Trendfolgende Grid-Strategie
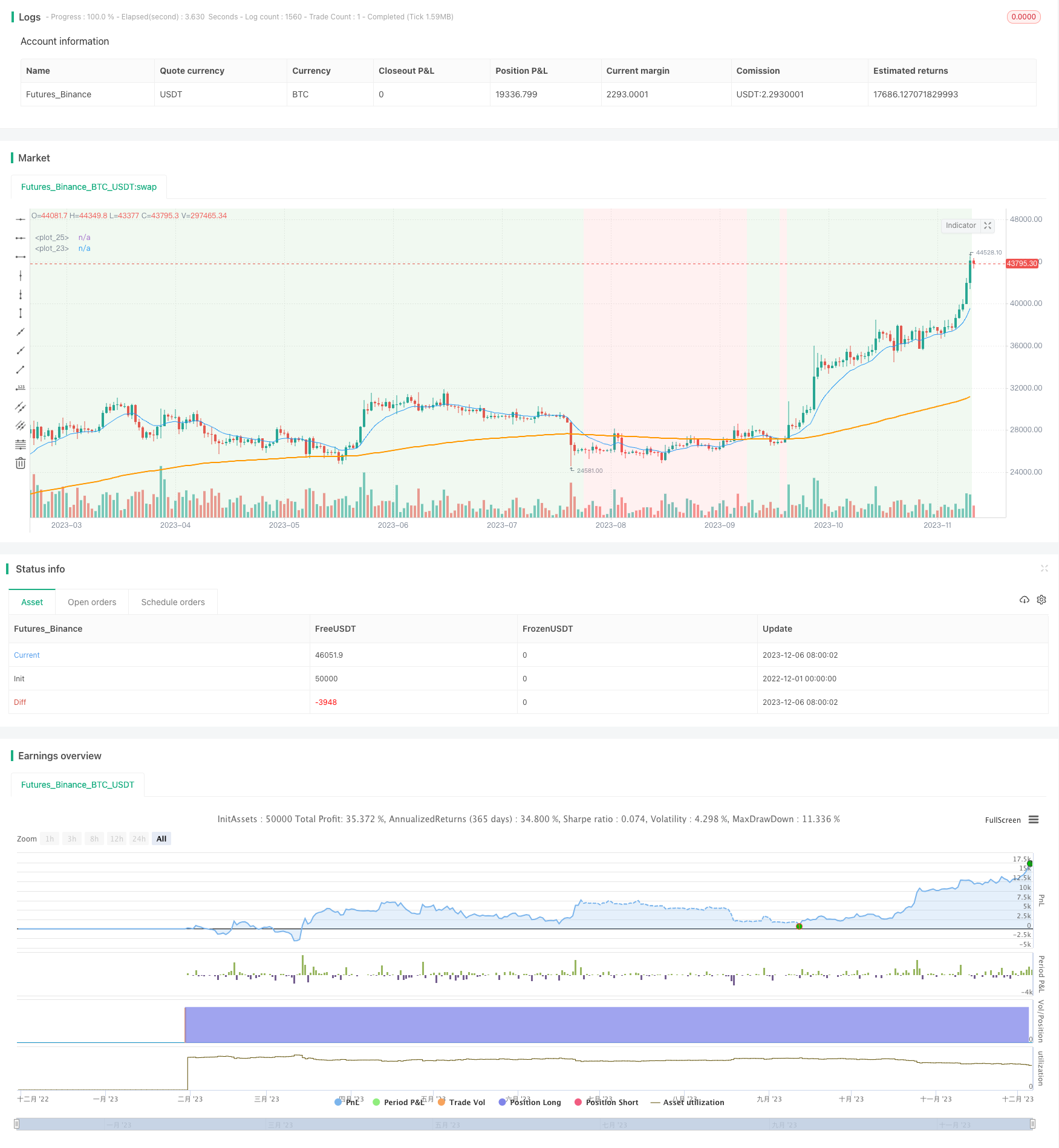
Überblick
Die Strategie ist eine Trend-Tracking-Gitter-Strategie, die nur mehr und keine Leerstellen auswählt und die Zeiträume der großen Aufwärtstrends auswählt. Die Standard-Gittergröße ist 1x der ATR, die Abwärtsverfolgung erstellt die Größen 1, 2 und 3 für die Nachbestellung, die 5. Größe für den Verlust. Wenn der Preis bei einer Leerstellung ein Gitter durchbricht, bewegt sich das gesamte Gitter nach oben.
