Стратегия, основанная на kNN
Автор:Чао Чжан, Дата: 2023-12-08 11:33:31Тэги:
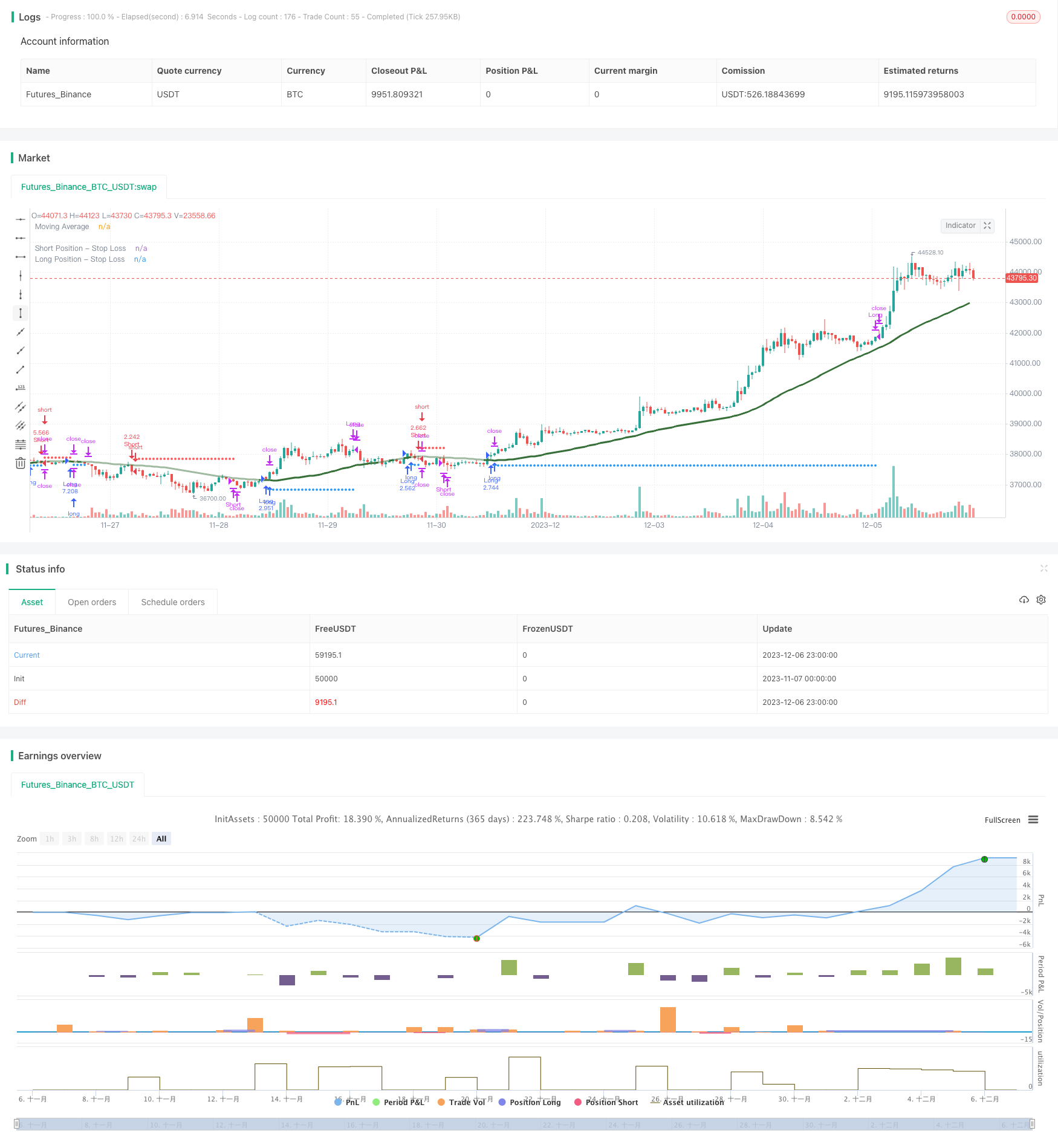
Обзор
Эта стратегия использует алгоритм машинного обучения kNN (k Ближайшие соседи), чтобы предсказать тенденции рынка и генерировать долгие и короткие сигналы соответственно.
Принцип стратегии
-
Собирать данные о обучении: собирать исторические данные, такие как цены закрытия, объемы торговли, а также технические показатели, такие как RSI, CCI с течением времени.
