"OKEX فیوچر معاہدے ہیجنگ حکمت عملی کا C ++ ورژن" جو آپ کو سخت مقداری حکمت عملی کے ذریعے لے جاتا ہے
مصنف:نیکی, تخلیق: 2019-08-29 16:05:07, تازہ کاری: 2025-01-15 22:07:49
ہیجنگ کی حکمت عملیوں کی بات کرتے ہوئے ، مختلف مارکیٹوں میں مختلف اقسام ، متنوع امتزاج ، اور متنوع نظریات موجود ہیں۔ ہم سب سے کلاسیکی انٹر ٹائمورل ہیجنگ سے ہیجنگ کی حکمت عملی کے ڈیزائن خیالات اور تصورات کی کھوج کرتے ہیں۔ آج ، کریپٹو کرنسی مارکیٹ شروع سے کہیں زیادہ فعال ہے ، اور بہت سارے فیوچر کنٹریکٹ ایکسچینج بھی ہیں جو ہینڈج ہیجنگ کے لئے بہت سارے مواقع پیش کرتے ہیں۔ اسپاٹ کراس مارکیٹ ہینڈجنگ ، کیش ہیجنگ ہینڈجنگ ، فیوچر انٹر ٹائمورل ہینڈجنگ ، فیوچر کراس مارکیٹ ہینڈجنگ وغیرہ ، ایک کے بعد ایک کرپٹو مقداری تجارتی حکمت عملی سامنے آتی ہے۔ آئیے ایک
حکمت عملی کا اصول
حکمت عملی کسی حد تک سخت کیوں ہے کیونکہ حکمت عملی C ++ میں لکھی گئی ہے اور حکمت عملی کی پڑھائی قدرے مشکل ہے۔ لیکن اس سے قارئین کو اس حکمت عملی کے ڈیزائن اور نظریات کا جوہر سیکھنے سے نہیں روکتا ہے۔ حکمت عملی کا منطق نسبتا simple آسان ہے ، کوڈ کی لمبائی اعتدال پسند ہے ، صرف 500 لائنیں۔ مارکیٹ کے اعداد و شمار کے حصول کے لحاظ سے ،
ڈیزائن کے لحاظ سے ، حکمت عملی کا ڈھانچہ معقول ہے ، کوڈ کاپلیشن کی ڈگری بہت کم ہے ، اور اس کی توسیع یا اصلاح کرنا آسان ہے۔ منطق واضح ہے ، اور اس طرح کا ڈیزائن نہ صرف سمجھنا آسان ہے۔ بطور تدریسی مواد ، اس حکمت عملی کے ڈیزائن کو سیکھنا بھی ایک اچھی مثال ہے۔ اس حکمت عملی کا اصول نسبتا simple آسان ہے ، یعنی ، کیا فارورڈ کنٹریکٹ اور حالیہ کنٹریکٹ کا پھیلاؤ مثبت ہے یا منفی؟ بنیادی اصول اجناس فیوچر کی انٹر ٹائمپورل ہیجنگ کے ساتھ مطابقت رکھتا ہے۔
- پھیلاؤ مثبت، مختصر مستقبل کے معاہدوں کی فروخت، طویل حالیہ معاہدوں کی خریداری.
- منفی پھیلاؤ، طویل مستقبل کے معاہدوں کی خریداری، مختصر حالیہ معاہدوں کی فروخت.
بنیادی اصولوں کو سمجھنے کے بعد، باقی یہ ہے کہ حکمت عملی ہیج کی افتتاحی پوزیشن کو کیسے چالو کرتی ہے، پوزیشن کو کیسے بند کرنا ہے، پوزیشنوں کو کیسے شامل کرنا ہے، کل پوزیشن کنٹرول کا طریقہ اور حکمت عملی کی دیگر تفصیلات کی پروسیسنگ.