Strategieprinzip
- Die EMA-Durchschnittslinie wird verwendet, um die Richtung des großen Trends zu bestimmen, wobei EMA12 größer als EMA144 als ein großer Trend nach oben bezeichnet wird
- Nur bei einem starken Aufwärtstrend mehr Geld zu investieren
- Größe des Rastergrößens ist standardmäßig 1 mal ATR, multiplizierbar
- Aufbau eines Grids für die Abwärtsverfolgung der Preise in den Stufen 1, 2 und 3
- Grade 5 setzt den Stop-Loss
- Stop-Loss- und Stop-Stop-Punkte nach der Börsenöffnung
- Wenn die Preiserhöhung die Stop-Limit-Gleichung überschreitet
- Wenn ein Preisrückgang eine Stop-Loss-Plating auslöst
- Wenn der Preis das letzte Grid erneut durchbricht, wird die Position und die Anzahl des Grids neu berechnet und nach oben verfolgt, nachdem alle Positionen ausgelöst wurden.
Die Strategie ermittelt die Richtung des großen Trends über die EMA und kann in Verbindung mit der Gitterstrategie verfolgt werden. Sie ermöglicht einen größeren Gewinn bei einem großen Aufwärtstrend. Die Gitter setzen mehrere Preispunkte ein, die Lager in Gruppen aufbauen und das Risiko einer einzelnen Position reduzieren. Die Stop-Loss-Einstellung ermöglicht die Sperrung der Gewinne und kontrolliert den maximalen Verlust.
Analyse der Stärken
- Vermeiden Sie negative Positionen, indem Sie die EMA nutzen, um die Richtung der großen Trends zu bestimmen
- Die Grid-Strategie reduziert das Risiko eines einzelnen Lagers
- Stop-Loss-Einstellungen, um Gewinne zu blockieren und maximale Verluste zu kontrollieren
- Nach dem Ausgleich der Position kann das Netz neu berechnet werden, um die Gewinne zu vergrößern.
Der Hauptvorteil dieser Strategie besteht darin, dass die Kombination von Trend- und Gitterhandel sowohl die Richtigkeit der Trendrichtung gewährleistet als auch die Risikodistribution der Gitterstrategie ermöglicht. Darüber hinaus kann das Gitter nach dem Ausgleich der Position neu berechnet werden.
Risikoanalyse
- Der Trend kann falsch beurteilt werden, in die falsche Richtung
- Die Netze sind in der Lage, ihre Kunden zu unterstützen, um ihre Kunden zu unterstützen.
- Die Verluste erreichten den Stop-Loss-Punkt zu schnell und die Positionen wurden vollständig ausgeglichen.
- Der Rückschlag verhindert den Wiedereintritt in die Startpunkte.
Das Risiko besteht hauptsächlich darin, dass ein großer Trend falsch beurteilt wird, was zu einem erheblichen Verlust bei der Aufstellung von Positionen im Gegenzug führt. Darüber hinaus werden die Verluste bei starken Marktschwankungen, bei denen mehrere Grids gleichzeitig eingesperrt sind, noch verstärkt.
Durch die Optimierung von EMA-Parametern kann die Genauigkeit der Beurteilung großer Trends verbessert werden. Die Anpassung der Gitterspannung und der Anzahl der ersten Aufträge kann auch den Gesamtverlust kontrollieren. Die Einstellung der Stop-Loss-Position muss die Häufigkeit der Marktfluktuation berücksichtigen.
Optimierungsrichtung
Die Strategie kann auch in folgenden Richtungen optimiert werden:
- Optimierung der EMA-Parameter zur Erhöhung der Genauigkeit bei der Beurteilung großer Trends
- Anpassung der Spannweite und Anzahl der Gitter, Optimierung des Gewinn-Risiko-Verhältnisses
- Verbesserte Stop-Loss-Logik, z. B. partielle Positionsstop, bewegliche Stop-Loss
- Erhöhung der Wiedereintrittsbeschränkungen, um eine vorzeitige Wiedereintrittsverhinderung im Rahmen der Rebound-Prozesse zu vermeiden
- Es ist eine Kombination aus mehreren Indikatoren, die den Einstieg bestimmen, wie z. B. die Form der K-Linie, die Sensitivität der Indikatoren usw.
- Es ist wichtig, dass wir uns in der Lage sehen, die Situation zu beurteilen und die Verluste zu vermeiden, die aus der Ausnahme resultieren.
Durch diese Optimierungsmaßnahmen kann die Strategie in einer großen Situation mehr Gewinn erzielen, während die Risiken kontrolliert und die Verluste in einer normalen bewegten Entwicklung verringert werden.
Zusammenfassen
Die Strategie ist eine organische Kombination aus Trendhandel und Grid-Handel. Es nutzt die EMA, um die Richtung zu bestimmen, und dann die Grid-Strategie, um Positionen in Schuhen zu errichten.
/*backtest
start: 2022-12-01 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-07 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © zxcvbnm3260
//@version=5
strategy("grid strategy long", overlay=true)
// 版本更新记录:
// v1.0 2021/11/09 只做多、不做空,选择大趋势向上的时间段。网格大小默认为1倍ATR,往下1、2、3个网格吃单,第5个网格止损。空仓时到达往上一个网格则网格整体抬升。(Only go long, not short, choose a time period when the general trend is up. The default grid size is 1x ATR, the next one, two, and three grids will take orders, and the fifth grid will stop loss. When the empty position reaches the upper grid, the grid as a whole rises.)
