとデジタル通貨取引所のAPIの違い
- 取引戦略におけるK線影部分の適用
- クリプト通貨の量的な取引戦略の交換構成
- 高頻度戦略バックテストのために開発された Tick レベルトランザクションマッチングメカニズム
- 取引戦略開発経験
- 定量取引におけるK線データ処理
- デジタル通貨量化取引戦略 取引所の配置詳細
- 取引における機械学習技術の応用
- "C++版 OKEXの契約ヘッジ戦略"
- 秩序ある排列の多空の均衡権益戦略を実現
- データ駆動技術によるペア取引
- デジタル通貨市場を量的に分析する
- Pythonで Dual Thrust デジタル通貨の量化取引戦略を実装する
- プログラム化取引におけるK線データ処理の浅谈
- Pythonで価格動力分析を実現する量的な取引戦略
- タイムシーケンスデータ分析とTickデータ復習
- 取引戦略開発の体験談