市場 コート コレクター 再びアップグレード
作者: リン・ハーン優しさ作成日:2020年5月26日 14:25:15 更新日:2024年12月10日 20:35:48
CSV形式のファイルインポートをサポートし,カスタムデータソースを提供
最近,トレーダーは自分のCSV形式のファイルを FMZプラットフォームバックテストシステムのためのデータソースとして使用する必要があります. 私たちのプラットフォームのバックテストシステムは多くの機能を持ち,使いやすくて効率的です. そのため,ユーザーが独自のデータを持っている限り,これらのデータに基づいてバックテストを行うことができます. これはもはや当社のプラットフォームデータセンターがサポートする取引所や品種に限定されていません.
デザインのアイデア
デザインのアイデアは,実際には非常にシンプルです. 我々は,前市場コレクターに基づいてそれを少し変更する必要があります. 我々はパラメータを追加します.isOnlySupportCSVバックテストシステムのデータソースとして CSV ファイルのみが使用されているかどうかを制御するために,市場収集者に.filePathForCSV市場収集ロボットが実行するサーバーに配置されたCSVデータファイルの経路を設定するために使用されます.isOnlySupportCSVパラメータは,Trueこの変更は主に,どのデータソースを使用するか (自分で収集したデータまたはCSVファイル内のデータ) を決定します.do_GET機能についてProvider class.
CSV ファイルとは?
CSVとしても知られ,分離文字もコンマであることもないため,文字分離値とも呼ばれます.そのファイルは,表データ (数字とテキスト) をプレーンテキストで保存します.プレーンテキストとは,ファイルは文字の連続であり,バイナリー数のように解釈されるべきデータを含まないことを意味します.CSVファイルは,任意の数個のレコードで構成され,いくつかのニューライン文字によって分離されます.各レコードはフィールドで構成され,フィールド間の分離点は他の文字または文字列であり,最も一般的なのはコンマまたはタブです.一般的に,すべてのレコードはフィールドの正確な同じ順序を持っています.それらは通常プレーンテキストファイルです.使用することが推奨されます.WORDPADまたはExcelオープンする
CSV ファイル形式の一般的な標準は存在しないが,特定のルールがある.一般的に一行あたり1つのレコードがあり,最初の行はヘッダである.各行内のデータはコンマで区切られている.
このようにノートパッドで開きます.
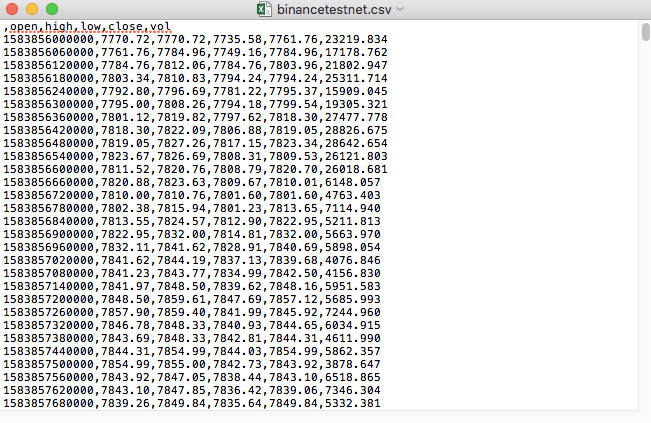
CSV ファイルの最初の行が表のヘッダーであることを確認しました.
,open,high,low,close,vol
バックテストシステムのカスタムデータソースが要求するフォーマットに構築する必要があります. このコードは,既に処理されています.
