레인보우 오시레이터 백테스팅 전략
저자:차오장, 날짜: 2023-12-26 15:08:17태그:
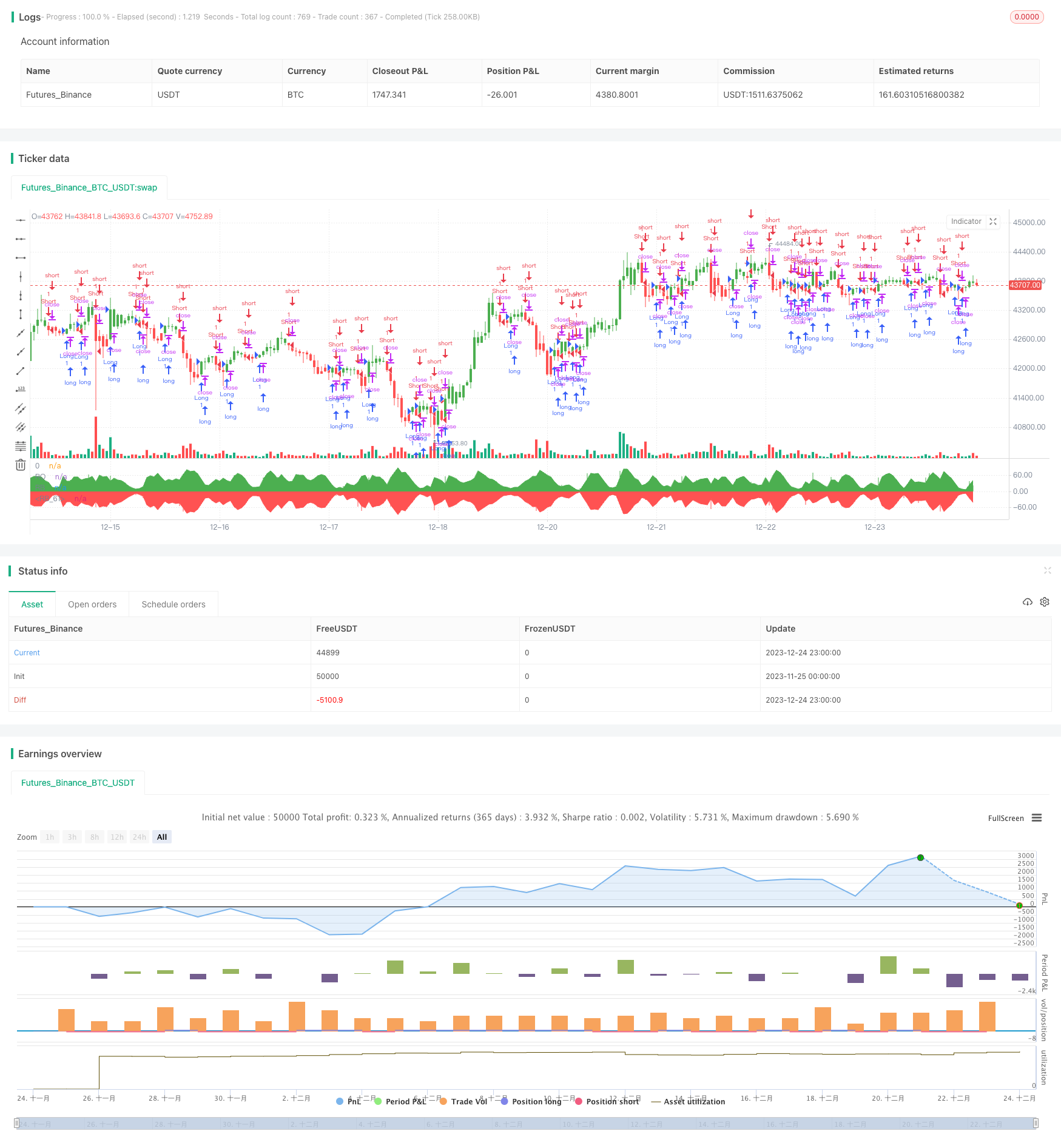
전반적인 설명
레인보우 오시일레이터 백테스팅 전략은 레인보우 오시일레이터 지표를 기반으로 한 양적 거래 전략입니다. 이 전략은 장기 및 단기 포지션을 결정하기 위해 가격과 이동 평균 사이의 오차를 계산하여 시장의 경향 방향과 힘을 판단합니다.