-
Предварительная обработка данных: нормализация показателей в диапазоне 0-100.
-
Подготовка к модели kNN: возьмите текущие две характеристики в модели kNN, вычислите евклидовые расстояния между этими векторами характеристик и историческими, выберите k самых близких соседей на основе расстояний и подсчитайте распределение этих k образцов.
-
Получить прогнозы: сделать прогнозы на текущей тенденции рынка на основе ярлыков k ближайших соседей. Если прогноз является бычьим, генерировать длинный сигнал. Если прогноз является медвежьим, генерировать короткий сигнал.
-
Торговля с использованием стоп-лосса, размещения позиций, фильтров скользящей средней.
Преимущества
-
Автоматическое распознавание технических закономерностей с помощью машинного обучения без ручного вмешательства.
-
Гибкость выбора различных технических показателей в качестве характеристик модели для оптимизации в реальном времени.
-
Интегрирует строгие механизмы управления рисками, такие как стоп-лосс, размещение позиций.
-
Визуализация линий остановки для ясности и интуиции.
Риски и решения
-
В машинном обучении могут существовать ошибки прогнозирования. Методы оптимизации включают корректировку k-значения, векторов характеристик, временного диапазона выборки.
-
Добавить разрешение на двустороннюю торговлю в коде для устранения ошибок.
-
Неправильные настройки параметров могут привести к переоценке.
Руководство по оптимизации
-
Испытать различные типы технических показателей в качестве входных характеристик kNN.
-
Попробуйте другие показатели расстояния, например, расстояние до Манхэттена.
-
Для корректировки размеров позиций используют расстояния выборки или качество классификации.
-
Добавить модель поезда/испытательный раздел для оптимизации проката.
Заключение
Эта стратегия реализует прогноз рыночных тенденций с использованием классического алгоритма kNN и выполняет тренд после торговли на основе предсказательных сигналов. Она имеет регулируемые параметры и контролируемые риски, обеспечивая эффективные автоматизированные торговые решения для пользователей. Пользователи могут постоянно улучшать производительность стратегии путем оптимизации комбинаций технических индикаторов, гиперпараметров моделей и многого другого.
/*backtest
start: 2023-11-07 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-07 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © sosacur01
//@version=5
strategy(title=" kNN-based| Trend Following | Trend Following", overlay=true, pyramiding=1, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.2, initial_capital=10000)
//==========================================
// This script, based on Capissimo's original indicator code, transforms a kNN-based machine learning indicator into a TradingView strategy.
// It incorporates a backtest date range filter, on/off controls for long and short positions, a moving average filter, and dynamic risk management for adaptive position sizing.
// Credit to Capissimo for the foundational kNN algorithm.
//==========================================
//BACKTEST RANGE
useDateFilter = input.bool(true, title="Filter Date Range of Backtest",
group="Backtest Time Period")
backtestStartDate = input(timestamp("1 jan 2017"),
title="Start Date", group="Backtest Time Period",
tooltip="This start date is in the time zone of the exchange " +
"where the chart's instrument trades. It doesn't use the time " +
"zone of the chart or of your computer.")
backtestEndDate = input(timestamp("1 Jul 2100"),
title="End Date", group="Backtest Time Period",
tooltip="This end date is in the time zone of the exchange " +
"where the chart's instrument trades. It doesn't use the time " +
"zone of the chart or of your computer.")
inTradeWindow = true
if not inTradeWindow and inTradeWindow[1]
strategy.cancel_all()
strategy.close_all(comment="Date Range Exit")
//--------------------------------------
//LONG/SHORT POSITION ON/OFF INPUT
LongPositions = input.bool(title='On/Off Long Postion', defval=true, group="Long & Short Position")
ShortPositions = input.bool(title='On/Off Short Postion', defval=true, group="Long & Short Position")
//--------------------------------------
// kNN-based Strategy (FX and Crypto)
// Description:
// This strategy uses a classic machine learning algorithm - k Nearest Neighbours (kNN) -
// to let you find a prediction for the next (tomorrow's, next month's, etc.) market move.
// Being an unsupervised machine learning algorithm, kNN is one of the most simple learning algorithms.
// To do a prediction of the next market move, the kNN algorithm uses the historic data,
// collected in 3 arrays - feature1, feature2 and directions, - and finds the k-nearest
// neighbours of the current indicator(s) values.
// The two dimensional kNN algorithm just has a look on what has happened in the past when
// the two indicators had a similar level. It then looks at the k nearest neighbours,
// sees their state and thus classifies the current point.
