Estrategia de seguimiento de tendencias basada en kNN
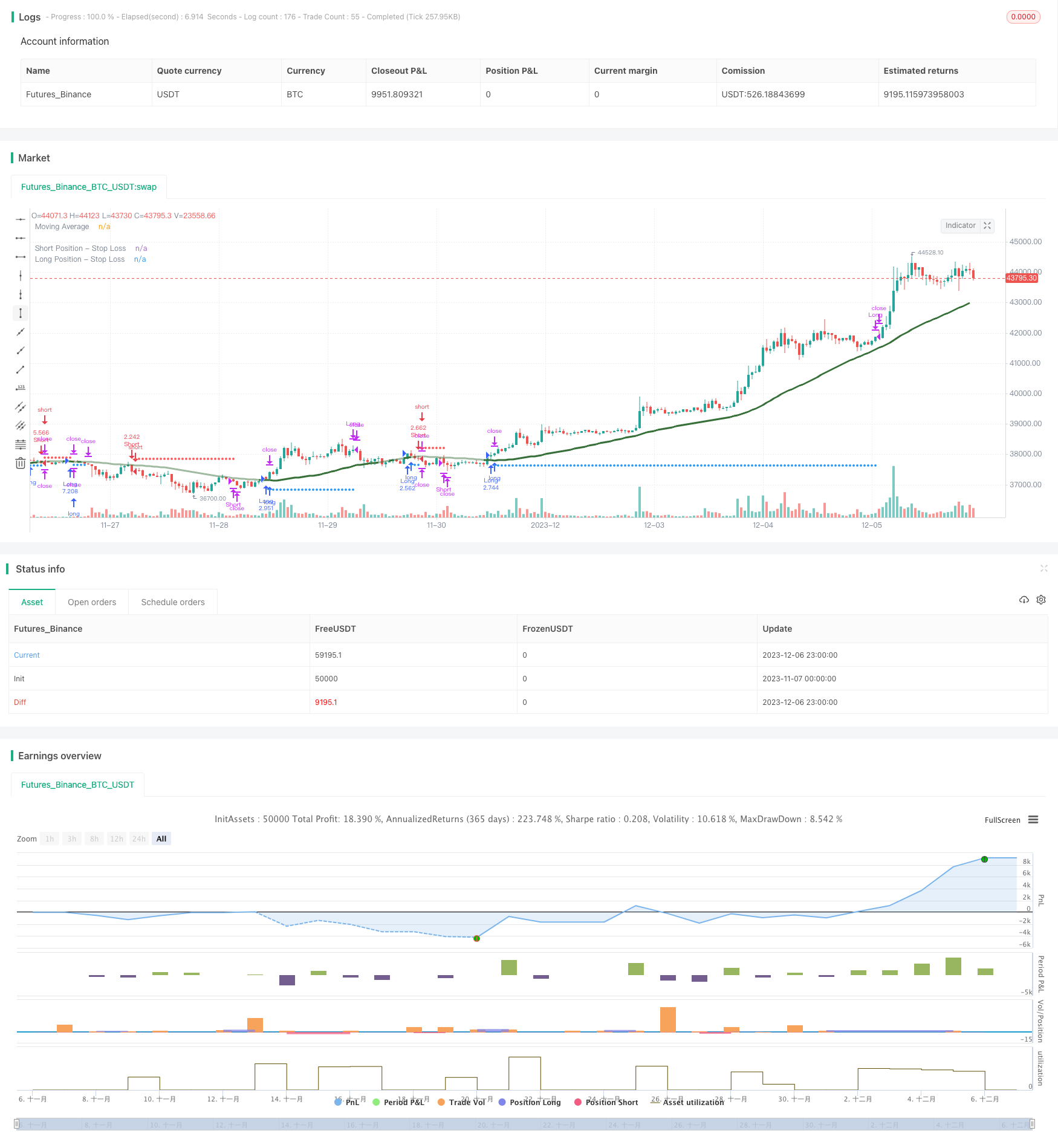
Descripción general
Esta estrategia utiliza kNN algoritmos de aprendizaje automático para predecir las tendencias del mercado y generar señales de posiciones largas y vacías en función de los resultados de la predicción. La estrategia considera de manera integral múltiples factores, como datos históricos, indicadores técnicos, y adquiere características del mercado mediante el entrenamiento de la dinámica del modelo de kNN para automatizar el seguimiento de tendencias de las operaciones.
