Estratégia de acompanhamento de tendências baseada no ATR
Autora:ChaoZhang, Data: 2024-01-05 16:28:48Tags:
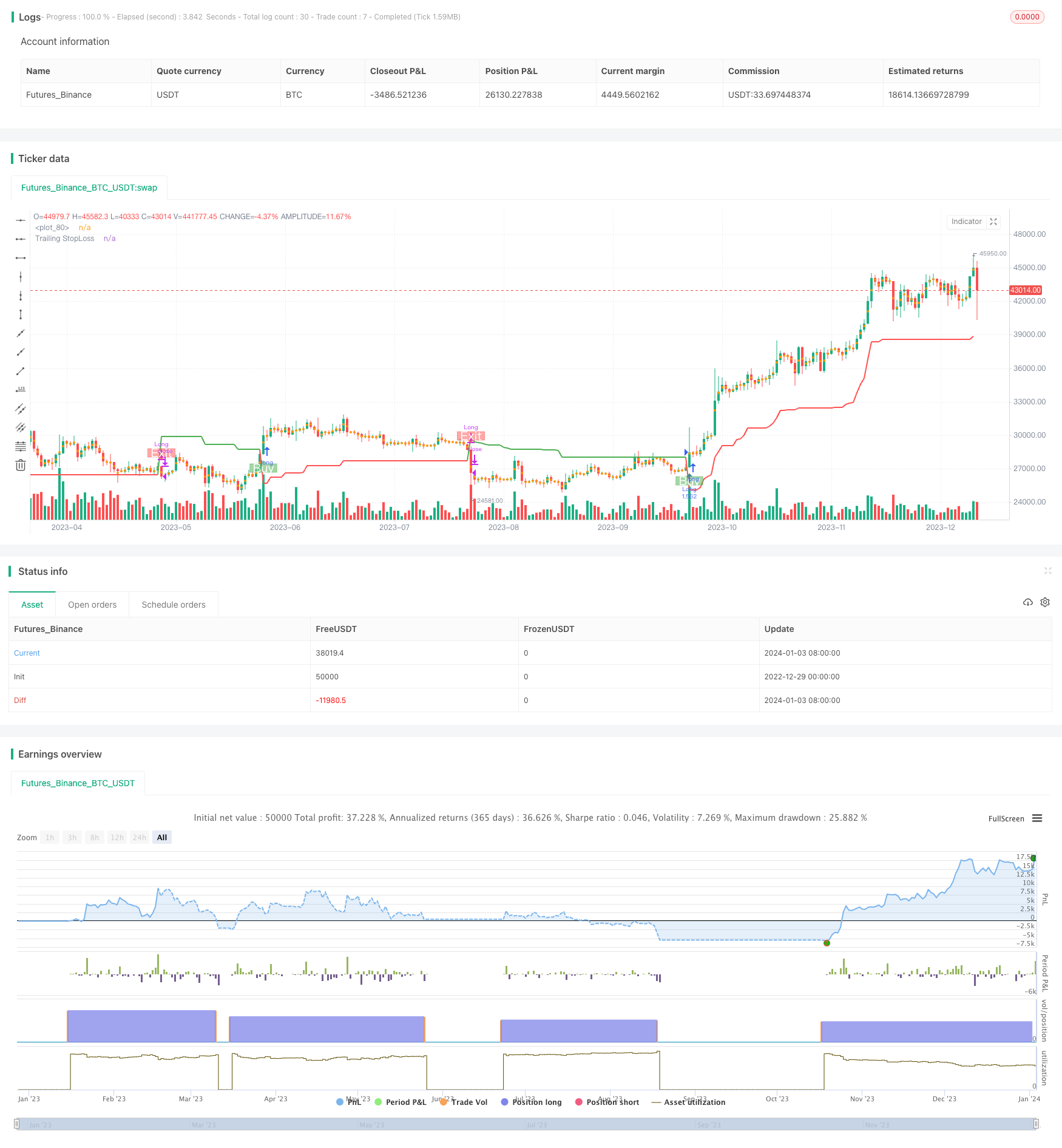
Resumo
Esta é uma estratégia de rastreamento de tendências baseada no Average True Range (ATR). Ele usa o ATR para calcular os valores do indicador e determinar a direção da tendência de preços.
Estratégia lógica
A estratégia utiliza três parâmetros principais: período, multiplicador e ponto de entrada/saída.
A estratégia calcula primeiro o preço médio longo (buyvg) e o preço médio curto (sellavg), em seguida, compara a relação de preços entre essas duas médias para determinar a direção da tendência atual.
