Dynamic balancing strategies based on digital currency
Author: , Created: 2020-03-03 10:17:43, Updated: 2023-10-09 22:49:27
A summary
Benjamin Graham, Warren Buffett's mentor, once wrote in his book, The Smarter Investor, about a trading model in which stocks and bonds are dynamically balanced. The transaction model is very simple:
The transaction model is very simple:
- Invest 50% of your money in a stock fund and the remaining 50% in a bond fund; that is, both stocks and bonds are half each.
- A re-balancing of assets at fixed intervals or market changes, returning the ratio of equity assets to bond assets to the original 1:1. That's the whole logic of the whole strategy, including when to buy and how much to buy.
Second, the principle of dynamic equilibrium
In this approach, the volatility of the bond fund is actually small, much lower than the volatility of the stock, so the bonds are considered here as a'reference peg', that is, the bond is used to measure whether the stock is earning too much or too little.
If the stock price rises, the market value of the stock is greater than the market value of the bond, and when the market value ratio of the two exceeds the set threshold, the total position is readjusted, the stock is sold, and the bond is bought, returning the stock-bond market value ratio to the original 1:1.
Instead, a fall in the stock price causes the market value of the stock to be less than the market value of the bond, and when the market value ratio of the two exceeds the set threshold, the total position is readjusted, stocks are bought and bonds are sold, bringing the stock-bond market value ratio back to the original 1:1 ratio.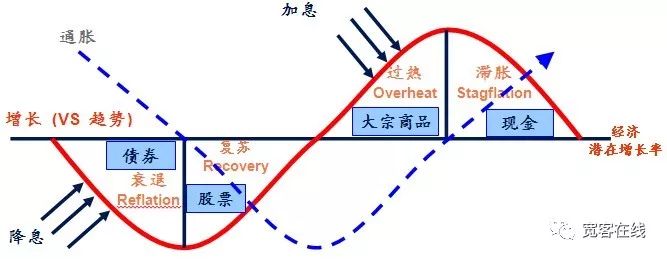
In this way, a dynamically balanced ratio between stocks and bonds is enough to enjoy the fruits of stock growth and reduce asset volatility. As a pioneer of value investing, Graham gave us a great idea.
Third, strategic logic
The dynamic balancing strategy in BTC, a blockchain asset
Strategic logic
- At the current value of BTC, the account balance retains ¥5000 in cash and 0.1 BTC, i.e. the initial ratio of cash to BTC market value is 1:1.
- If the price of BTC rises to ¥6000, i.e. the market value of BTC is greater than the account balance, and the difference between them is greater than the set threshold, sell ((6000-5000) / 6000/2 coins.
- If the price of BTC drops to ¥4,000, i.e. the market value of BTC is less than the account balance, and the difference between them is more than the set threshold, buy ¥5000-4000/4000/2 coins.
In this way, regardless of whether BTC is appreciated or depreciated, the account balance is always kept dynamically equal to the market value of BTC. If BTC is depreciated, buy some, wait for it to come back, sell some more, as if it were normal.
Four, the strategic framework
So, how do we do this with code? Let's take inventors to quantify trading platforms as an example, first let's look at the strategic framework:
// 撤单函数
function CancelPendingOrders() {}
// 下单函数
function onTick() {}
// 主函数
function main() {
// 过滤非重要信息
SetErrorFilter("GetRecords:|GetOrders:|GetDepth:|GetAccount|:Buy|Sell|timeout");
while (true) { // 轮询模式
if (onTick()) { // 执行 onTick 函数
CancelPendingOrders(); // 取消未成交的挂单
Log(_C(exchange.GetAccount)); // 打印当前账户信息
}
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000); // 休眠
}
}
The whole policy framework is actually quite simple, with a main main function, an onTick sub-function, a CancelPendingOrders function, and the necessary parameters.
