Dual Moving Average Trading Strategy
Author: ChaoZhang, Date: 2023-12-01 14:36:33Tags:
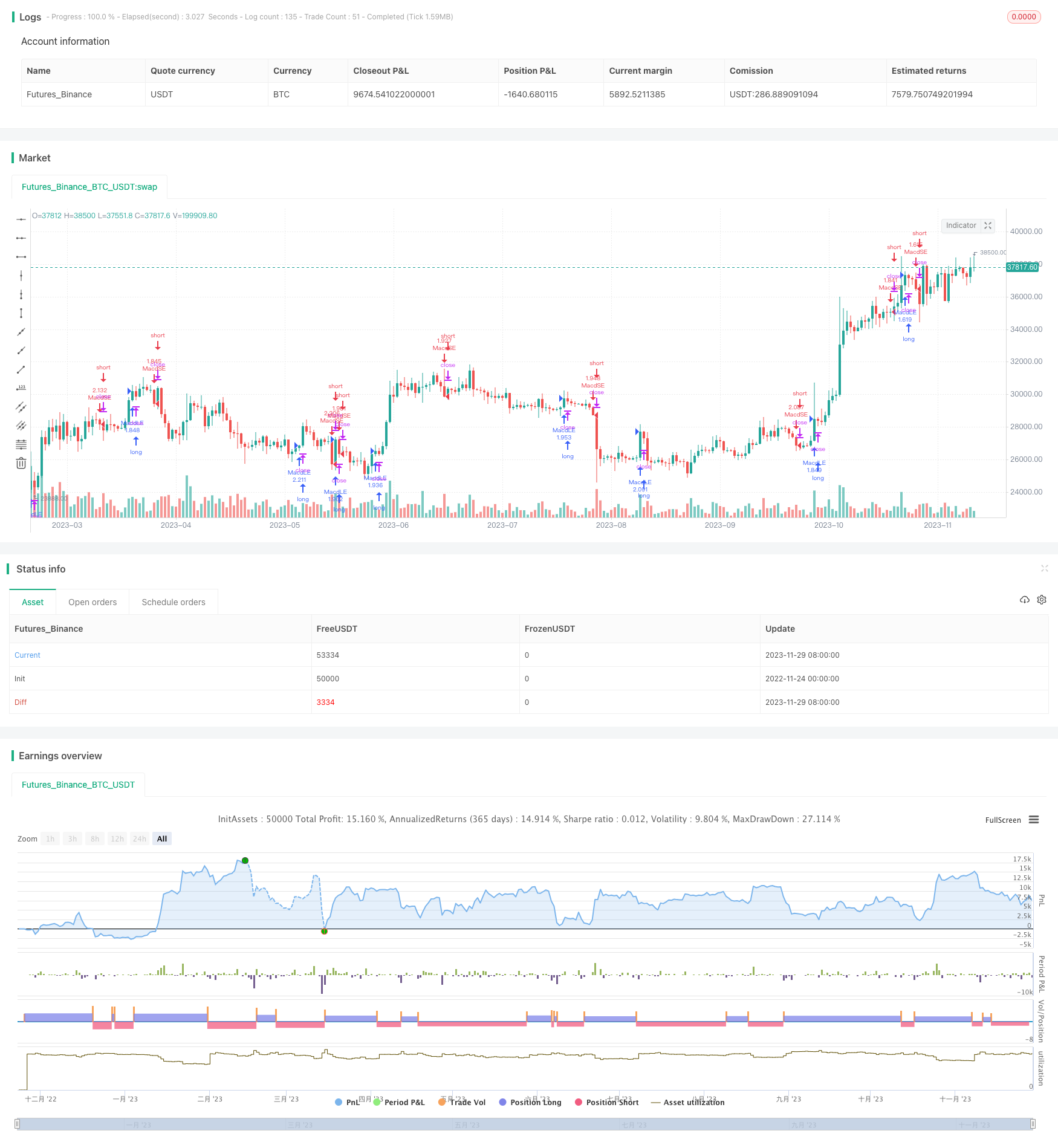
Overview
The dual moving average trading strategy generates trading signals by calculating exponential moving averages (EMAs) of different timeframes to form a fast EMA and slow EMA, and observing their golden crosses and death crosses. It goes long when the fast EMA crosses above the slow EMA, and goes short when the fast EMA crosses below the slow EMA. This strategy captures the trend reversal points of the moving averages and is a commonly used trend following strategy.