変更されたコード
import _thread
import pymongo
import json
import math
import csv
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from urllib.parse import parse_qs, urlparse
def url2Dict(url):
query = urlparse(url).query
params = parse_qs(query)
result = {key: params[key][0] for key in params}
return result
class Provider(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
global isOnlySupportCSV, filePathForCSV
try:
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
self.end_headers()
dictParam = url2Dict(self.path)
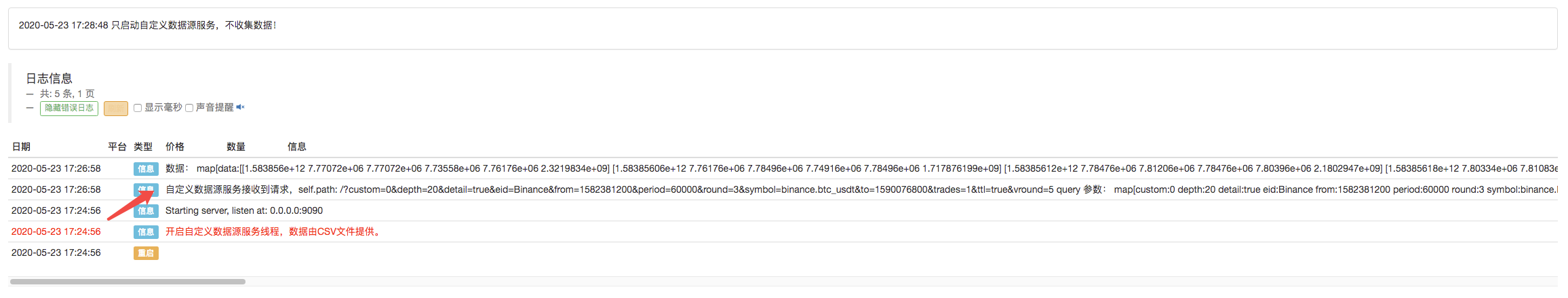
Log("The custom data source service receives the request,self.path:", self.path, "query parameter:", dictParam)
# At present, the backtest system can only select the exchange name from the list. When adding a custom data source, set it to Binance, that is: Binance
exName = exchange.GetName()
# Note that period is the bottom K-line period
tabName = "%s_%s" % ("records", int(int(dictParam["period"]) / 1000))
priceRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["round"]))
amountRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["vround"]))
fromTS = int(dictParam["from"]) * int(1000)
toTS = int(dictParam["to"]) * int(1000)
# Request data
data = {
"schema" : ["time", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"],
"data" : []
}
if isOnlySupportCSV:
# Handle CSV reading, filePathForCSV path
listDataSequence = []
with open(filePathForCSV, "r") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
# Get table header
header = next(reader)
headerIsNoneCount = 0
if len(header) != len(data["schema"]):
Log("The CSV file format is wrong, the number of columns is different, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
for ele in header:
for i in range(len(data["schema"])):
if data["schema"][i] == ele or ele == "":
if ele == "":
headerIsNoneCount += 1
if headerIsNoneCount > 1:
Log("The CSV file format is incorrect, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
listDataSequence.append(i)
break
# Read content
while True:
record = next(reader, -1)
if record == -1:
break
index = 0
arr = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for ele in record:
arr[listDataSequence[index]] = int(ele) if listDataSequence[index] == 0 else (int(float(ele) * amountRatio) if listDataSequence[index] == 5 else int(float(ele) * priceRatio))
index += 1
data["data"].append(arr)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
return
# Connect to the database
Log("Connect to the database service to obtain data, the database: ", exName, "table: ", tabName)
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
exRecords = ex_DB[tabName]
# Construct query conditions: greater than a certain value {'age': {'$ gt': 20}} less than a certain value {'age': {'$lt': 20}}
dbQuery = {"$and":[{'Time': {'$gt': fromTS}}, {'Time': {'$lt': toTS}}]}
Log("Query conditions: ", dbQuery, "Number of inquiries: ", exRecords.find(dbQuery).count(), "Total number of databases: ", exRecords.find().count())
for x in exRecords.find(dbQuery).sort("Time"):
# Need to process data accuracy according to request parameters round and vround
bar = [x["Time"], int(x["Open"] * priceRatio), int(x["High"] * priceRatio), int(x["Low"] * priceRatio), int(x["Close"] * priceRatio), int(x["Volume"] * amountRatio)]
data["data"].append(bar)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
# Write data response
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
except BaseException as e:
Log("Provider do_GET error, e:", e)
def createServer(host):
try:
server = HTTPServer(host, Provider)
Log("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host)
server.serve_forever()
except BaseException as e:
Log("createServer error, e:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
def main():
LogReset(1)
if (isOnlySupportCSV):
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Start the custom data source service thread, and the data is provided by the CSV file. ", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message: ", e)
raise Exception("stop")
while True:
LogStatus(_D(), "Only start the custom data source service, do not collect data!")