5th, the sub-module
// 下单函数
function onTick() {
var acc = _C(exchange.GetAccount); // 获取账户信息
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker); // 获取 Tick 数据
var spread = ticker.Sell - ticker.Buy; // 获取 Tick 数据的买卖价差
// 账户余额与当前持仓价值的差值的 0.5倍
var diffAsset = (acc.Balance - (acc.Stocks * ticker.Sell)) / 2;
var ratio = diffAsset / acc.Balance; // diffAsset / 账户余额
LogStatus('ratio:', ratio, _D()); // 打印 ratio和当前时间
if (Math.abs(ratio) < threshold) { // 如果 ratio的绝对值小于指定阈值
return false; // 返回 false
}
if (ratio > 0) { // 如果 ratio大于 0
var buyPrice = _N(ticker.Sell + spread, ZPrecision); // 计算下单价格
var buyAmount = _N(diffAsset / buyPrice, XPrecision); // 计算下单量
if (buyAmount < MinStock) { // 如果下单量小于最小交易量
return false; // 返回 false
}
exchange.Buy(buyPrice, buyAmount, diffAsset, ratio); // 买入下单
} else {
var sellPrice = _N(ticker.Buy - spread, ZPrecision); // 计算下单价格
var sellAmount = _N(-diffAsset / sellPrice, XPrecision); // 计算下单量
if (sellAmount < MinStock) { // 如果下单量小于最小交易量
return false; // 返回 false
}
exchange.Sell(sellPrice, sellAmount, diffAsset, ratio); // 卖出下单
}
return true; // 返回 true
}
The following transaction logic is clear, all the annotations have been written in the code, you can click on the image to enlarge it.
The main processes are as follows:
- Get your account information.
- Get the Tick data.
- Tick data is calculated as the difference between the bid and offer prices.
- Calculate the account balance and BTC market price difference.
- Calculate the purchase and sale conditions, order price, order quantity.
- Subscribe and return true.
6th, withdrawal modules
// 撤单函数
function CancelPendingOrders() {
Sleep(1000); // 休眠 1秒
var ret = false;
while (true) {
var orders = null;
// 持续获取未成交订单数组,如果返回异常,则继续获取
while (!(orders = exchange.GetOrders())) {
Sleep(1000); // 休眠 1秒
}