ہیجنگ کی حکمت عملی بنیادی طور پر موضوع کی قیمت کے فرق (اسپرڈ) کے اتار چڑھاؤ اور اس کے رجعت سے متعلق ہے۔ تاہم ، فرق میں قدرے اتار چڑھاؤ ، یا تیزی سے اتار چڑھاؤ ، یا ایک ہی سمت میں ہونے کا امکان ہے۔
یہ منافع اور نقصانات کو ہیج کرنے کے بارے میں غیر یقینی صورتحال لاتا ہے ، لیکن خطرہ اب بھی یکطرفہ رجحان سے بہت کم ہے۔ انٹر ٹائمورل حکمت عملی کی مختلف اصلاحات کے ل we ، ہم پوزیشن کنٹرولنگ لیول اور افتتاحی اور اختتامی ٹرگر کی شرط سے شروع کرنے کا انتخاب کرسکتے ہیں۔ مثال کے طور پر ، ہم قیمت کی اتار چڑھاؤ کا تعین کرنے کے لئے کلاسیکی
حکمت عملی کوڈ کا تجزیہ
پورے کوڈ کو دیکھ کر آپ یہ نتیجہ اخذ کر سکتے ہیں کہ کوڈ تقریباً چار حصوں میں تقسیم ہے۔
قدر کی تعریفوں کی فہرست بنائیں ، کچھ ریاست کی اقدار کی وضاحت کریں ، اور ریاستوں کو نشان زد کرنے کے لئے استعمال کریں۔ کچھ فنکشنل افعال جو حکمت عملی سے متعلق نہیں ہیں ، جیسے یو آر ایل انکوڈنگ افعال ، وقت کی تبادلوں کے افعال ، وغیرہ ، کا حکمت عملی منطق سے کوئی تعلق نہیں ہے ، صرف ڈیٹا پروسیسنگ کے لئے۔
K لائن ڈیٹا جنریٹر کلاس: حکمت عملی جنریٹر کلاس آبجیکٹ کے ذریعہ تیار کردہ K لائن ڈیٹا سے چلتی ہے۔
ہیجنگ کلاس: اس کلاس کے اشیاء مخصوص ٹریڈنگ منطق، ہیجنگ آپریشنز اور حکمت عملی کی تفصیلات کی پروسیسنگ انجام دے سکتے ہیں۔
حکمت عملی کا بنیادی کام ، جو
main فنکشن ہے۔ اہم کام حکمت عملی کا انٹری فنکشن ہے۔ مرکزی لوپ اس فنکشن کے اندر ہی انجام دیا جاتا ہے۔ اس کے علاوہ ، یہ فنکشن ایک اہم آپریشن بھی انجام دیتا ہے ، یعنی ، تبادلے کے ویب ساکٹ انٹرفیس تک رسائی حاصل کرنا ، اور K- لائن ڈیٹا جنریٹر کی حیثیت سے دھکیلے جانے والے خام ٹک مارکیٹ ڈیٹا کو حاصل کرنا۔
حکمت عملی کے کوڈ کی مجموعی تفہیم کے ذریعے، ہم آہستہ آہستہ حکمت عملی کے مختلف پہلوؤں کو سیکھ سکتے ہیں، اور پھر حکمت عملی کے ڈیزائن، خیالات اور مہارتوں کا مطالعہ کرسکتے ہیں.
- تعداد کی قدر کی تعریف، دیگر فنکشن افعال
- درج کردہ قسم
Stateبیان
enum State { // Enum type defines some states
STATE_NA, // Abnormal state
STATE_IDLE, // idle
STATE_HOLD_LONG, // holding long positions
STATE_HOLD_SHORT, // holding short positions
};
کیونکہ کوڈ میں کچھ افعال ایک ریاست واپس، ان ریاستوں enumeration کی قسم میں بیان کر رہے ہیںState.
یہ دیکھ کرSTATE_NAکوڈ میں ظاہر غیر معمولی ہے، اورSTATE_IDLEغیر فعال ہے، یعنی آپریشن کی حالت کو ہیج کیا جا سکتا ہے۔STATE_HOLD_LONGوہ حالت ہے جس میں مثبت ہیج پوزیشن رکھی جاتی ہے۔STATE_HOLD_SHORTوہ حالت ہے جس میں منفی ہیج پوزیشن رکھی جاتی ہے۔
- اسٹریٹجی میں نہیں بلایا گیا ، ایک متبادل افادیت کا فنکشن ہے ، جو بنیادی طور پر تاروں سے نمٹتا ہے۔
string replace(string s, const string from, const string& to)
- ہیکساڈیسمل حروف میں تبدیل کرنے کے لئے ایک فنکشن
toHex
inline unsigned char toHex(unsigned char x)
- ہینڈلنگ یو آر ایل کوڈت افعال
std::string urlencode(const std::string& str)
- ایک ٹائم کنورشن فنکشن جو سٹرنگ فارمیٹ میں وقت کو ٹائم اسٹیمپ میں تبدیل کرتا ہے۔
uint64_t _Time(string &s)
- K لائن ڈیٹا جنریٹر کلاس
class BarFeeder { // K line data generator class
public:
BarFeeder(int period) : _period(period) { // constructor with argument "period" period, initialized in initialization list
_rs.Valid = true; // Initialize the "Valid" property of the K-line data in the constructor body.