Sleep(2000)
exName = exchange.GetName()
period = exchange.GetPeriod()
Log("collect", exName, "Exchange K-line data,", "K line cycle:", period, "Second")
# Connect to the database service, service address mongodb: //127.0.0.1: 27017 See the settings of mongodb installed on the server
Log("Connect to the mongodb service of the hosting device, mongodb://localhost:27017")
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
# Create a database
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
# Print the current database table
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
Log("mongodb", exName, "collist:", collist)
# Check if the table is deleted
arrDropNames = json.loads(dropNames)
if isinstance(arrDropNames, list):
for i in range(len(arrDropNames)):
dropName = arrDropNames[i]
if isinstance(dropName, str):
if not dropName in collist:
continue
tab = ex_DB[dropName]
Log("dropName:", dropName, "delete:", dropName)
ret = tab.drop()
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
if dropName in collist:
Log(dropName, "failed to delete")
else :
Log(dropName, "successfully deleted")
# Start a thread to provide a custom data source service
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Open the custom data source service thread", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
# Create the records table
ex_DB_Records = ex_DB["%s_%d" % ("records", period)]
Log("Start collecting", exName, "K-line data", "cycle:", period, "Open (create) the database table:", "%s_%d" % ("records", period), "#FF0000")
preBarTime = 0
index = 1
while True:
r = _C(exchange.GetRecords)
if len(r) < 2:
Sleep(1000)
continue
if preBarTime == 0:
# Write all BAR data for the first time
for i in range(len(r) - 1):
bar = r[i]
# Write root by root, you need to determine whether the data already exists in the current database table, based on timestamp detection, if there is the data, then skip, if not write
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
# Write bar to the database table
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
elif preBarTime != r[-1]["Time"]:
bar = r[-2]
# Check before writing data, whether the data already exists, based on time stamp detection
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
LogStatus(_D(), "preBarTime:", preBarTime, "_D(preBarTime):", _D(preBarTime/1000), "index:", index)
# Increase drawing display
ext.PlotRecords(r, "%s_%d" % ("records", period))
Sleep(10000)
実行テスト
まず 市場収集ロボットを起動し ロボットに交換装置を加え ロボットが動かせます
パラメータ設定:
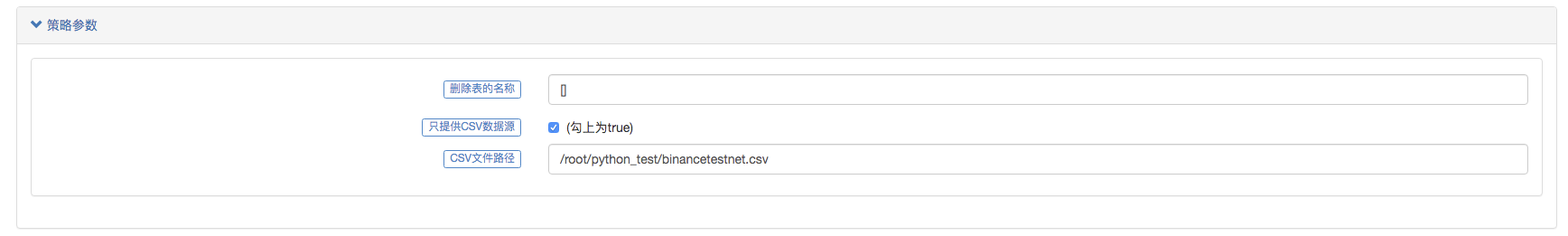
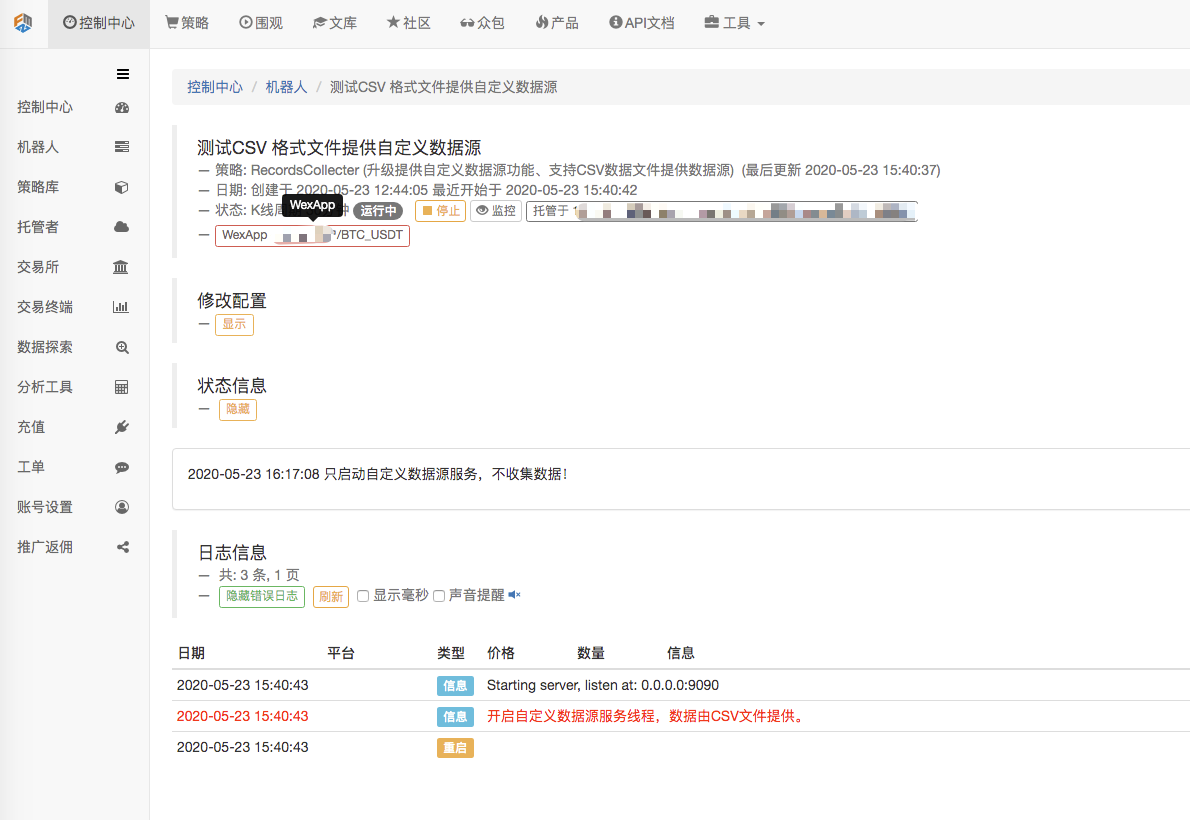
テスト戦略を作ります
function main() {
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
}
戦略はとてもシンプルです 3回だけK線データを取得して印刷します
バックテストページでは,バックテストシステムのデータソースをカスタムデータソースとして設定し,市場収集ロボットが実行するサーバーのアドレスを記入します. CSV ファイル内のデータは 1 分間の K 行であるため,バックテストでは,K 行期間を 1 分に設定します.