Principio de estrategia
Recopilación de datos de entrenamiento: recopilación de secuencias de tiempo como el precio de cierre histórico, el volumen de operaciones, así como indicadores técnicos como el RSI, el CCI.
Preprocesamiento de datos: Unificación de los valores del indicador en el intervalo de 0 a 100.
Entrenamiento del modelo kNN: introducir dos características del modelo kNN actual, calcular la distancia europea entre estos vectores de características y los vectores de características históricas, seleccionar la distancia más cercana a k muestras históricas y estadizar la distribución de las etiquetas de esta k muestra:
Obtención de predicciones: predicción de la tendencia actual del mercado basado en las etiquetas de k muestras más cercanas. Si la predicción es de más cabezas, produce una señal de posición larga; si la predicción es de cabezas vacías, produce una señal de posición vacía.
Se puede negociar con filtros como el Stop Loss, el Control de Posiciones y el Moving Average.
Ventajas estratégicas
Utiliza algoritmos de aprendizaje automático para identificar formas de tecnología sin necesidad de intervención humana.
Se puede elegir con flexibilidad diferentes indicadores técnicos como características del modelo y estrategias de optimización en tiempo real.
Estricto mecanismo de control de riesgos, incluido el control de pérdidas y la gestión de posiciones.
La visualización presenta una línea de pérdida, clara e intuitiva.
Riesgos y soluciones
La predicción de aprendizaje automático puede presentar errores. Se pueden elegir modelos de optimización como el valor de k, el vector de característica y el rango de tiempo de muestra adecuados.
Hay un riesgo potencial de transacciones unilaterales. Se puede agregar transacciones bilaterales en el código para eliminar errores.
Si no se ajustan correctamente los parámetros, pueden ocasionar exceso de operaciones. Se deben ajustar adecuadamente los parámetros de tamaño de posición, frecuencia de operaciones, etc.
Dirección de optimización
Prueba de diferentes tipos de indicadores técnicos como características de la entrada de KNN.
Prueba otras medidas de distancia, como la distancia de Manhattan.
Ajuste el tamaño de la posición con la distancia de la muestra o la clasificación de la calidad.
Añadir el conjunto de entrenamiento del modelo, dividir el conjunto de pruebas y lograr la optimización de la rotación.
Resumir
Esta estrategia utiliza el clásico algoritmo de KNN para realizar predicciones de tendencias del mercado y realizar operaciones de seguimiento de tendencias según las señales de predicción. La estrategia tiene características de ajustabilidad de parámetros y control de riesgos, que pueden proporcionar a los usuarios un programa de comercio automatizado eficaz.
/*backtest
start: 2023-11-07 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-07 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © sosacur01
//@version=5
strategy(title=" kNN-based| Trend Following | Trend Following", overlay=true, pyramiding=1, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.2, initial_capital=10000)
//==========================================
// This script, based on Capissimo's original indicator code, transforms a kNN-based machine learning indicator into a TradingView strategy.
// It incorporates a backtest date range filter, on/off controls for long and short positions, a moving average filter, and dynamic risk management for adaptive position sizing.
// Credit to Capissimo for the foundational kNN algorithm.
//==========================================
//BACKTEST RANGE
useDateFilter = input.bool(true, title="Filter Date Range of Backtest",
group="Backtest Time Period")
backtestStartDate = input(timestamp("1 jan 2017"),
title="Start Date", group="Backtest Time Period",
tooltip="This start date is in the time zone of the exchange " +
"where the chart's instrument trades. It doesn't use the time " +
"zone of the chart or of your computer.")
backtestEndDate = input(timestamp("1 Jul 2100"),
title="End Date", group="Backtest Time Period",
tooltip="This end date is in the time zone of the exchange " +
"where the chart's instrument trades. It doesn't use the time " +
"zone of the chart or of your computer.")
inTradeWindow = true
if not inTradeWindow and inTradeWindow[1]
strategy.cancel_all()
strategy.close_all(comment="Date Range Exit")
//--------------------------------------
//LONG/SHORT POSITION ON/OFF INPUT
LongPositions = input.bool(title='On/Off Long Postion', defval=true, group="Long & Short Position")
ShortPositions = input.bool(title='On/Off Short Postion', defval=true, group="Long & Short Position")
//--------------------------------------
// kNN-based Strategy (FX and Crypto)
// Description:
// This strategy uses a classic machine learning algorithm - k Nearest Neighbours (kNN) -
// to let you find a prediction for the next (tomorrow's, next month's, etc.) market move.