X_ATR = input.float(title='网格大小是多少倍ATR?', defval = 1)
// 1.基础变量
ema169 = ta.ema(close, 169)
ema144 = ta.ema(close, 144)
ema12 = ta.ema(close, 12)
ema576 = ta.ema(close, 576)
ema676 = ta.ema(close, 676)
plot(ema169, color=color.new(color.orange, 0), linewidth=2)
// plot(ema144, color=color.orange)
plot(ema12, color=color.blue)
// plot(ema676, color=color.orange, linewidth=1)
mtr = math.max(high - low, math.abs(close[1] - high), math.abs(close[1] - low))
atr = ta.ema(mtr, 30)
is_0930 = hour(time, 'GMT-4') == 9 and minute(time, 'GMT-4') == 30
is_1500 = hour(time, 'GMT-4') == 15 and minute(time, 'GMT-4') == 00
is_1530 = hour(time, 'GMT-4') == 15 and minute(time, 'GMT-4') == 30
is_yangxian = close>open
is_yinxian = close<open
// 2.基本趋势标记
big_trend = ema12 >= ema169 ? 1 : 0
big_trend2 = ema12 <= ema169 ? 1 : 0
// 背景的变色处理:
bgcolor(big_trend == 1 ? color.new(color.green, 90) : color.new(color.red, 90) )
// 3.网格点位初始化
grid_size = atr * X_ATR // 网格大小
price_entry1 = open - grid_size*1
price_entry2 = open - grid_size*2
price_entry3 = open - grid_size*3
price_stop_loss = open - grid_size*5
price_exit1 = price_entry1 + grid_size*1
price_exit2 = price_entry2 + grid_size*1
price_exit3 = price_entry3 + grid_size*1
qty1 = int(1000/price_entry1)
qty2 = int(1000/price_entry2)
qty3 = int(1000/price_entry3)
// 标出各种点位
slm_lines_time(time, price_entry1, price_entry2, price_entry3, price_stop_loss, price_exit1)=>
time2 = time + 1000*3600*24*5
line.new(time, price_stop_loss, time2, price_stop_loss, color=color.red, xloc = xloc.bar_time, width=2) // 止损位
line.new(time, price_entry1, time2, price_entry1, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_time) //
line.new(time, price_entry2, time2, price_entry2, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_time) //
line.new(time, price_entry3, time2, price_entry3, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_time) //
line.new(time, price_exit1, time2, price_exit1, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_time, width=2) //
slm_lines(time, price_entry1, price_entry2, price_entry3, price_stop_loss, price_exit1)=>
line.new(bar_index, price_stop_loss, bar_index[5], price_stop_loss, color=color.red, xloc = xloc.bar_index, width=2) // 止损位
line.new(bar_index, price_entry1, bar_index[5], price_entry1, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_index) //
line.new(bar_index, price_entry2, bar_index[5], price_entry2, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_index) //
line.new(bar_index, price_entry3, bar_index[5], price_entry3, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_index) //
line.new(bar_index, price_exit1, bar_index[5], price_exit1, color=color.green, xloc = xloc.bar_index, width=2) //
// 4.网格点位更新和下单
is_entry0 = big_trend==1 and year>=2020
var is_entry = false
// 未进场时:
if is_entry0 and not is_entry
is_entry := true
grid_size := atr * X_ATR // 网格大小
price_entry1 := close - grid_size*1
price_entry2 := close - grid_size*2
price_entry3 := close - grid_size*3
price_stop_loss := close - grid_size*5
price_exit1 := price_entry1 + grid_size*1
price_exit2 := price_entry2 + grid_size*1
price_exit3 := price_entry3 + grid_size*1
qty1 := int(1000/price_entry1)
qty2 := int(1000/price_entry2)
qty3 := int(1000/price_entry3)
// slm_lines(time, price_entry1, price_entry2, price_entry3, price_stop_loss, price_exit1)
strategy.entry("open1", strategy.long, qty1, limit = price_entry1)
strategy.entry("open2", strategy.long, qty2, limit = price_entry2)
strategy.entry("open3", strategy.long, qty3, limit = price_entry3)
strategy.exit("close1", qty = qty1, limit = price_exit1, stop = price_stop_loss)
strategy.exit("close2", qty = qty2, limit = price_exit2, stop = price_stop_loss)
strategy.exit("close3", qty = qty3, limit = price_exit3, stop = price_stop_loss)
// 已进场的各类情况
// 1.止损
if is_entry and close <= price_stop_loss
strategy.close_all()
is_entry := false
// 2.网格抬升
if is_entry and close >= price_exit1
is_entry := false