// The kNN algorithm offers a framework to test all kinds of indicators easily to see if they
// have got any *predictive value*. One can easily add cog, wpr and others.
// Note: TradingViews's playback feature helps to see this strategy in action.
// Warning: Signals ARE repainting.
// Style tags: Trend Following, Trend Analysis
// Asset class: Equities, Futures, ETFs, Currencies and Commodities
// Dataset: FX Minutes/Hours+++/Days
//-- Preset Dates
int startdate = timestamp('01 Jan 2000 00:00:00 GMT+10')
int stopdate = timestamp('31 Dec 2025 23:45:00 GMT+10')
//-- Inputs
StartDate = input (startdate, 'Start Date', group="kNN-based Inputs")
StopDate = input (stopdate, 'Stop Date', group="kNN-based Inputs")
Indicator = input.string('RSI', 'Indicator', ['RSI','ROC','CCI','Volume','All'], group="kNN-based Inputs")
ShortWinow = input.int (8, 'Short Period [1..n]', 1, group="kNN-based Inputs")
LongWindow = input.int (29, 'Long Period [2..n]', 2, group="kNN-based Inputs")
BaseK = input.int (400, 'Base No. of Neighbours (K) [5..n]', 5, group="kNN-based Inputs")
Filter = input.bool (false, 'Volatility Filter', group="kNN-based Inputs")
Bars = input.int (300, 'Bar Threshold [2..5000]', 2, 5000, group="kNN-based Inputs")
//-- Constants
var int BUY = 1
var int SELL =-1
var int CLEAR = 0
var int k = math.floor(math.sqrt(BaseK)) // k Value for kNN algo
//-- Variable
// Training data, normalized to the range of [0,...,100]
var array<float> feature1 = array.new_float(0) // [0,...,100]
var array<float> feature2 = array.new_float(0) // ...
var array<int> directions = array.new_int(0) // [-1; +1]
// Result data
var array<int> predictions = array.new_int(0)
var float prediction = 0.0
var array<int> bars = array.new<int>(1, 0) // array used as a container for inter-bar variables
// Signals
var int signal = CLEAR
//-- Functions
minimax(float x, int p, float min, float max) =>
float hi = ta.highest(x, p), float lo = ta.lowest(x, p)
(max - min) * (x - lo)/(hi - lo) + min
cAqua(int g) => g>9?#0080FFff:g>8?#0080FFe5:g>7?#0080FFcc:g>6?#0080FFb2:g>5?#0080FF99:g>4?#0080FF7f:g>3?#0080FF66:g>2?#0080FF4c:g>1?#0080FF33:#00C0FF19
cPink(int g) => g>9?#FF0080ff:g>8?#FF0080e5:g>7?#FF0080cc:g>6?#FF0080b2:g>5?#FF008099:g>4?#FF00807f:g>3?#FF008066:g>2?#FF00804c:g>1?#FF008033:#FF008019
inside_window(float start, float stop) =>
time >= start and time <= stop ? true : false
//-- Logic
bool window = true
// 3 pairs of predictor indicators, long and short each
float rs = ta.rsi(close, LongWindow), float rf = ta.rsi(close, ShortWinow)
float cs = ta.cci(close, LongWindow), float cf = ta.cci(close, ShortWinow)
float os = ta.roc(close, LongWindow), float of = ta.roc(close, ShortWinow)
float vs = minimax(volume, LongWindow, 0, 99), float vf = minimax(volume, ShortWinow, 0, 99)
// TOADD or TOTRYOUT:
// ta.cmo(close, LongWindow), ta.cmo(close, ShortWinow)
// ta.mfi(close, LongWindow), ta.mfi(close, ShortWinow)
// ta.mom(close, LongWindow), ta.mom(close, ShortWinow)
float f1 = switch Indicator
'RSI' => rs
'CCI' => cs
'ROC' => os
'Volume' => vs
=> math.avg(rs, cs, os, vs)
float f2 = switch Indicator
'RSI' => rf
'CCI' => cf
'ROC' => of
'Volume' => vf
=> math.avg(rf, cf, of, vf)
// Classification data, what happens on the next bar
int class_label = int(math.sign(close[1] - close[0])) // eq. close[1]<close[0] ? SELL: close[1]>close[0] ? BUY : CLEAR
// Use particular training period
if window
// Store everything in arrays. Features represent a square 100 x 100 matrix,
// whose row-colum intersections represent class labels, showing historic directions
array.push(feature1, f1)
array.push(feature2, f2)
array.push(directions, class_label)
// Ucomment the followng statement (if barstate.islast) and tab everything below
// between BOBlock and EOBlock marks to see just the recent several signals gradually
// showing up, rather than all the preceding signals
//if barstate.islast
//==BOBlock
// Core logic of the algorithm
int size = array.size(directions)
float maxdist = -999.0
// Loop through the training arrays, getting distances and corresponding directions.