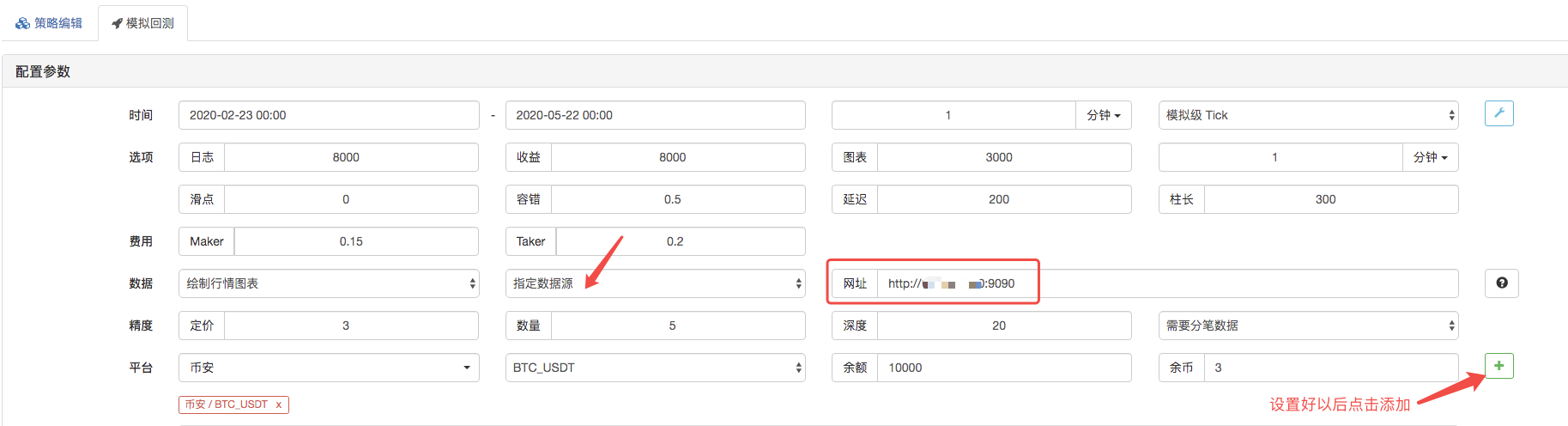
バックテストをクリックすると,市場収集ロボットはデータ要求を受け取ります.
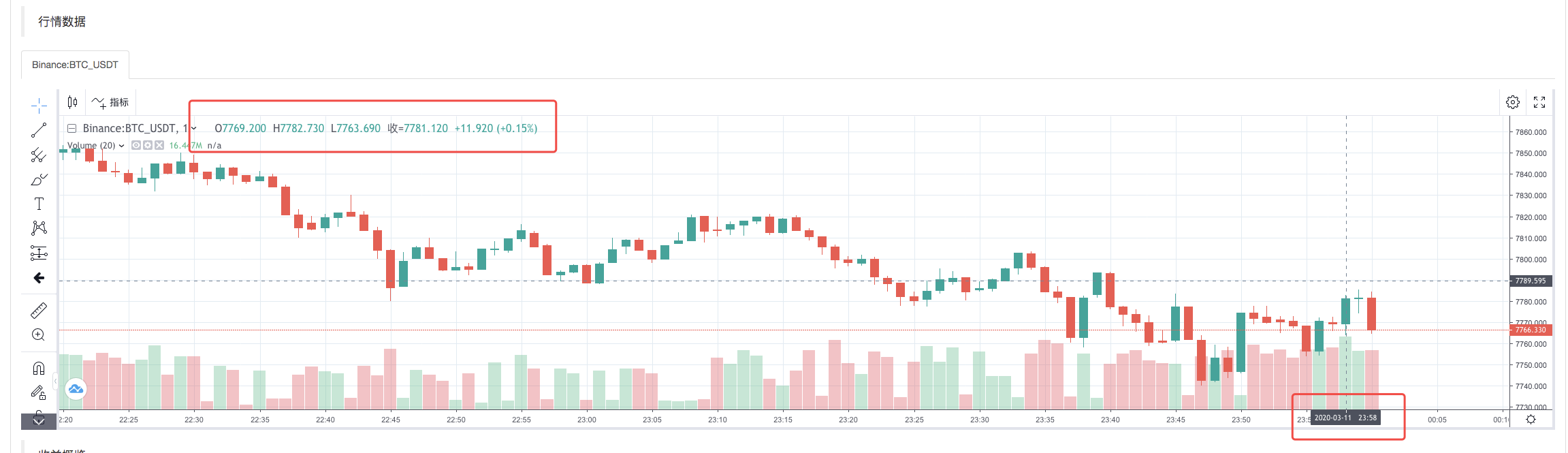
バックテストシステムの実行戦略が完了すると,データソースのK線データに基づいてK線チャートが生成されます.