Strategy Logic
The core indicators of the dual moving average strategy are the fast EMA and slow EMA. The fast EMA has a default parameter of 12 days, while the slow EMA has a default parameter of 26 days. The formula for exponential moving average is:
EMA(t) = (C(t) - EMA(t-1)) x SF + EMA(t-1)
Where C(t) is today’s closing price, and SF is the smoothing factor. Different from simple moving average, EMA assigns more weight to the recent data and thus responds faster to price changes.
The trading rules are:
-
Enter long positions on golden cross of fast EMA crossing above slow EMA from below.
-
Enter short positions on death cross of fast EMA crossing below slow EMA from above.
-
Exit positions on divergence of the EMAs.
By capturing the crossover patterns of the EMAs, it can reflect the market trends and increase profitability.
Advantages
As a mature technical indicator strategy, the dual moving average strategy has the following strengths:
-
Its logic is clear and easy to understand and implement.
-
It gives highly accurate judgement on market supply and demand and thus has relatively high win rate.
-
It effectively filters market noise and captures main trends.
-
It can be applied across different instruments and timeframes.
-
It can be combined with other indicators for strategy enrichment.
-
It has a high capital utilization efficiency for large capital trading.
Risk Analysis
There are also certain limitations of the strategy:
-
It fails to react to intense market moves like sharp bear market selloffs.
-
It tends to generate frequent false signals and whipsaws in sideways rangebound markets.
-
Its parameters need optimization across different markets and timeframes.
-
It cannot determine appropriate reversal levels of the trend.
The risks can be mitigated by adjusting EMA periods, adding supplementary filters etc. to make the strategy more robust.
Enhancement Opportunities
The dual moving average strategy can be improved from the following aspects:
-
Incorporate MACD indicator to judge trend strength and avoid wrong trades.
-
Add trading volumes to confirm true breakout signals.
-
Combine with Bollinger Bands, candlestick patterns for more precise entry and exit rules.
-
Utilize machine learning approaches like LSTM to auto optimize parameters for better adaptiveness.
Conclusion
The dual moving average trading strategy captures trading opportunities from EMA golden crosses and death crosses to determine trend reversal points for steady profits. With the advantages of simplicity, capital efficiency and ease of implementation, it is a preferred choice for algorithmic trading beginners. But it also has certain flaws like generating false signals. More indicators should be introduced to optimize it for specific markets and environments. Overall speaking, it is a very practical and useful technical indicator strategy.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-24 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-30 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © antondmt
//@version=5
strategy("Returns & Drawdowns Table", "R & DD", true, calc_on_every_tick = false, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 100, process_orders_on_close = true)
i_eq_to_dd = input.string("Compound Equity", "Mode", ["Simple Equity", "Compound Equity", "Drawdown"], group = "R & DD Table")
i_precision = input.int(2, "Return Precision", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_col = input.color(#D4D4D4, "Headers Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_text_col = input.color(color.black, "Headers Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_pos_col = input.color(color.green, "Positive Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_neg_col = input.color(color.red, "Negative Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_zero_col = input.color(#DDDDDD, "Zero Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_cell_text_col = input.color(color.white, "Cell Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
// TIME {
var month_times = array.new_int(0) // Array of all month times
new_month = month(time) != month(time[1])
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(month_times, time)
var year_times = array.new_int(0)
new_year = year(time) != year(time[1])
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(year_times, time)
//}
// SIMPLE EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Simple equity is strictly calculated from start to end of each month/year equity. There is no compound
var monthly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Simple Equity")
var initial_monthly_equity = strategy.equity // Starting equity for each month
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_monthly_equity) / initial_monthly_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
initial_monthly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(monthly_simp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_simp_pnls, array.size(monthly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
var initial_yearly_equity = strategy.equity
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_yearly_equity) / initial_yearly_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
initial_yearly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(yearly_simp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_simp_pnls, array.size(yearly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// COMPOUND EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Compound equity is strictly calculated based on equity state from the beginning of time until the end of each month/year equity. It shows the exact equity movement through time
var monthly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Compound Equity")
var initial_equity = strategy.equity