}
void feed(double price, chart *c=nullptr, int chartIdx=0) { // input data, "nullptr" null pointer type, "chartIdx" index default parameter is 0
uint64_t epoch = uint64_t(Unix() / _period) * _period * 1000; // The second-level timestamp removes the incomplete time period (incomplete _period seconds) and is converted to a millisecond timestamp.
bool newBar = false; // mark the tag variable of the new K line Bar
if (_rs.size() == 0 || _rs[_rs.size()-1].Time < epoch) { // if the K line data is 0 in length. Or the last bar's timestamp is less than epoch (the last bar of the K line is more than the current most recent cycle timestamp)
record r; // declare a K line bar structure
r.Time = epoch; // construct the K line bar of the current cycle
r.Open = r.High = r.Low = r.close = price; // Initialize the property
_rs.push_back(r); // K line bar is pressed into the K line data structure
if (_rs.size() > 2000) { // if the K-line data structure length exceeds 2000, the oldest data is removed.
_rs.erase(_rs.begin());
}
newBar = true; // tag
} else { // In other cases, it is not the case of a new bar.
record &r = _rs[_rs.size() - 1]; // Reference the data of the last bar in the data.
r.High = max(r.High, price); // The highest price update operation for the referenced data.
r.Low = min(r.Low, price); // The lowest price update operation for the referenced data.
r.close = price; // Update the closing price of the referenced data.
}
auto bar = _rs[_rs.size()-1]; // Take the last column data and assign it to the bar variable
json point = {bar.Time, bar.Open, bar.High, bar.Low, bar.close}; // construct a json type data
if (c != nullptr) { // The chart object pointer is not equal to the null pointer, do the following.
if (newBar) { // judge if the new Bar appears
c->add(chartIdx, point); // call the chart object member function add to insert data into the chart object (new k line bar)
c->reset(1000); // retain only 1000 bar of data
} else {
c->add(chartIdx, point, -1); // Otherwise update (not new bar), this point (update this bar).
}
}
}
records & get() { // member function, method for getting K line data.
Return _rs; // Returns the object's private variable _rs . (ie generated K-line data)
}
private:
int _period;
records _rs;
};
یہ کلاس بنیادی طور پر حکمت عملی ہیجنگ منطق کو چلانے کے لئے ایک فرق K لائن میں حاصل کردہ ٹک ڈیٹا کو پروسیسنگ کے لئے ذمہ دار ہے.
کچھ قارئین کے پاس سوالات ہوسکتے ہیں ، ٹک ڈیٹا کا استعمال کیوں کریں؟ اس طرح کے کے لائن ڈیٹا جنریٹر کی تعمیر کیوں کریں؟ کیا براہ راست کے لائن ڈیٹا کا استعمال کرنا اچھا نہیں ہے؟ اس طرح کا سوال تین دھماکوں میں جاری کیا گیا ہے۔ جب میں نے کچھ ہیجنگ کی حکمت عملی لکھی تو میں نے بھی ہلچل مچا دی۔ جب میں نے
دو معاہدوں کے مابین فرق کے K لائن ڈیٹا ایک خاص مدت میں فرق کی قیمت میں تبدیلی کے اعدادوشمار ہیں۔ لہذا ، ہر دو معاہدوں میں سے ہر ایک کے K لائن ڈیٹا کو گھٹانے اور ہر K لائن بار پر ہر ڈیٹا کے فرق کا حساب لگانا ممکن نہیں ہے۔ سب سے زیادہ واضح غلطی ، مثال کے طور پر ، دو معاہدوں کی سب سے زیادہ قیمت اور کم قیمت ہے ، ضروری نہیں کہ ایک ہی وقت میں۔ لہذا گھٹایا ہوا قدر زیادہ معنی نہیں رکھتا ہے۔
لہذا ، ہمیں حقیقی وقت میں فرق کا حساب لگانے اور حقیقی وقت میں کسی خاص مدت میں قیمت کی تبدیلی کا حساب لگانے کے لئے ریئل ٹائم ٹِک ڈیٹا کا استعمال کرنے کی ضرورت ہے (یعنی ، K لائن کالم پر سب سے زیادہ ، سب سے کم ، کھلی اور بند قیمت) ۔ لہذا ہمیں K لائن ڈیٹا جنریٹر کی ضرورت ہے ، بطور کلاس ، پروسیسنگ منطق کی اچھی علیحدگی۔
- ہیجنگ کلاس
class Hedge { // Hedging class, the main logic of the strategy.
public:
Hedge() { // constructor
...
};
State getState(string &symbolA, depth &depthA, string &symbolB, depth &depthB) { // Get state, parameters: contract A name, contract A depth data, contract B name, contract B depth data
...
}
bool Loop(string &symbolA, depth &depthA, string &symbolB, depth &depthB, string extra="") { // Opening and closing position main logic
...