Além disso, a estratégia incorpora o ATR para definir um stop loss final. Especificamente, ele usa a média móvel ponderada de 14 períodos do ATR multiplicada por um multiplicador (padrão 4) como a distância de stop loss. Isso permite que a distância de stop loss seja ajustada com base na volatilidade do mercado.
Quando o stop loss é acionado, a estratégia fechará a posição para garantir lucros.
Vantagens
- Com base no julgamento da tendência, pode seguir a tendência continuamente para obter lucro
- Usar o ATR para ajustar dinamicamente a distância de perda de parada, controlar eficazmente os riscos
- Simples e diretos para calcular pontos de entrada e saída, fáceis de compreender e implementar
Riscos e soluções
- Pode sofrer grandes perdas quando a tendência mudar
- Ajustar razoavelmente o período de ATR e o multiplicador para otimizar a distância de stop loss
- GERARÁ perdas pequenas múltiplas em mercados variados
- Adicionar condições de filtro para evitar mercados variados
- Ajustes de parâmetros incorretos podem piorar o desempenho da estratégia
- Realizar otimização multi-parâmetro para encontrar o ideal
Orientações de otimização
- Adicionar outros indicadores de filtragem para evitar a abertura de posições em mercados variados
- Otimizar o período de ATR e os parâmetros do multiplicador para tornar a distância de parada mais razoável
- Adicionar controlo de dimensionamento de posição com base nas condições de mercado
Conclusão
Em geral, esta é uma estratégia simples e prática de rastreamento de tendências. Ele só precisa de alguns parâmetros para implementar, e usa ATR para ajustar dinamicamente paradas para controlar efetivamente os riscos. Quando combinado com outros indicadores de assistência para filtragem, ele pode ser ainda mais otimizado.
/*backtest
start: 2022-12-29 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-04 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy('Trend Strategy by zdmre', shorttitle='Trend Strategy', overlay=true, pyramiding=0, currency=currency.USD, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, initial_capital=10000, default_qty_value=100, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.005)
show_STOPLOSSprice = input(true, title='Show TrailingSTOP Prices')
src = input(close, title='Source')
out2 = ta.ema(src, 20)
buyavg = (close + high) / 2.02 - high * (1 - open / close) * (1 - low * open / (high * close))
sellavg = ((low + close) / 1.99 + low * (1 - low / open) * (1 - low * open / (close * high)) / 1.1 + out2 )/ 2
// === INPUT BACKTEST RANGE ===
fromMonth = input.int(defval=1, title='From Month', minval=1, maxval=12)
fromDay = input.int(defval=1, title='From Day', minval=1, maxval=31)
fromYear = input.int(defval=2021, title='From Year', minval=1970)
thruMonth = input.int(defval=1, title='Thru Month', minval=1, maxval=12)
thruDay = input.int(defval=1, title='Thru Day', minval=1, maxval=31)
thruYear = input.int(defval=2100, title='Thru Year', minval=1970)
// === INPUT SHOW PLOT ===
showDate = input(defval=true, title='Show Date Range')
// === FUNCTION EXAMPLE ===
start = timestamp(fromYear, fromMonth, fromDay, 00, 00) // backtest start window
finish = timestamp(thruYear, thruMonth, thruDay, 23, 59) // backtest finish window
window() => true
// === TRAILING STOP LOSS === //
ATR_Period = input(14)
ATR_Mult = input(4.0)
var float ATR_TrailSL = na
var int pos = na
atr = ta.rma (ta.tr(true), 14)
xATR = ta.atr(ATR_Period)
nLoss = ATR_Mult * xATR
iff_1 = close > nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) ? close - nLoss : close + nLoss
iff_2 = close < nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) and close[1] < nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) ? math.min(nz(ATR_TrailSL[1]), close + nLoss) : iff_1
ATR_TrailSL := close > nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) and close[1] > nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) ? math.max(nz(ATR_TrailSL[1]), close - nLoss) : iff_2
iff_3 = close[1] > nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) and close < nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) ? -1 : nz(pos[1], 0)
pos := close[1] < nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) and close > nz(ATR_TrailSL[1], 0) ? 1 : iff_3
atr_color = pos == -1 ? color.green : pos == 1 ? color.red : color.aqua
atrtrend = plot(ATR_TrailSL, 'Trailing StopLoss', atr_color, linewidth=2)
// === Stop Loss === //
slGroup = 'Stop Loss'
useSL = input.bool(false, title='╔══════ Enable ══════╗', group=slGroup, tooltip='If you are using this strategy for Scalping or Futures market, we do not recommend using Stop Loss.')
