중재에 기반한 적응형 암호화폐 그리드 거래 전략
저자:차오장날짜: 2024-01-19 14:17:50태그:
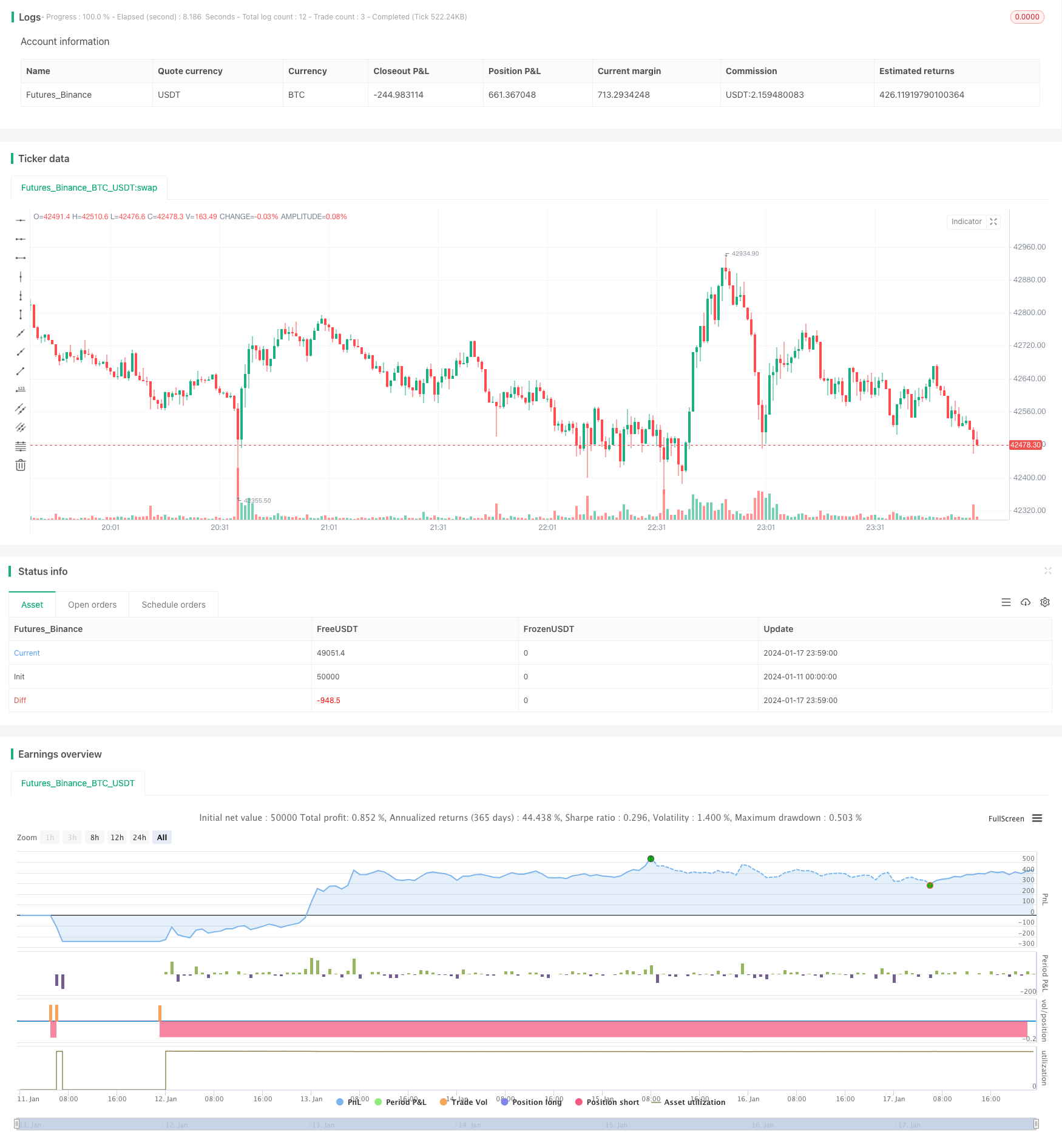
전반적인 설명
이것은 기재에 대한 기재 거래 방법론을 기반으로 한 적응성 암호화폐 그리드 거래 전략입니다. 시장 변동에 따라 그리드 거래의 가격 범위를 자동으로 조정하고 그 가격 범위 내에서 효율적인 기재 거래를 수행 할 수 있습니다.
전략 원칙
이 전략의 핵심 아이디어는 다음과 같습니다.
-
역동적으로 역사적인 높은 가격과 낮은 가격에 기초한 거래 그리드 가격 범위를 계산합니다.
-
이 가격 범위 내에서 N 개의 그리드 라인을 동등한 간격으로 설정합니다.
-
가격이 각 격자선을 통과하면 고정된 금액으로 긴 또는 짧은 포지션을 개척합니다.