if (orders.length == 0) { // 如果订单数组为空
return ret; // 返回撤单状态
}
for (var j = 0; j < orders.length; j++) { // 遍历未成交订单数组
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j].Id); // 依次取消未成交订单
ret = true;
if (j < (orders.length - 1)) {
Sleep(1000); // 休眠 1秒
}
}
}
}
It's easier to remove modules, the steps are as follows:
- I'm not going to be able to do it, but I'm going to have to wait a second before I can withdraw it, individual exchange, you know.
- Continue to retrieve the array of outstanding orders, and continue to retrieve if an exception is returned.
- If the pending order array is empty, immediately return the withdrawal status.
- If there are outstanding orders, go through the entire array and cancel them in order of order number.
7 Complete policy source code
// 回测环境
/*backtest
start: 2018-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2018-08-01 11:00:00
period: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Bitfinex","currency":"BTC_USD"}]
*/
// 撤单函数
function CancelPendingOrders() {
Sleep(1000); // 休眠 1秒
var ret = false;
while (true) {
var orders = null;
// 持续获取未成交订单数组,如果返回异常,则继续获取
while (!(orders = exchange.GetOrders())) {
Sleep(1000); // 休眠 1秒
}
if (orders.length == 0) { // 如果订单数组为空
return ret; // 返回撤单状态
}
for (var j = 0; j < orders.length; j++) { // 遍历未成交订单数组
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j].Id); // 依次取消未成交订单
ret = true;
if (j < (orders.length - 1)) {
Sleep(1000); // 休眠 1秒
}
}
}
}
// 下单函数
function onTick() {
var acc = _C(exchange.GetAccount); // 获取账户信息
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker); // 获取 Tick 数据
var spread = ticker.Sell - ticker.Buy; // 获取 Tick 数据的买卖价差
// 账户余额与当前持仓价值的差值的 0.5倍
var diffAsset = (acc.Balance - (acc.Stocks * ticker.Sell)) / 2;
var ratio = diffAsset / acc.Balance; // diffAsset / 账户余额
LogStatus('ratio:', ratio, _D()); // 打印 ratio和当前时间