}
private:
vector<double> _addArr; // Hedging adding position list
string _state_desc[4] = {"NA", "IDLE", "LONG", "SHORT"}; // Status value Description
int _countOpen = 0; // number of opening positions
int _countcover = 0; // number of closing positions
int _lastcache = 0; //
int _hedgecount = 0; // number of hedging
int _loopcount = 0; // loop count (cycle count)
double _holdPrice = 0; // holding position price
BarFeeder _feederA = BarFeeder(DPeriod); // A contract Quote K line generator
BarFeeder _feederB = BarFeeder(DPeriod); // B contract Quote K line generator
State _st = STATE_NA; // Hedging type Object Hedging position status
string _cfgStr; // chart configuration string
double _holdAmount = 0; // holding position amount
bool _iscover = false; // the tag of whether to close the position
bool _needcheckOrder = true; // Set whether to check the order
chart _c = chart(""); // chart object and initialize
};
کیونکہ کوڈ نسبتا long لمبا ہے ، کچھ حصے خارج کردیئے گئے ہیں ، یہ بنیادی طور پر اس ہیج کلاس کی ساخت کو ظاہر کررہا ہے ، کنسٹرکٹر ہیج فنکشن کو خارج کردیا گیا ہے ، بنیادی طور پر مقصد آبجیکٹ کی ابتدائیہ کے لئے۔ اگلا ، ہم دو اہم
getState
یہ فنکشن بنیادی طور پر آرڈر انسپکشن ، آرڈر کی منسوخی ، پوزیشن کا پتہ لگانے ، پوزیشن بیلنسنگ وغیرہ سے متعلق ہے۔ کیونکہ ہیجنگ ٹرانزیکشنز کے عمل میں ، ایک ہی ٹانگ سے بچنا ناممکن ہے (یعنی ، ایک معاہدہ انجام دیا جاتا ہے ، دوسرا نہیں ہوتا ہے) ، اگر جانچ پڑتال ترتیب دینے کی منطق میں کی جاتی ہے ، اور پھر دوبارہ بھیجنے کے آرڈر آپریشن یا بند کرنے کی پوزیشن آپریشن کی پروسیسنگ ، حکمت عملی کی منطق افراتفری ہوگی۔
تو اس حصے کو ڈیزائن کرتے وقت، میں نے ایک اور خیال لیا. اگر ہیجنگ آپریشن شروع کیا جاتا ہے، جب تک کہ آرڈر ایک بار رکھا جاتا ہے، قطع نظر اس سے قطع نظر کہ آیا ایک ٹانگ ہیجنگ ہے، ڈیفالٹ ہیجنگ کامیاب ہے کہ ہے، اور پھر پوزیشن توازن میں پتہ چلا ہےgetStateفنکشن، اور توازن کی پروسیسنگ کے لئے منطق کو آزادانہ طور پر نمٹا جائے گا.
لوپ
حکمت عملی کی ٹریڈنگ منطق اس فنکشن میں شامل ہے، جس میںgetStateاس کے علاوہ چارٹ کے لئے کچھ ڈیٹا اپ ڈیٹ آپریشنز بھی کیے جاتے ہیں۔
- حکمت عملی کا بنیادی کام
void main() {
...
string realSymbolA = exchange.SetcontractType(symbolA)["instrument"]; // Get the A contract (this_week / next_week / quarter ), the real contract ID corresponding to the week, next week, and quarter of the OKEX futures contract.
string realSymbolB = exchange.SetcontractType(symbolB)["instrument"]; // ...
string qs = urlencode(json({{"op", "subscribe"}, {"args", {"futures/depth5:" + realSymbolA, "futures/depth5:" + realSymbolB}}}).dump()) ; // jSON encoding, url encoding for the parameters to be passed on the ws interface
Log("try connect to websocket"); // Print the information of the connection WS interface.
auto ws = Dial("wss://real.okex.com:10442/ws/v3|compress=gzip_raw&mode=recv&reconnect=true&payload="+qs); // call the FMZ API "Dial" function to acess the WS interface of OKEX Futures
Log("connect to websocket sucess");
depth depthA, depthB; // Declare two variables of the depth data structure to store the depth data of the A contract and the B contract
auto filldepth = [](json &data, depth &d) { // construct the code for the depth data with the json data returned by the interface.
d.Valid = true;
d.Asks.clear();
d.Asks.push_back({atof(string(data["asks"][0][0]).c_str()), atof(string(data["asks"][0][1]).c_str( ))});
d.Bids.clear();
d.Bids.push_back({atof(string(data["bids"][0][0]).c_str()), atof(string(data["bids"][0][1]).c_str( ))});
};
string timeA; // time string A
string timeB; // time string B
while (true) {
auto buf = ws.read(); // Read the data pushed by the WS interface
...