-
인접한 그리드 라인과 수익을 위해 포지션을 닫는 중재.
-
가격이 그리드 범위로 다시 들어가면 그리드 라인의 한계 비용으로 포지션을 계속 개척합니다.
-
이 순환은 네트워크 가격 범위 내의 고주파 중재 거래에 반복됩니다.
구체적으로, 전략은 먼저 구성된 룩백 윈도우 (i_boundLookback) 및 변동성 범위 (i_boundDev) 파라미터에 따라 실시간으로 그리드의 상부와 하부 한도를 계산합니다.
그 다음 N 그리드 라인 (i_gridQty) 은 상위와 하위 한계 사이에 균등하게 분할됩니다. 이러한 그리드 라인의 가격은 gridLineArr 배열에 저장됩니다.
가격이 그리드 라인을 뚫을 때, 고정된 양 (그리드 수로 나눈 전략 자본) 이 긴 또는 짧은 포지션을 열기 위해 사용됩니다. 오더 레코드는 오더Arr 배열에 보관됩니다.
가격이 또다시 인접한 그리드 라인을 넘어서면 이전 오더와 맞출 수 있고 수익을 위해 포지션을 닫을 수 있습니다.
가격 변동 범위 내에서 높은 빈도 중재에 이 주기를 반복합니다.
이점 분석
전통적인 네트워크 전략에 비해 이 전략의 가장 큰 장점은 네트워크 범위가 자동으로 시장 변동에 적응하도록 조정된다는 것입니다.
-
완전 자동화, 수동 개입이 필요하지 않습니다.
-
가격 동향을 파악하고 트렌드 방향으로 거래할 수 있습니다.
-
통제 가능한 위험, 일방적인 추격 위험을 피합니다.
-
높은 거래 빈도와 수익률
-
이해하기 쉽고 간단한 구성입니다.
-
높은 자본 활용률, 쉽게 포획되지 않습니다.
-
실시간 시장 변화를 반영하고 알고리즘 거래에 적합합니다.
위험 분석
이 전략은 많은 장점을 가지고 있지만, 다음과 같은 위험 요소도 있습니다.
-
극심한 가격 변동으로 인해 더 큰 손실이 발생할 가능성
-
적당한 보유 기간과 거래 쌍이 필요해 수익을 얻으려면
-
자본 규모는 변동성 범위와 일치해야 합니다.
-
매개 변수를 자주 모니터링하고 최적화 할 수 있습니다.
대책은 다음과 같습니다.
-
그리드 범위를 넓히기 위해 그리드 간격을 늘려
-
더 안정적인 거래 쌍을 선택하세요.
-
충분한 유동성을 확보하기 위해 자본 규모를 조정합니다.
-
자동 모니터링 및 경보 메커니즘을 구축합니다.
최적화 방향
이 전략은 다음과 같은 측면에서 최적화 될 수 있습니다.
-
동적 격자: 변동성에 따라 네트워크 매개 변수를 자동으로 조정합니다.
-
스톱 로스 메커니즘: 극심한 위험을 제한하기 위해 합리적인 스톱 로스 위치를 설정합니다.
-
복합 격자: 시간 사용량을 극대화하기 위해 서로 다른 기간에 다른 매개 변수를 사용하여 그리드를 결합합니다.
-
기계 학습: 규칙 대신 매개 변수를 자동으로 최적화하기 위해 신경망을 사용합니다.
-
시장 간 중재: 거래소 또는 통화 쌍 사이의 중재.
요약
요약하자면, 이것은 중재에 대한 매우 실용적인 적응형 암호화 그리드 거래 전략입니다. 전통적인 그리드 전략과 비교하면 가장 큰 특징은 시장 변화에 따라 그리드 범위를 자동으로 조정하여 거래자가 자신의 거래 범위를 구성할 수 있습니다. 전략 논리는 명확하고 이해하기 쉽고 구성 할 수 있습니다.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-18 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("(IK) Grid Script", overlay=true, pyramiding=14, close_entries_rule="ANY", default_qty_type=strategy.cash, initial_capital=100.0, currency="USD", commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.1)
i_autoBounds = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="Use Auto Bounds?", defval=true, type=input.bool) // calculate upper and lower bound of the grid automatically? This will theorhetically be less profitable, but will certainly require less attention
i_boundSrc = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Auto) Bound Source", defval="Hi & Low", options=["Hi & Low", "Average"]) // should bounds of the auto grid be calculated from recent High & Low, or from a Simple Moving Average
i_boundLookback = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Auto) Bound Lookback", defval=250, type=input.integer, maxval=500, minval=0) // when calculating auto grid bounds, how far back should we look for a High & Low, or what should the length be of our sma
i_boundDev = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Auto) Bound Deviation", defval=0.10, type=input.float, maxval=1, minval=-1) // if sourcing auto bounds from High & Low, this percentage will (positive) widen or (negative) narrow the bound limits. If sourcing from Average, this is the deviation (up and down) from the sma, and CANNOT be negative.