if (Math.abs(ratio) < threshold) { // 如果 ratio的绝对值小于指定阈值
return false; // 返回 false
}
if (ratio > 0) { // 如果 ratio大于 0
var buyPrice = _N(ticker.Sell + spread, ZPrecision); // 计算下单价格
var buyAmount = _N(diffAsset / buyPrice, XPrecision); // 计算下单量
if (buyAmount < MinStock) { // 如果下单量小于最小交易量
return false; // 返回 false
}
exchange.Buy(buyPrice, buyAmount, diffAsset, ratio); // 买入下单
} else {
var sellPrice = _N(ticker.Buy - spread, ZPrecision); // 计算下单价格
var sellAmount = _N(-diffAsset / sellPrice, XPrecision); // 计算下单量
if (sellAmount < MinStock) { // 如果下单量小于最小交易量
return false; // 返回 false
}
exchange.Sell(sellPrice, sellAmount, diffAsset, ratio); // 卖出下单
}
return true; // 返回 true
}
// 主函数
function main() {
// 过滤非重要信息
SetErrorFilter("GetRecords:|GetOrders:|GetDepth:|GetAccount|:Buy|Sell|timeout");
while (true) { // 轮询模式
if (onTick()) { // 执行 onTick 函数
CancelPendingOrders(); // 取消未成交的挂单
Log(_C(exchange.GetAccount)); // 打印当前账户信息
}
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000); // 休眠
}
}
External parameters
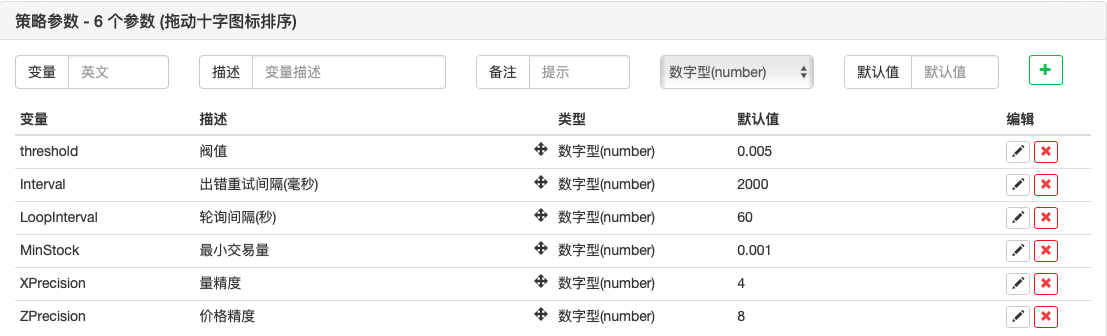
8 Strategic retesting
Next, let's test this simple dynamic balancing strategy to see if it works. Below is a review of BTC's historical data for reference only.
Reviewing the environment
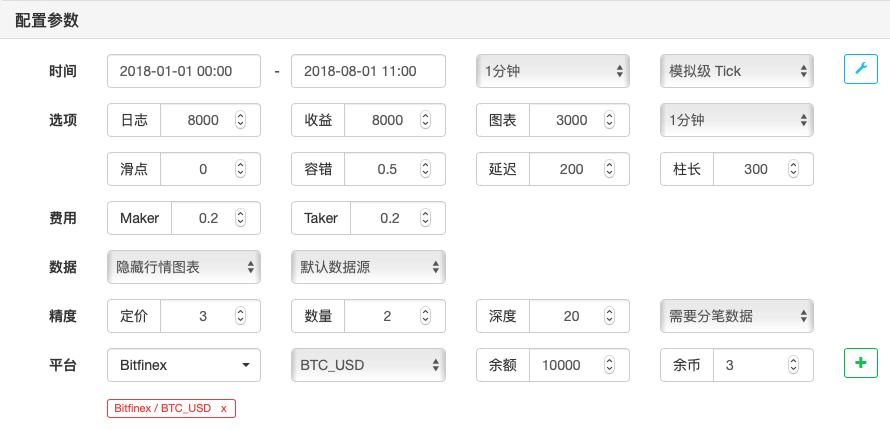
Re-tested performance
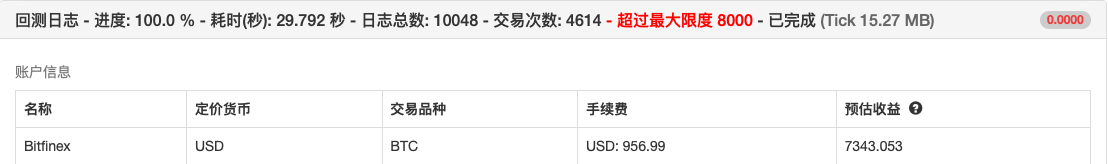
The retest curve
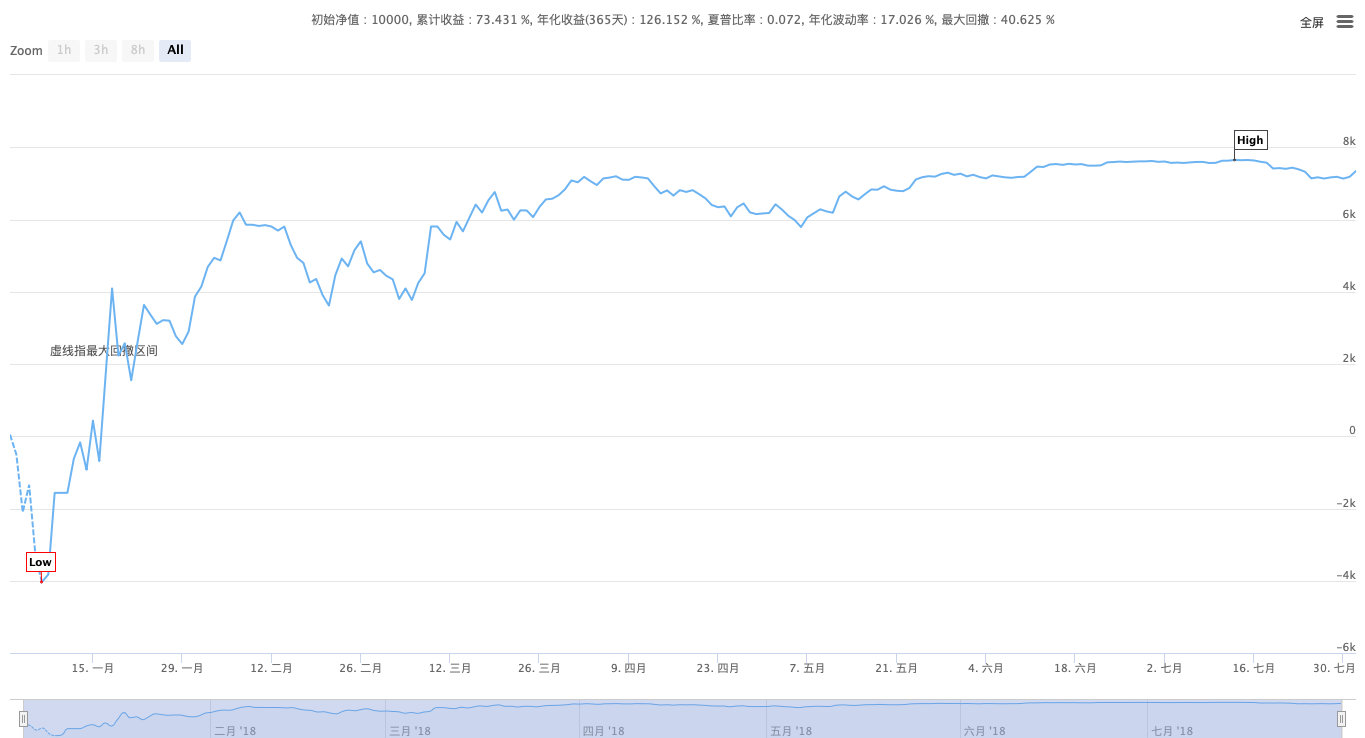
Here's another chart of the price movement of BTC over the same period.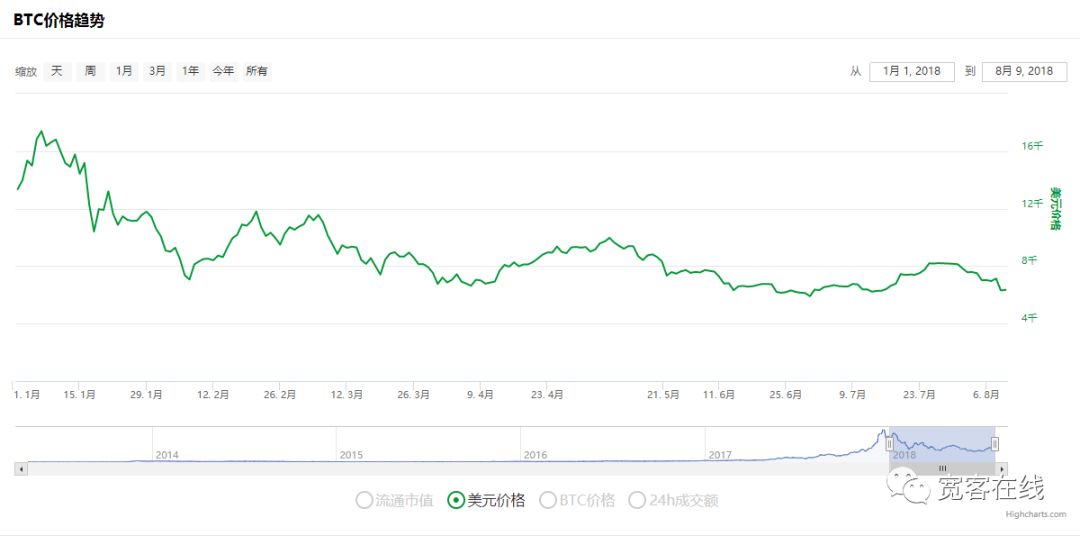
Over the review period, BTC has been declining for eight months, with a maximum decline of more than 70%, which has caused many investors to lose confidence in blockchain assets. This strategy has a cumulative return of up to 160% and an annualized return risk ratio of more than 5%.