}
حکمت عملی شروع ہونے کے بعد ، اسے مرکزی فنکشن سے عمل میں لایا جاتا ہے۔ مرکزی فنکشن کے آغاز میں ، حکمت عملی ویب ساکٹ انٹرفیس کے ٹِک مارکیٹ کو سبسکرائب کرتی ہے۔ مرکزی فنکشن کا بنیادی کام ایک مین لوپ بنانا ہے جو ایکسچینج
نوٹ کرنے کا ایک نقطہ یہ ہے کہ مذکورہ بالا ٹِک مارکیٹ دراصل سبسکرپشن آرڈر پتلی گہرائی ڈیٹا انٹرفیس ہے ، جو ہر فائل کے لئے آرڈر بک ڈیٹا ہے۔ تاہم ، حکمت عملی صرف اعداد و شمار کی پہلی فائل استعمال کرتی ہے ، در حقیقت ، یہ ٹِک مارکیٹ کے اعداد و شمار کی طرح ہی ہے۔ حکمت عملی دوسری فائلوں کے اعداد و شمار کا استعمال نہیں کرتی ہے ، اور نہ ہی یہ پہلی فائل کی آرڈر ویلیو کا استعمال کرتی ہے۔
ویب ساکٹ انٹرفیس کے اعداد و شمار کو کس طرح سبسکرائب کرتا ہے اور یہ کس طرح ترتیب دیا جاتا ہے اس پر قریب سے نظر ڈالیں.
string qs = urlencode(json({{"op", "subscribe"}, {"args", {"futures/depth5:" + realSymbolA, "futures/depth5:" + realSymbolB}}}).dump());
Log("try connect to websocket");
auto ws = Dial("wss://real.okex.com:10442/ws/v3|compress=gzip_raw&mode=recv&reconnect=true&payload="+qs);
Log("connect to websocket sucess");
سب سے پہلے، سبسکرپشن پیغام json پیرامیٹر سبسکرپٹ انٹرفیس کی طرف سے منظور کی url کوڈنگ، یعنی قدرpayloadپیرامیٹر۔ پھر ایک اہم قدم FMZ کوانٹ پلیٹ فارم کی API انٹرفیس فنکشن کو کال کرنا ہے۔Dialفنکشن.Dialتقریب کا استعمال کیا جا سکتا ہے تبادلہ qsسلسلہpayloadپیرامیٹر) ، اس فنکشن کو حاصل کرنے کے لئے، آپ کی ضرورت ہے کی پیرامیٹر تار میں ترتیب شامل کریںDial function.
کے آغازDialفنکشن پیرامیٹر مندرجہ ذیل ہے:
wss://real.okex.com:10442/ws/v3
یہ ویب ساکٹ انٹرفیس کا پتہ ہے جس تک رسائی حاصل کرنے کی ضرورت ہے، اور
|Parameter name|description|
|-|-|
|compress|compress is compression mode, OKEX websocket interface uses gzip_raw this way, so it is set to gzip_raw|
|mode|Mode is mode, optional dual, send and recv three kind. Dual is bidirectional, sending compressed data and receiving compressed data. Send is to send compressed data. Recv receives the compressed data and decompresses it locally.|
|reconnect|Reconnect is set to reconnect, reconnect=true to enable reconnection, no default is not reconnected.|
|payload|The payload is a subscription message that needs to be sent when ws is reconnected.|
After this setting, even if the websocket connection is disconnected, FMZ Quant trading platform's underlying system of the docker system will automatically reconnect and get the latest market data in time.
Grab every price fluctuation and quickly capture the right hedge.
- Position control
Position control is controlled using a ratio of hedge positions similar to the “Fibonaci” series.
for (int i = 0; i < AddMax + 1; i++) { // ایک ڈیٹا ڈھانچہ تعمیر کریں جو اسکیلپنگ کی تعداد کو کنٹرول کرتا ہے ، جو بوفیناک ترتیب کے تناسب سے ہیج کی تعداد کی طرح ہے۔
if (_addArr.size() < 2) { // پہلی دو شامل پوزیشنوں کے طور پر تبدیل کر رہے ہیں: ہیج کی تعداد میں دوگنا
_addArr.push_back (((i+1) *OpenAmount) ؛
}
_addArr.push_back ((_addArr[_addArr.size() -1] + _addArr[_addArr.size()-2]); // آخری دو جمع کرنے والی پوزیشنوں کو ایک ساتھ شامل کیا جاتا ہے ، اور موجودہ پوزیشن کی مقدار کا حساب لگایا جاتا ہے اور
It can be seen that the number of additional positions added each time is the sum of the last two positions.