SLbased = input.string(title='Based on', defval='Percent', options=['ATR', 'Percent'], group=slGroup, tooltip='ATR: Average True Range\nPercent: eg. 5%.')
multiATR = input.float(10.0, title='ATR Mult', group=slGroup, inline='atr')
lengthATR = input.int(14, title='Length', group=slGroup, inline='atr')
SLPercent = input.float(5, title='Percent', group=slGroup) * 0.01
Shortposenter = input.bool(false, title='ShortPosition')
longStop = 0.0
shortStop = 0.0
if SLbased == 'ATR'
longStop := ta.valuewhen(pos == 1, low, 0) - ta.valuewhen(pos == 1, ta.rma(ta.tr(true), lengthATR), 0) * multiATR
longStopPrev = nz(longStop[1], longStop)
longStop := close[1] > longStopPrev ? math.max(longStop, longStopPrev) : longStop
shortStop := ta.valuewhen(pos == -1, ta.rma(ta.tr(true), lengthATR), 0) * multiATR + ta.valuewhen(pos == -1, high, 0)
shortStopPrev = nz(shortStop[1], shortStop)
shortStop := close[1] > shortStopPrev ? math.max(shortStop, shortStopPrev) : shortStop
shortStop
if SLbased == 'Percent'
longStop := strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - SLPercent)
shortStop := strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + SLPercent)
shortStop
exitLong = pos == -1
// === PlotColor === //
buySignal = pos == 1 and pos[1] == -1
plotshape(buySignal, title="Long", location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, size=size.normal, color=color.new(color.green,50), text='Buy', textcolor=color.white)
exitSignal = pos == -1 and pos[1] == 1
plotshape(exitSignal, title="Exit", location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, size=size.normal, color=color.new(color.red,50), text='Exit', textcolor=color.white)
hPlot = plot(ohlc4, title="", style=plot.style_circles, linewidth=0, editable = false)
longFill = (pos == 1 ? color.new(color.green,80) : na)
shortFill = (pos == -1 ? color.new(color.red,80) : na)
fill(hPlot, atrtrend,color=longFill)
fill(hPlot,atrtrend, color=shortFill)
// === Strategy === //
strategy.entry('Long', strategy.long,limit = buyavg, when=window() and pos == 1,comment="Entry: "+str.tostring(buyavg))
strategy.close('Long', when=window() and exitLong , comment='Exit: '+str.tostring(sellavg) )
if Shortposenter
strategy.entry('Short', strategy.short, when=window() and pos== -1,comment="Entry: "+str.tostring(close))
strategy.close('Short', when=window() and pos == 1 , comment='Exit: ')
if useSL
strategy.exit('Stop Loss', 'Long', stop=longStop)
// === Show StopLoss Price === //
if show_STOPLOSSprice
if pos == -1
label ShortStop = label.new(bar_index, na, 'SL: ' + str.tostring(ATR_TrailSL), color=color.green, textcolor=color.white, style=label.style_none, yloc=yloc.abovebar, size=size.small)
label.delete(ShortStop[1])
if pos == 1
label LongStop = label.new(bar_index, na, 'SL: ' + str.tostring(ATR_TrailSL), color=color.red, textcolor=color.white, style=label.style_none, yloc=yloc.belowbar, size=size.small)
label.delete(LongStop[1])
- Estratégia de contra-tendência de média móvel dupla
- Estratégia de ruptura em percentagem de barras positivas
- Estratégia de avanço RSI de dupla via
- Estratégia de crudeiro cru cru
- Estratégia de ensaio posterior do filtro vertical horizontal
- RSI e Bandas de Bollinger Estratégia quantitativa de negociação
- Tendência ZigZag Seguindo a Estratégia
- Estratégia Supertrend Advance
- Estratégia de cor da vela da meia-noite com stop loss e take profit
- Tendência ATR Seguindo uma estratégia baseada no canal de desvio padrão
- Estratégia de negociação quantitativa que combina RSI, MACD e suporte/resistência
- Estratégia de acompanhamento da tendência do RSI de longo prazo
- Estratégia da Tartaruga do Canal Duplo
- Melhoria da estratégia de média móvel do RSI MACD
- Estratégia de decisão da EMA de curto e longo prazo combinada
- Estratégia de saída do candelabro
- A tendência de confirmação tripla impulsionada pela estratégia
- Fisher Turnaround EMA Multi-Take Profit e Multi-Stop Strategy
- Estratégia de negociação do sistema de média móvel
- Estratégia de negociação cruzada do MACD