9 Acquire the source code of the strategy
The source code of the strategy has been made public on the inventor quantification website.https://www.fmz.com/strategy/110545There is no need to configure the online retrieval directly.
10 and summary
This dynamic balancing strategy, with only one core parameter (threshold threshold), is a very simple investment method that seeks not excessive returns, but solid returns. In contrast to the trend strategy, the dynamic balancing strategy is counter-moving. While the dynamic balancing strategy is just the opposite, when the market is hot, the stock decreases, and when the market is cold, the stock fluctuates, somewhat similar to macroeconomic regulation.
In fact, the dynamic balancing strategy is one that embraces the idea of price unpredictability, while also capturing price volatility. The key core of the dynamic balancing strategy is setting and adjusting asset allocation ratios, and triggering thresholds. Given the length of the article, an article cannot do it face to face, except to know the words, mind to mind.
Let's end with a famous quote from Benjamin Graham in his book, The Intelligent Investor:The stock market is not a "weighing scale" that can accurately measure value, but rather it is a "voting machine", where the decisions made by countless people are a mixture of rational and emotional, and often these choices and rational value judgments are far apart. The secret to investing is to invest when the price is far below the intrinsic value and believe that the market trend will recover.Benjamin Graham is a brilliant investor.
- Introduction to Lead-Lag Arbitrage in Cryptocurrency (2)
- Introduction to the Lead-Lag suite in the digital currency (2)
- Discussion on External Signal Reception of FMZ Platform: A Complete Solution for Receiving Signals with Built-in Http Service in Strategy
- Discussing FMZ platform external signal reception: a complete set of strategies for the reception of signals from built-in HTTP services
- Introduction to Lead-Lag Arbitrage in Cryptocurrency (1)
- Introduction to the Lead-Lag suite in digital currency (1)
- Discussion on External Signal Reception of FMZ Platform: Extended API VS Strategy Built-in HTTP Service
- External signal reception on FMZ platforms: extended API vs. built-in HTTP services
- Discussion on Strategy Testing Method Based on Random Ticker Generator
- Strategy testing methods based on random market generators explored
- New Feature of FMZ Quant: Use _Serve Function to Create HTTP Services Easily
- JavaScript version SuperTrend strategy
- SuperTrend V.1 - Supertrend line system
- JavaScript version of the SuperTrend policy
- [Millennium War] Currency exchange multi-currency hedging strategies Recent recaps and results of the minute-level K-line review ((Part 4)
- Hands-on teaches you how to implement a data collector
- [Millennium War] Bitcoin futures do nothing and do more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more]
- [Millennium War] Bitcoin futures do nothing and do more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more.
- [Millennium War] Research on multi-currency hedging strategies in the field of currency exchange (part 1)
- 98 undergraduate coins and the way to quantify
- Python iceberg delegation policy
- Use a trading terminal plug-in to facilitate manual transactions
- Python version of the MACD graph example
- The strategy of cross-currency arbitrage based on the Brin Belt
- Timing start or stop widgets for quantified trading robots using Python
- Corrupt Sisters Speak at the First Session of the General Assembly
- Quantitative fractional rate trading strategy
- The Python spreadsheet platform balancing strategy
- The old farmer's journey to the pit
- The story of a post-95 coin collector
- Hands-on teaches you how to convert a Python single-variety policy into a multi-variety policy.