Such position control can realize the larger the difference, the relative increase of the arbitrage hedge, and the dispersion of the position, so as to grasp the small position of the small price fluctuation, and the large price fluctuation position is appropriately increased.
- closing position: stop loss and take profit
Fixed stop loss spread and take profit spread.
When the position difference reaches the take profit position and the stop loss position, the take profit and stop loss are carried out.
- The designing of entering the market and leaving the market
The period of the parameter ```NPeriod``` control provides some dynamic control over the opening and closing position of the strategy.
- Strategy chart
The strategy automatically generates a spread K-line chart to mark relevant transaction information.
c++ strategy custom chart drawing operation is also very simple. You can see that in the constructor of the hedge class, we use the written chart configuration string ```_cfgStr``` to configure the chart object ```_c```, ```_c``` is the private component of the hedge class. When the private member is initialized, the ```chart``` object constructed by the FMZ Quant platform custom chart API interface function is called.
_cfgStr = R
کال _c.update(_cfgStr) ؛ استعمال کریں _cfgStr چارٹ آبجیکٹ کے لئے ترتیب دینے کے لئے.
call _c.reset(); چارٹ کے اعداد و شمار کو ری سیٹ کرنے کے لئے.
When the strategy code needs to insert data into the chart, it also calls the member function of the ```_c``` object directly, or passes the reference of ```_c``` as a parameter, and then calls the object member function (method) of ```_c``` to update the chart data and insert operation.