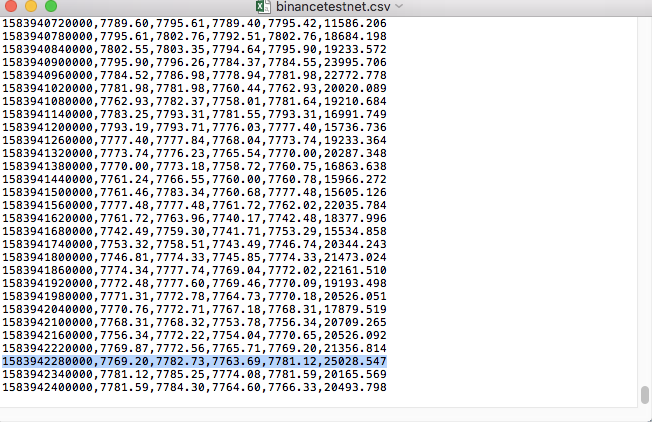
ファイル内のデータを比較する:

- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (3)
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (2)
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (2)
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する議論: 戦略におけるHttpサービス内蔵の信号受信のための完全なソリューション
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する探求:戦略内蔵Httpサービス信号受信の完全な方案
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (1)
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (1)
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する議論:拡張API VS戦略内蔵HTTPサービス
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する探究:拡張API vs 戦略内蔵HTTPサービス
- ランダム・ティッカー・ジェネレーターに基づく戦略テスト方法に関する議論
- ランダム市場生成器に基づく戦略テスト方法について
- 仮想通貨先物取引の論理について
- Alpha101 の文法開発に基づいた強化分析ツール
- カスタムデータソースをバックテストする
- 筆付取引に基づく高周波回音システムとK線回音の欠陥
- FMZシミュレーションレベルバックテストメカニズムの説明
- Linux VPS に FMZ ドッカー をインストールしてアップグレードする最良の方法
- コモディティ・フューチャーズR-ブレイカー戦略
- デジタル通貨の先物取引の論理について考える
- 市場 コート 収集器の実装を教えます
- Python バージョン コモディティ・フューチャーズ 移動平均戦略
- 行事収集器再アップグレード - CSV形式のファイル輸入をサポートし,カスタマイズされたデータソースを提供します
- C++ で書かれた高周波取引戦略
- ラリー・コナーズ RSI2 平均逆転戦略
- JSでFMZ拡張APIを学ぶ
- 日中戦略における新しい相対強度指数の使用に基づいて
- ビナンス・フューチャーズ・マルチ通貨ヘッジ戦略に関する研究 第4部分
- ラリー・コナーズ ラリー・コナーズ RSI2 平均回帰戦略
- ビナンス・フューチャーズ・マルチ通貨・ヘッジ戦略に関する研究 第3部
- ビナンス・フューチャーズ・マルチ通貨・ヘッジ戦略に関する研究 第2部
- バイナンス・フューチャーズ・マルチ通貨・ヘッジ戦略に関する研究 第1部