// Being an unsupervised machine learning algorithm, kNN is one of the most simple learning algorithms.
// To do a prediction of the next market move, the kNN algorithm uses the historic data,
// collected in 3 arrays - feature1, feature2 and directions, - and finds the k-nearest
// neighbours of the current indicator(s) values.
// The two dimensional kNN algorithm just has a look on what has happened in the past when
// the two indicators had a similar level. It then looks at the k nearest neighbours,
// sees their state and thus classifies the current point.
// The kNN algorithm offers a framework to test all kinds of indicators easily to see if they
// have got any *predictive value*. One can easily add cog, wpr and others.
// Note: TradingViews's playback feature helps to see this strategy in action.
// Warning: Signals ARE repainting.
// Style tags: Trend Following, Trend Analysis
// Asset class: Equities, Futures, ETFs, Currencies and Commodities
// Dataset: FX Minutes/Hours+++/Days
//-- Preset Dates
int startdate = timestamp('01 Jan 2000 00:00:00 GMT+10')
int stopdate = timestamp('31 Dec 2025 23:45:00 GMT+10')
//-- Inputs
StartDate = input (startdate, 'Start Date', group="kNN-based Inputs")
StopDate = input (stopdate, 'Stop Date', group="kNN-based Inputs")
Indicator = input.string('RSI', 'Indicator', ['RSI','ROC','CCI','Volume','All'], group="kNN-based Inputs")
ShortWinow = input.int (8, 'Short Period [1..n]', 1, group="kNN-based Inputs")
LongWindow = input.int (29, 'Long Period [2..n]', 2, group="kNN-based Inputs")
BaseK = input.int (400, 'Base No. of Neighbours (K) [5..n]', 5, group="kNN-based Inputs")
Filter = input.bool (false, 'Volatility Filter', group="kNN-based Inputs")
Bars = input.int (300, 'Bar Threshold [2..5000]', 2, 5000, group="kNN-based Inputs")
//-- Constants
var int BUY = 1
var int SELL =-1
var int CLEAR = 0
var int k = math.floor(math.sqrt(BaseK)) // k Value for kNN algo
//-- Variable
// Training data, normalized to the range of [0,...,100]
var array<float> feature1 = array.new_float(0) // [0,...,100]
var array<float> feature2 = array.new_float(0) // ...
var array<int> directions = array.new_int(0) // [-1; +1]
// Result data
var array<int> predictions = array.new_int(0)
var float prediction = 0.0
var array<int> bars = array.new<int>(1, 0) // array used as a container for inter-bar variables
// Signals
var int signal = CLEAR
//-- Functions
minimax(float x, int p, float min, float max) =>
float hi = ta.highest(x, p), float lo = ta.lowest(x, p)
(max - min) * (x - lo)/(hi - lo) + min
cAqua(int g) => g>9?#0080FFff:g>8?#0080FFe5:g>7?#0080FFcc:g>6?#0080FFb2:g>5?#0080FF99:g>4?#0080FF7f:g>3?#0080FF66:g>2?#0080FF4c:g>1?#0080FF33:#00C0FF19
cPink(int g) => g>9?#FF0080ff:g>8?#FF0080e5:g>7?#FF0080cc:g>6?#FF0080b2:g>5?#FF008099:g>4?#FF00807f:g>3?#FF008066:g>2?#FF00804c:g>1?#FF008033:#FF008019
inside_window(float start, float stop) =>
time >= start and time <= stop ? true : false
//-- Logic
bool window = true
// 3 pairs of predictor indicators, long and short each
float rs = ta.rsi(close, LongWindow), float rf = ta.rsi(close, ShortWinow)
float cs = ta.cci(close, LongWindow), float cf = ta.cci(close, ShortWinow)
float os = ta.roc(close, LongWindow), float of = ta.roc(close, ShortWinow)
float vs = minimax(volume, LongWindow, 0, 99), float vf = minimax(volume, ShortWinow, 0, 99)
// TOADD or TOTRYOUT:
// ta.cmo(close, LongWindow), ta.cmo(close, ShortWinow)
// ta.mfi(close, LongWindow), ta.mfi(close, ShortWinow)
// ta.mom(close, LongWindow), ta.mom(close, ShortWinow)
float f1 = switch Indicator
'RSI' => rs
'CCI' => cs
'ROC' => os
'Volume' => vs
=> math.avg(rs, cs, os, vs)
float f2 = switch Indicator
'RSI' => rf
'CCI' => cf
'ROC' => of
'Volume' => vf
=> math.avg(rf, cf, of, vf)
// Classification data, what happens on the next bar