i_upperBound = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Manual) Upper Boundry", defval=0.285, type=input.float) // for manual grid bounds only. The upperbound price of your grid
i_lowerBound = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Manual) Lower Boundry", defval=0.225, type=input.float) // for manual grid bounds only. The lowerbound price of your grid.
i_gridQty = input(group="Grid Lines", title="Grid Line Quantity", defval=8, maxval=15, minval=3, type=input.integer) // how many grid lines are in your grid
f_getGridBounds(_bs, _bl, _bd, _up) =>
if _bs == "Hi & Low"
_up ? highest(close, _bl) * (1 + _bd) : lowest(close, _bl) * (1 - _bd)
else
avg = sma(close, _bl)
_up ? avg * (1 + _bd) : avg * (1 - _bd)
f_buildGrid(_lb, _gw, _gq) =>
gridArr = array.new_float(0)
for i=0 to _gq-1
array.push(gridArr, _lb+(_gw*i))
gridArr
f_getNearGridLines(_gridArr, _price) =>
arr = array.new_int(3)
for i = 0 to array.size(_gridArr)-1
if array.get(_gridArr, i) > _price
array.set(arr, 0, i == array.size(_gridArr)-1 ? i : i+1)
array.set(arr, 1, i == 0 ? i : i-1)
break
arr
var upperBound = i_autoBounds ? f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, true) : i_upperBound // upperbound of our grid
var lowerBound = i_autoBounds ? f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, false) : i_lowerBound // lowerbound of our grid
var gridWidth = (upperBound - lowerBound)/(i_gridQty-1) // space between lines in our grid
var gridLineArr = f_buildGrid(lowerBound, gridWidth, i_gridQty) // an array of prices that correspond to our grid lines
var orderArr = array.new_bool(i_gridQty, false) // a boolean array that indicates if there is an open order corresponding to each grid line
var closeLineArr = f_getNearGridLines(gridLineArr, close) // for plotting purposes - an array of 2 indices that correspond to grid lines near price
var nearTopGridLine = array.get(closeLineArr, 0) // for plotting purposes - the index (in our grid line array) of the closest grid line above current price
var nearBotGridLine = array.get(closeLineArr, 1) // for plotting purposes - the index (in our grid line array) of the closest grid line below current price
strategy.initial_capital = 50000
for i = 0 to (array.size(gridLineArr) - 1)
if close < array.get(gridLineArr, i) and not array.get(orderArr, i) and i < (array.size(gridLineArr) - 1)
buyId = i
array.set(orderArr, buyId, true)
strategy.entry(id=tostring(buyId), long=true, qty=(strategy.initial_capital/(i_gridQty-1))/close, comment="#"+tostring(buyId))
if close > array.get(gridLineArr, i) and i != 0
if array.get(orderArr, i-1)
sellId = i-1
array.set(orderArr, sellId, false)
strategy.close(id=tostring(sellId), comment="#"+tostring(sellId))
if i_autoBounds
upperBound := f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, true)
lowerBound := f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, false)
gridWidth := (upperBound - lowerBound)/(i_gridQty-1)
gridLineArr := f_buildGrid(lowerBound, gridWidth, i_gridQty)
closeLineArr := f_getNearGridLines(gridLineArr, close)
nearTopGridLine := array.get(closeLineArr, 0)
nearBotGridLine := array.get(closeLineArr, 1)
- 아룬 + 윌리엄스 + MA + BB + ADX 강력한 다중 지표 전략
- 근접한 전략으로 기하급수적인 이동 평균과 이동 평균의 교차
- 이치모쿠 클라우드 차트에 기초한 트렌드 전략 최적화
- 트렌드 역전과 10 오시레이터 두 가지 전략이 결합된 크로스 트렌드 역전
- 양적 거래에 이동 평균 전략과 함께 피보나치 평균 촛불
- 간단한 트레일링 스톱 & 구매 전략
- 가우스 오류 함수에 기초한 양적 거래 전략의 분석
- RSI 반전 전략
- RSI-VWAP 단기 양성 전략
- 이중 이동 평균 크로스오버 전략
- 이중 이동 평균 거래 전략
- EMA와 트레일링 스톱을 가진 수요와 공급 구역에 기반한 거래 전략
- 볼링거 밴드 (Bollinger Bands) 에 기반한 트렌드 다음 전략
- 확장된 가격량 트렌드 전략
- 오스실레이션 추적 단기 전략
- 공격적 인 바닥 스니핑 양적 전략
- T3 지표에 기초한 거래 전략을 따르는 경향
- 스토카스틱 인덱스에 기초한 단기 거래 전략
- 런던 SMA 크로스 ETH 리버설 거래 전략