E.g:
_c.add(chartIdx، {{
After placing the order, mark the K line chart.
As follows, when drawing a K line, a reference to the chart object ```_c``` is passed as a parameter when calling the member function ```feed``` of the ```BarFeeder``` class.
void feed ((ڈبل قیمت، چارٹ *c=nullptr، int چارٹIdx=0)
That is, the formal parameter ```c``` of the ```feed``` function.
json نقطہ = {bar.Time، bar.Open، bar.High، bar.Low، bar.close}؛ // ایک json قسم کے اعداد و شمار کی تعمیر
اگر (c!= nullptr) { // چارٹ آبجیکٹ پوائنٹر نل پوائنٹر کے برابر نہیں ہے، مندرجہ ذیل کریں.
if (newBar) { // اگر نیا بار ظاہر ہوتا ہے تو فیصلہ
c->add(chartIdx, point); // چارٹ آبجیکٹ ممبر فنکشن
Insert a new K-line Bar data into the chart by calling the ```add``` member function of the chart object ```_c```.
c->add ((chartIdx، نقطہ) ؛
بیک ٹیسٹ
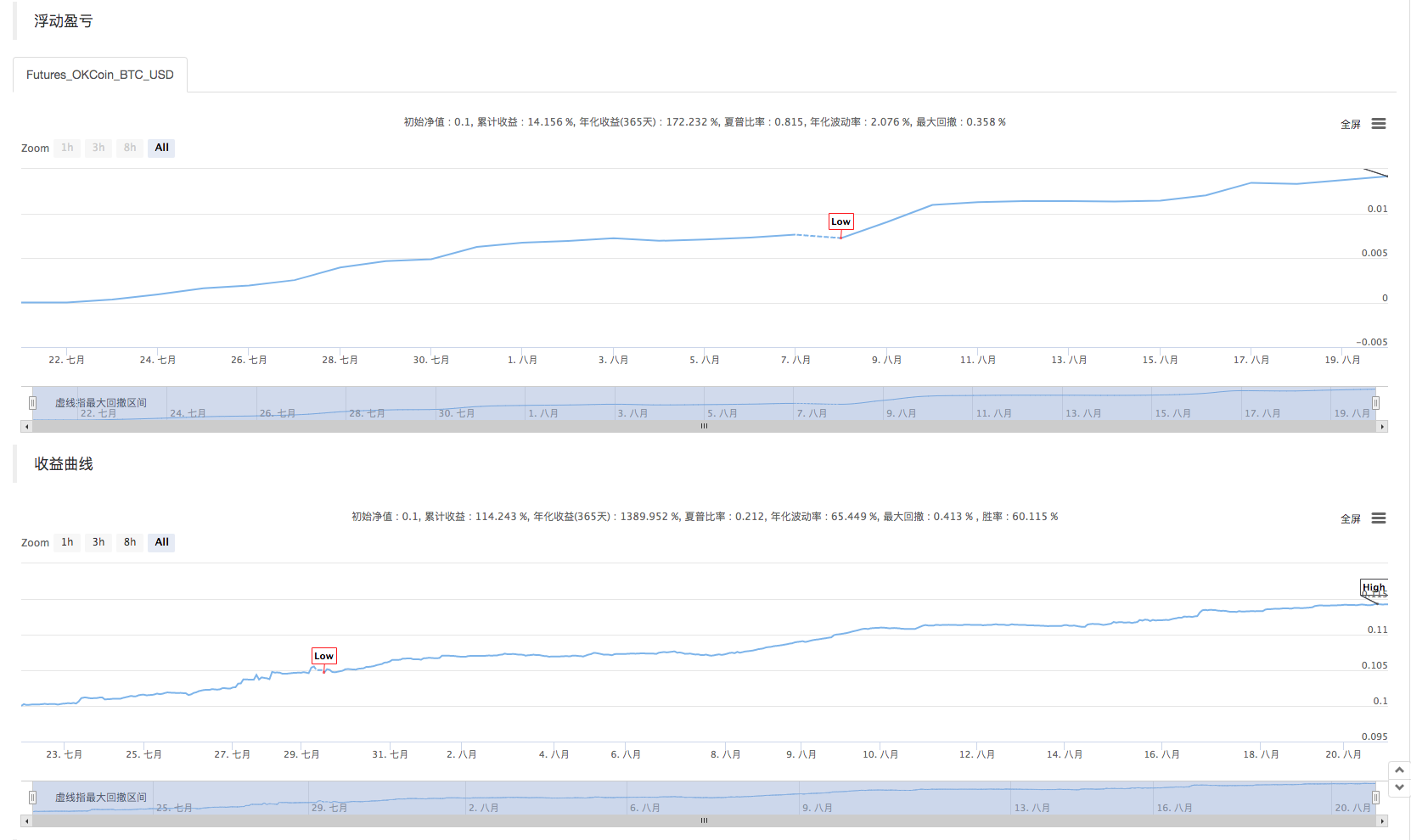
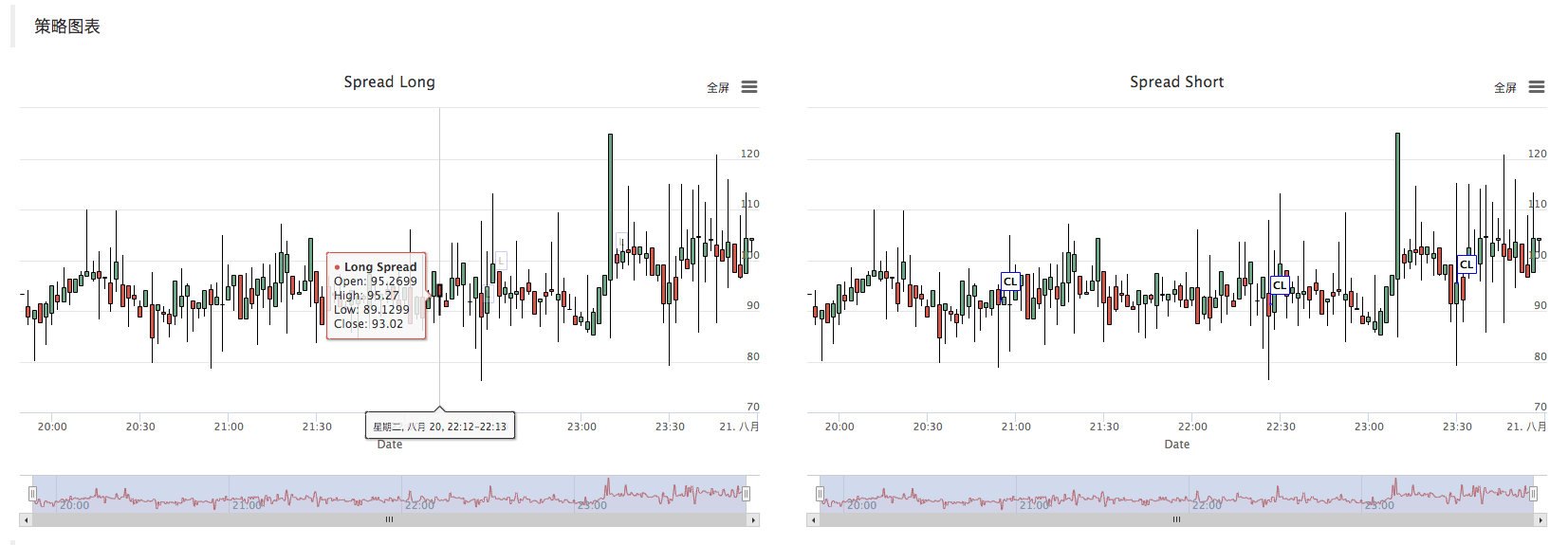

یہ حکمت عملی صرف سیکھنے اور مواصلات کے مقاصد کے لئے ہے۔ جب اسے حقیقی مارکیٹ میں لاگو کیا جائے تو ، براہ کرم مارکیٹ کی اصل صورتحال کے مطابق اس میں ترمیم اور اصلاح کریں۔
حکمت عملی کا پتہ:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/163447
مزید دلچسپ حکمت عملی FMZ Quant پلیٹ فارم میں ہیں:https://www.fmz.com
- ڈی ای ایکس ایکسچینجز کی مقداری مشق (2) -- ہائپر لیکویڈ صارف گائیڈ
- ڈی ای ایکس ایکسچینج کی مقدار سازی کی مشقیں ((2) -- Hyperliquid استعمال کرنے کا رہنما
- ڈی ای ایکس ایکسچینجز کی مقداری مشق (1) -- ڈی وائی ڈی ایکس وی 4 صارف گائیڈ
- کریپٹوکرنسی میں لیڈ لیگ ثالثی کا تعارف (3)
- ڈی ای ایکس ایکسچینج کی کوانٹیٹیشن پریکٹس ((1) -- dYdX v4 استعمال کرنے کا رہنما
- ڈیجیٹل کرنسیوں میں لیڈ لیگ سوٹ کا تعارف (3)