int class_label = int(math.sign(close[1] - close[0])) // eq. close[1]<close[0] ? SELL: close[1]>close[0] ? BUY : CLEAR
// Use particular training period
if window
// Store everything in arrays. Features represent a square 100 x 100 matrix,
// whose row-colum intersections represent class labels, showing historic directions
array.push(feature1, f1)
array.push(feature2, f2)
array.push(directions, class_label)
// Ucomment the followng statement (if barstate.islast) and tab everything below
// between BOBlock and EOBlock marks to see just the recent several signals gradually
// showing up, rather than all the preceding signals
//if barstate.islast
//==BOBlock
// Core logic of the algorithm
int size = array.size(directions)
float maxdist = -999.0
// Loop through the training arrays, getting distances and corresponding directions.
for i=0 to size-1
// Calculate the euclidean distance of current point to all historic points,
// here the metric used might as well be a manhattan distance or any other.
float d = math.sqrt(math.pow(f1 - array.get(feature1, i), 2) + math.pow(f2 - array.get(feature2, i), 2))
if d > maxdist
maxdist := d
if array.size(predictions) >= k
array.shift(predictions)
array.push(predictions, array.get(directions, i))
//==EOBlock
// Note: in this setup there's no need for distances array (i.e. array.push(distances, d)),
// but the drawback is that a sudden max value may shadow all the subsequent values.
// One of the ways to bypass this is to:
// 1) store d in distances array,
// 2) calculate newdirs = bubbleSort(distances, directions), and then
// 3) take a slice with array.slice(newdirs) from the end
// Get the overall prediction of k nearest neighbours
prediction := array.sum(predictions)
bool filter = Filter ? ta.atr(10) > ta.atr(40) : true // filter out by volatility or ex. ta.atr(1) > ta.atr(10)...
// Now that we got a prediction for the next market move, we need to make use of this prediction and
// trade it. The returns then will show if everything works as predicted.
// Over here is a simple long/short interpretation of the prediction,
// but of course one could also use the quality of the prediction (+5 or +1) in some sort of way,
// ex. for position sizing.
bool long = prediction > 0 and filter
bool short = prediction < 0 and filter
bool clear = not(long and short)
if array.get(bars, 0)==Bars // stop by trade duration
signal := CLEAR
array.set(bars, 0, 0)
else
array.set(bars, 0, array.get(bars, 0) + 1)
signal := long ? BUY : short ? SELL : clear ? CLEAR : nz(signal[1])
int changed = ta.change(signal)
bool startLongTrade = changed and signal==BUY
bool startShortTrade = changed and signal==SELL
// bool endLongTrade = changed and signal==SELL
// bool endShortTrade = changed and signal==BUY
bool clear_condition = changed and signal==CLEAR //or (changed and signal==SELL) or (changed and signal==BUY)
float maxpos = ta.highest(high, 10)
float minpos = ta.lowest (low, 10)
//----//MA INPUTS
MAFilter = input.bool(title='Use MA as Filter', defval=true, group = "MA Inputs")
averageType1 = input.string(defval="SMA", group="MA Inputs", title="MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "WMA", "HMA", "RMA", "SWMA", "ALMA", "VWMA", "VWAP"])
averageLength1 = input.int(defval=40, title="MA Length", group="MA Inputs")
averageSource1 = input(close, title="MA Source", group="MA Inputs")
//MA TYPE
MovAvgType1(averageType1, averageSource1, averageLength1) =>
switch str.upper(averageType1)
"SMA" => ta.sma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"EMA" => ta.ema(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"WMA" => ta.wma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"HMA" => ta.hma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"RMA" => ta.rma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"SWMA" => ta.swma(averageSource1)