전략 논리
이 전략의 핵심 지표는 다음과 같이 계산되는 레인보우 오시레이터 (Rainbow Oscillator, RO) 입니다.
RO = 100 * ((Close - 10-day Moving Average) / (HHV(High, N) - LLV(Low, N)))
10일 이동 평균은 지난 10 기간 동안의 폐쇄 가격의 단순한 이동 평균입니다. 이 지표는 자신의 이동 평균에 대한 가격의 편차를 반영합니다. RO > 0이면 가격이 이동 평균보다 높다는 것을 의미합니다.
이 전략은 또한 보조 지표인 대역폭 (RB) 를 계산합니다.
RB = 100 * ((Highest value of moving averages - Lowest value of moving averages) / (HHV(High, N) - LLV(Low, N)))
RB는 이동 평균 사이의 폭을 반영합니다. RB가 클수록 가격 변동이 커지고 반대로 가격이 더 안정적입니다. RB 지표는 시장의 안정성을 판단하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
RO와 RB 지표의 값에 따라 전략은 가격 오차와 시장 안정의 정도를 판단하고, 긴 위치와 짧은 위치에 대한 거래 신호를 생성합니다.
장점
이 전략의 장점은 다음과 같습니다.
- 이중 지표 판단은 단일 지표 판단의 한계를 피합니다.
- 가격 동향과 시장 안정성을 동시에 판단할 수 있습니다.
- 계산하기 쉽고 이해하기 쉽고 실행하기 쉽습니다.
- 시각화 된 지표는 직관적이고 읽기 쉬운
rainbow 효과를 형성합니다.
위험성
이 전략에는 몇 가지 위험도 있습니다.
- RO와 RB 지표의 잘못된 매개 변수 설정은 잘못된 거래 신호를 일으킬 수 있습니다.
- 이중 이동 평균 전략은 잘못된 신호를 생성하고 자주 거래하는 경향이 있습니다.
- 부적절한 백테스팅 기간과 제품 선택은 전략의 효과에 영향을 줄 것입니다.
- 거래 비용은 고려되지 않습니다. 실제 결과는 좋지 않을 수 있습니다.
대책:
- RO와 RB 지표의 매개 변수를 최적화합니다.
- 빈번한 거래를 피하기 위해 필터 조건을 추가합니다.
- 적절한 백테스팅 사이클과 종류를 선택합니다.
- 거래 비용을 계산하고 고려하십시오.
최적화
이 전략은 또한 다음과 같은 방법으로 최적화 될 수 있습니다.
- 극적인 변동을 피하기 위해 RO 표시기에 부드러운 기능을 추가하십시오.
- 단일 손실을 통제하기 위해 스톱 로스 전략을 추가합니다.
- 수익성을 높이기 위해 포트폴리오 거래의 다른 지표와 결합하십시오.
- 예측을 위한 기계 학습 모델을 추가하고 지표의 효과를 평가합니다.
- 다양한 품종에 대한 매개 변수를 최적화하여 적응력을 향상시킵니다.
결론
레인보우 오시레이터 백테스팅 전략은 가격과 이동 평균 사이의 오차를 계산하여 시장 추세와 안정성을 판단하고, 이 정보를 사용하여 장기/단기 거래 결정을 내린다. 이 전략은 직관적이고, 구현하기 쉽고, 실질적인 가치가 있다. 그러나 실제 거래 성과를 개선하고 위험을 줄이기 위해 매개 변수와 거래 규칙을 최적화함으로써 완화해야 하는 몇 가지 위험도 있다.
/*backtest
start: 2023-11-25 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-25 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Copyright by HPotter v1.0 18/03/2018
// Ever since the people concluded that stock market price movements are not
// random or chaotic, but follow specific trends that can be forecasted, they
// tried to develop different tools or procedures that could help them identify
// those trends. And one of those financial indicators is the Rainbow Oscillator
// Indicator. The Rainbow Oscillator Indicator is relatively new, originally
// introduced in 1997, and it is used to forecast the changes of trend direction.