for i=0 to size-1
// Calculate the euclidean distance of current point to all historic points,
// here the metric used might as well be a manhattan distance or any other.
float d = math.sqrt(math.pow(f1 - array.get(feature1, i), 2) + math.pow(f2 - array.get(feature2, i), 2))
if d > maxdist
maxdist := d
if array.size(predictions) >= k
array.shift(predictions)
array.push(predictions, array.get(directions, i))
//==EOBlock
// Note: in this setup there's no need for distances array (i.e. array.push(distances, d)),
// but the drawback is that a sudden max value may shadow all the subsequent values.
// One of the ways to bypass this is to:
// 1) store d in distances array,
// 2) calculate newdirs = bubbleSort(distances, directions), and then
// 3) take a slice with array.slice(newdirs) from the end
// Get the overall prediction of k nearest neighbours
prediction := array.sum(predictions)
bool filter = Filter ? ta.atr(10) > ta.atr(40) : true // filter out by volatility or ex. ta.atr(1) > ta.atr(10)...
// Now that we got a prediction for the next market move, we need to make use of this prediction and
// trade it. The returns then will show if everything works as predicted.
// Over here is a simple long/short interpretation of the prediction,
// but of course one could also use the quality of the prediction (+5 or +1) in some sort of way,
// ex. for position sizing.
bool long = prediction > 0 and filter
bool short = prediction < 0 and filter
bool clear = not(long and short)
if array.get(bars, 0)==Bars // stop by trade duration
signal := CLEAR
array.set(bars, 0, 0)
else
array.set(bars, 0, array.get(bars, 0) + 1)
signal := long ? BUY : short ? SELL : clear ? CLEAR : nz(signal[1])
int changed = ta.change(signal)
bool startLongTrade = changed and signal==BUY
bool startShortTrade = changed and signal==SELL
// bool endLongTrade = changed and signal==SELL
// bool endShortTrade = changed and signal==BUY
bool clear_condition = changed and signal==CLEAR //or (changed and signal==SELL) or (changed and signal==BUY)
float maxpos = ta.highest(high, 10)
float minpos = ta.lowest (low, 10)
//----//MA INPUTS
MAFilter = input.bool(title='Use MA as Filter', defval=true, group = "MA Inputs")
averageType1 = input.string(defval="SMA", group="MA Inputs", title="MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "WMA", "HMA", "RMA", "SWMA", "ALMA", "VWMA", "VWAP"])
averageLength1 = input.int(defval=40, title="MA Length", group="MA Inputs")
averageSource1 = input(close, title="MA Source", group="MA Inputs")
//MA TYPE
MovAvgType1(averageType1, averageSource1, averageLength1) =>
switch str.upper(averageType1)
"SMA" => ta.sma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"EMA" => ta.ema(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"WMA" => ta.wma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"HMA" => ta.hma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"RMA" => ta.rma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"SWMA" => ta.swma(averageSource1)
"ALMA" => ta.alma(averageSource1, averageLength1, 0.85, 6)
"VWMA" => ta.vwma(averageSource1, averageLength1)
"VWAP" => ta.vwap(averageSource1)
=> runtime.error("Moving average type '" + averageType1 +
"' not found!"), na
// MA COLOR VALUES
ma = MovAvgType1(averageType1, averageSource1, averageLength1)
ma_plot = close > ma ? color.rgb(54, 111, 56) : color.rgb(54, 111, 56, 52)
// MA BUY/SELL CONDITIONS
bullish_ma = MAFilter ? close > ma : inTradeWindow
bearish_ma = MAFilter ? close < ma : inTradeWindow
// MA ALTERNATING PLOT
plot(MAFilter ? ma : na, color=ma_plot, title="Moving Average", linewidth=3)
//--------------------------------------
//ENTRIES AND EXITS
long_entry = if inTradeWindow and startLongTrade and bullish_ma and LongPositions
true
long_exit = if inTradeWindow and startShortTrade
true
short_entry = if inTradeWindow and startShortTrade and bearish_ma and ShortPositions
true
short_exit = if inTradeWindow and startLongTrade
true
//--------------------------------------
//RISK MANAGEMENT - SL, MONEY AT RISK, POSITION SIZING