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(monthly_comp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_comp_pnls, array.size(monthly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(yearly_comp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_comp_pnls, array.size(yearly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// DRAWDOWN CALCULATIONS {
// Drawdowns are calculated from highest equity to lowest trough for the month/year
var monthly_dds = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly drawdowns
var yearly_dds = array.new_float(0)
if (i_eq_to_dd == "Drawdown")
total_equity = strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
var cur_month_dd = 0.0
var m_ATH = total_equity // Monthly All-Time-High (ATH). It is reset each month
m_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(m_ATH[1]))
m_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / m_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100 // Drawdown at current bar
if(m_drawdown < cur_month_dd)
cur_month_dd := m_drawdown
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
cur_month_dd := 0.0
m_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(monthly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(monthly_dds, array.size(monthly_dds) - 1, cur_month_dd)
var cur_year_dd = 0.0
var y_ATH = total_equity
y_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(y_ATH[1]))
y_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / y_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100
if(y_drawdown < cur_year_dd)
cur_year_dd := y_drawdown
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
cur_year_dd := 0.0
y_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(yearly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(yearly_dds, array.size(yearly_dds) - 1, cur_year_dd)
// }
// TABLE LOGIC {
var main_table = table(na)
table.clear(main_table, 0, 0, 13, new_year ? array.size(year_times) - 1 : array.size(year_times))
main_table := table.new(position.bottom_right, columns = 14, rows = array.size(year_times) + 1, border_width = 1)
t_set_headers() => // Sets time headers of the table
// Set month headers
table.cell(main_table, 0, 0, "", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 1, 0, "Jan", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 2, 0, "Feb", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 3, 0, "Mar", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 4, 0, "Apr", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 5, 0, "May", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 6, 0, "Jun", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 7, 0, "Jul", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 8, 0, "Aug", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 9, 0, "Sep", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 10, 0, "Oct", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 11, 0, "Nov", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 12, 0, "Dec", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 13, 0, str.tostring(i_eq_to_dd), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
// Set year headers
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
table.cell(main_table, 0, i + 1, str.tostring(year(array.get(year_times, i))), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
t_set_months() => // Sets inner monthly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => monthly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => monthly_comp_pnls
=> monthly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(month_times) - 1
m_row = year(array.get(month_times, i)) - year(array.get(year_times, 0)) + 1
m_col = month(array.get(month_times, i))
m_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 30) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 30)
table.cell(main_table, m_col, m_row, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = m_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_years() => // Sets inner yearly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => yearly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => yearly_comp_pnls
=> yearly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
y_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 20) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 20)
table.cell(main_table, 13, i + 1, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = y_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_headers()
t_set_months()
t_set_years()
// }
// PLACE YOUR STRATEGY CODE HERE {
// This is a sample code of a working strategy to show the table in action
fastLength = input(12)
slowlength = input(26)
MACDLength = input(9)
MACD = ta.ema(close, fastLength) - ta.ema(close, slowlength)
aMACD = ta.ema(MACD, MACDLength)
delta = MACD - aMACD
if (ta.crossover(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdLE", strategy.long, comment = "MacdLE")
if (ta.crossunder(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdSE", strategy.short, comment = "MacdSE")
// }
- Triple SuperTrend Quantitative Trading Strategy
- Supertrend Trading Strategy Based on ATR and MA Combination
- Supertrend Bollinger Bands Strategy
- Double Reversal Tracking Strategy
- Holy Grail Strategy
- Multiple Percentage Profit Exits Strategy
- Modified Price-Volume Trend Strategy Based on Price-Volume Changes
- Dual Moving Average Crossover Strategy
- Dual Indicators Combo Crazy Intraday Scalping Strategy
- Dynamic Grid Trading Strategy
- Early Profit-Taking Moving Average Opening Bell Exit Strategy
- Monthly Parabolic Breakout Strategy
- Trend Filter Moving Average Crossover Quantitative Strategy
- RSI and Moving Average Based Quantitative Trading Strategy
- Volatility Capture RSI-Bollinger Band Strategy
- Reverse Triad Quantitative Strategy
- FiboBuLL Wave Strategy Based on Bollinger Bands Breakout
- Bitcoin Quantitative Band Trading Strategy Based on Multiple Timeframes
- Trend Following Exponential Moving Average Strategy
- Trailing Stop Loss Reversal Strategy