"ALMA" => ta.alma(averageSource1, averageLength1, 0.85, 6)
"VWMA" => ta.vwma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"VWAP" => ta.vwap(averageSource1)
=> runtime.error("Moving average type '" + averageType1 +
"' not found!"), na
// MA COLOR VALUES
ma = MovAvgType1(averageType1, averageSource1, averageLength1)
ma_plot = close > ma ? color.rgb(54, 111, 56) : color.rgb(54, 111, 56, 52)
// MA BUY/SELL CONDITIONS
bullish_ma = MAFilter ? close > ma : inTradeWindow
bearish_ma = MAFilter ? close < ma : inTradeWindow
// MA ALTERNATING PLOT
plot(MAFilter ? ma : na, color=ma_plot, title="Moving Average", linewidth=3)
//--------------------------------------
//ENTRIES AND EXITS
long_entry = if inTradeWindow and startLongTrade and bullish_ma and LongPositions
true
long_exit = if inTradeWindow and startShortTrade
true
short_entry = if inTradeWindow and startShortTrade and bearish_ma and ShortPositions
true
short_exit = if inTradeWindow and startLongTrade
true
//--------------------------------------
//RISK MANAGEMENT - SL, MONEY AT RISK, POSITION SIZING
atrPeriod = input.int(7, "ATR Length", group="Risk Management Inputs")
sl_atr_multiplier = input.float(title="Long Position - Stop Loss - ATR Multiplier", defval=2, group="Risk Management Inputs", step=0.5)
sl_atr_multiplier_short = input.float(title="Short Position - Stop Loss - ATR Multiplier", defval=2, group="Risk Management Inputs", step=0.5)
i_pctStop = input.float(2, title="% of Equity at Risk", step=.5, group="Risk Management Inputs")/100
//ATR VALUE
_atr = ta.atr(atrPeriod)
//CALCULATE LAST ENTRY PRICE
lastEntryPrice = strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1)
//STOP LOSS - LONG POSITIONS
var float sl = na
//CALCULTE SL WITH ATR AT ENTRY PRICE - LONG POSITION
if (strategy.position_size[1] != strategy.position_size)
sl := lastEntryPrice - (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier)
//IN TRADE - LONG POSITIONS
inTrade = strategy.position_size > 0
//PLOT SL - LONG POSITIONS
plot(inTrade ? sl : na, color=color.blue, style=plot.style_circles, title="Long Position - Stop Loss")
//CALCULATE ORDER SIZE - LONG POSITIONS
positionSize = (strategy.equity * i_pctStop) / (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier)
//============================================================================================
//STOP LOSS - SHORT POSITIONS
var float sl_short = na
//CALCULTE SL WITH ATR AT ENTRY PRICE - SHORT POSITIONS
if (strategy.position_size[1] != strategy.position_size)
sl_short := lastEntryPrice + (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier_short)
//IN TRADE SHORT POSITIONS
inTrade_short = strategy.position_size < 0
//PLOT SL - SHORT POSITIONS
plot(inTrade_short ? sl_short : na, color=color.red, style=plot.style_circles, title="Short Position - Stop Loss")
//CALCULATE ORDER - SHORT POSITIONS
positionSize_short = (strategy.equity * i_pctStop) / (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier_short)
//===============================================
//LONG STRATEGY
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, comment="Long", when = long_entry and not short_entry, qty=positionSize)
if (strategy.position_size > 0)
strategy.close("Long", when = (long_exit), comment="Close Long")
strategy.exit("Long", stop = sl, comment="Exit Long")
//SHORT STRATEGY
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, comment="Short", when = short_entry and not long_entry, qty=positionSize_short)
if (strategy.position_size < 0)
strategy.close("Short", when = (short_exit), comment="Close Short")
strategy.exit("Short", stop = sl_short, comment="Exit Short")
//ONE DIRECTION TRADING COMMAND (BELLOW ONLY ACTIVATE TO CORRECT BUGS)
//strategy.risk.allow_entry_in(strategy.direction.long)