atrPeriod = input.int(7, "ATR Length", group="Risk Management Inputs")
sl_atr_multiplier = input.float(title="Long Position - Stop Loss - ATR Multiplier", defval=2, group="Risk Management Inputs", step=0.5)
sl_atr_multiplier_short = input.float(title="Short Position - Stop Loss - ATR Multiplier", defval=2, group="Risk Management Inputs", step=0.5)
i_pctStop = input.float(2, title="% of Equity at Risk", step=.5, group="Risk Management Inputs")/100
//ATR VALUE
_atr = ta.atr(atrPeriod)
//CALCULATE LAST ENTRY PRICE
lastEntryPrice = strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1)
//STOP LOSS - LONG POSITIONS
var float sl = na
//CALCULTE SL WITH ATR AT ENTRY PRICE - LONG POSITION
if (strategy.position_size[1] != strategy.position_size)
sl := lastEntryPrice - (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier)
//IN TRADE - LONG POSITIONS
inTrade = strategy.position_size > 0
//PLOT SL - LONG POSITIONS
plot(inTrade ? sl : na, color=color.blue, style=plot.style_circles, title="Long Position - Stop Loss")
//CALCULATE ORDER SIZE - LONG POSITIONS
positionSize = (strategy.equity * i_pctStop) / (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier)
//============================================================================================
//STOP LOSS - SHORT POSITIONS
var float sl_short = na
//CALCULTE SL WITH ATR AT ENTRY PRICE - SHORT POSITIONS
if (strategy.position_size[1] != strategy.position_size)
sl_short := lastEntryPrice + (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier_short)
//IN TRADE SHORT POSITIONS
inTrade_short = strategy.position_size < 0
//PLOT SL - SHORT POSITIONS
plot(inTrade_short ? sl_short : na, color=color.red, style=plot.style_circles, title="Short Position - Stop Loss")
//CALCULATE ORDER - SHORT POSITIONS
positionSize_short = (strategy.equity * i_pctStop) / (_atr * sl_atr_multiplier_short)
//===============================================
//LONG STRATEGY
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, comment="Long", when = long_entry and not short_entry, qty=positionSize)
if (strategy.position_size > 0)
strategy.close("Long", when = (long_exit), comment="Close Long")
strategy.exit("Long", stop = sl, comment="Exit Long")
//SHORT STRATEGY
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, comment="Short", when = short_entry and not long_entry, qty=positionSize_short)
if (strategy.position_size < 0)
strategy.close("Short", when = (short_exit), comment="Close Short")
strategy.exit("Short", stop = sl_short, comment="Exit Short")
//ONE DIRECTION TRADING COMMAND (BELLOW ONLY ACTIVATE TO CORRECT BUGS)
//strategy.risk.allow_entry_in(strategy.direction.long)
- Стратегия тренда биномиальной скользящей средней
- Стратегия перекрестного использования скользящей средней
- Многофункциональная алгоритмическая стратегия торговли, основанная на перекрестном использовании тренда и скользящей средней
- Стратегия прорыва скользящей средней полосы Боллинджера
- Тенденция, следующая за сетевой стратегией
- Количественная стратегия торговли, объединяющая обратные и будущие линии демаркации
- Стратегия пересечения между диапазонами Боллинджера и индикатором Халла
- Приспособленная стратегия торговли Turtle Breakout Drawdown
- RSI Trend Following Strategy with Trailing Stop Loss (Тенденция RSI в соответствии со стратегией с последующим остановкой потери)
- Инверсия динамических поворотных точек Экспоненциальная стратегия скользящей средней
- Простая стратегия импульса на основе SMA, EMA и объема
- Концепция объемной торговли Donchian Channels
- N Последовательное повышение закрывает стратегию прорыва
- Умная количественная стратегия торговли с обратным движением вниз
- Двойная стратегия Bollinger + RSI (только длинная) v1.2
- Стратегия CCI по нулевой перекрестной торговле
- Стратегия двойного перемещения средней цены
- Стратегия обратной торговли движущимися средними
- Движущаяся средняя агрегация Williams Коммерческая стратегия индикатора давления покупки и продажи
- Стратегия отслеживания двойной переменной средней