- کریپٹوکرنسی میں لیڈ لیگ اربیٹریج کا تعارف (2)
- ڈیجیٹل کرنسیوں میں لیڈ لیگ سوٹ کا تعارف ((2)
- ایف ایم زیڈ پلیٹ فارم کی بیرونی سگنل وصولی پر بحث: حکمت عملی میں بلٹ ان ایچ ٹی پی سروس کے ساتھ سگنل وصول کرنے کے لئے ایک مکمل حل
- ایف ایم زیڈ پلیٹ فارم کے بیرونی سگنل وصول کرنے کا جائزہ: حکمت عملی بلٹ میں HTTP سروس سگنل وصول کرنے کا مکمل نظام
- کریپٹوکرنسی میں لیڈ لیگ اربیٹریج کا تعارف (1)
- اجناس کے فیوچر اور کریپٹوکرنسی ایکسچینج API کے مابین مماثلت اور اختلافات
- ہینڈ ہینڈ آپ کو سکھاتا ہے کہ کس طرح ایک پرانے پرانے حکمت عملی کے ساتھ ہموار ویب ساکٹ مارکیٹ انٹرفیس کو جوڑنے
- کثیر سطح کا منافع لینے کا فیصد حکمت عملی
- اجناس کے مستقبل اور ڈیجیٹل کرنسی کے تبادلے کے API میں اختلافات
- تجارتی حکمت عملی میں K لائن کے سائے حصے کا اطلاق
- کریپٹوکرنسی کی کوانٹیٹیو ٹریڈنگ حکمت عملی تبادلہ ترتیب
- ہائی فریکوئنسی حکمت عملی بیک ٹسٹنگ کے لئے تیار کردہ ٹِک لیول ٹرانزیکشن میچنگ میکانزم
- تجارتی حکمت عملی تیار کرنے کا تجربہ
- مقداری تجارت میں K لائن ڈیٹا پروسیسنگ
- ڈیجیٹل کرنسی کی مقدار کی تجارت کی حکمت عملی تبادلہ کی تشکیل کی تفصیلات
- ٹرانزیکشن میں مشین لرننگ ٹیکنالوجی کا استعمال
- آپ کو ہارڈ کور حکمت عملی سیکھنے کے لئے لے جاتا ہے "C++ OKEX معاہدہ ہیجنگ حکمت عملی"
- منظم صف بندی کے ساتھ متعدد خالی متوازن حقوق اور مفادات کی حکمت عملی کا حصول
- ڈیٹا سے چلنے والی ٹکنالوجی کے ذریعہ جوڑے کی تجارت
- ڈیجیٹل کرنسی مارکیٹ کا مقداری تجزیہ
- پیتھون کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے ایک دوہری تھرو ڈیجیٹل کرنسی کی مقدار کی تجارت کی حکمت عملی کو لاگو کرنے کے لئے
- K لائن ڈیٹا پروسیسنگ میں غیر معمولی بات چیت
- پیتھون کے ساتھ قیمت کی حرکیات کا تجزیہ کرنے کے لئے مقداری تجارت کی حکمت عملی
- ٹائم سیریز ڈیٹا تجزیہ اور ٹِک ڈیٹا ریورس
- تجارت کی حکمت عملی تیار کرنے کے تجربات