//
// As market prices go up and down, the oscillator appears as a direction of the
// trend, but also as the safety of the market and the depth of that trend. As
// the rainbow grows in width, the current trend gives signs of continuity, and
// if the value of the oscillator goes beyond 80, the market becomes more and more
// unstable, being prone to a sudden reversal. When prices move towards the rainbow
// and the oscillator becomes more and more flat, the market tends to remain more
// stable and the bandwidth decreases. Still, if the oscillator value goes below 20,
// the market is again, prone to sudden reversals. The safest bandwidth value where
// the market is stable is between 20 and 80, in the Rainbow Oscillator indicator value.
// The depth a certain price has on a chart and into the rainbow can be used to judge
// the strength of the move.
//
// You can change long to short in the Input Settings
// WARNING:
// - For purpose educate only
// - This script to change bars colors.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
strategy(title="Rainbow Oscillator Backtest")
Length = input(2, minval=1)
LengthHHLL = input(10, minval=2, title="HHV/LLV Lookback")
reverse = input(false, title="Trade reverse")
xMA1 = sma(close, Length)
xMA2 = sma(xMA1, Length)
xMA3 = sma(xMA2, Length)
xMA4 = sma(xMA3, Length)
xMA5 = sma(xMA4, Length)
xMA6 = sma(xMA5, Length)
xMA7 = sma(xMA6, Length)
xMA8 = sma(xMA7, Length)
xMA9 = sma(xMA8, Length)
xMA10 = sma(xMA9, Length)
xHH = highest(close, LengthHHLL)
xLL = lowest(close, LengthHHLL)
xHHMAs = max(xMA1,max(xMA2,max(xMA3,max(xMA4,max(xMA5,max(xMA6,max(xMA7,max(xMA8,max(xMA9,xMA10)))))))))
xLLMAs = min(xMA1,min(xMA2,min(xMA3,min(xMA4,min(xMA5,min(xMA6,min(xMA7,min(xMA8,min(xMA9,xMA10)))))))))
xRBO = 100 * ((close - ((xMA1+xMA2+xMA3+xMA4+xMA5+xMA6+xMA7+xMA8+xMA9+xMA10) / 10)) / (xHH - xLL))
xRB = 100 * ((xHHMAs - xLLMAs) / (xHH - xLL))
clr = iff(xRBO >= 0, green, red)
pos = iff(xRBO > 0, 1,
iff(xRBO < 0, -1, nz(pos[1], 0)))
possig = iff(reverse and pos == 1, -1,
iff(reverse and pos == -1, 1, pos))
if (possig == 1)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (possig == -1)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
barcolor(possig == -1 ? red: possig == 1 ? green : blue )
plot(xRBO, color=clr, title="RO", style= histogram, linewidth=2)
p0 = plot(0, color = gray, title="0")
p1 = plot(xRB, color=green, title="RB")
p2 = plot(-xRB, color=red, title="RB")
fill(p1, p0, color=green)
fill(p2, p0, color=red)
- 이치모쿠 균형선 전략
- 이치모쿠 클라우드, 이중 이동 평균 크로스오버 전략
- ATR 및 브레이크아웃에 기반한 ETF 거래 전략
- 슈퍼트렌드 전략 추적
- 이동평균 거래 전략
- 이중 이동 평균 금십자 양적 전략
- 양적 반전 지수 전략 두 가지 트렌드 신호를 통합
- 관성 지표 거래 전략
- 볼링거 밴드 RSI 듀얼라인 전략
- 동적 지원 저항 파업 트렌드 전략
- 래리 윌리엄스의 이동평균 크로스오버 전략
- 오시레이터 미세 이동 평균 시점 전략
- 동적 스톱 로스로 DMI 및 스토카스틱 거래 전략
- 이중 요인 복합 역전 및 질량 지수 전략
- 이중 트렌드 필터 기반의 양적 거래 전략
- 스토카스틱 RSI 모멘텀 오스실레이션 거래 전략
- RSI 콜백으로 볼링거스 대역이 가격 이하로 넘어가면 단축 판매의 거래 전략
- 이동 평균 크로스오버 전략
- 동적 회전 대역에 기반한 트렌드 추적 전략
- 볼링거 밴드 추진 동향 전략