Realisierung von Fisher Indicator in JavaScript und Plotting auf FMZ
Schriftsteller:- Ich bin ein Idiot., Erstellt: 2022-04-07 16:04:22, aktualisiert:Realisierung von Fisher Indicator in JavaScript und Plotting auf FMZ
Während der technischen Analyse im Handel nehmen alle Händler Aktienpreisdaten als normal verteilte Daten zur Analyse und Untersuchung.Fisher Transformationist eine Methode, die Preisdaten in etwas verwandeln kann, das einer normalen Verteilung ähnelt.Fisher TransformationDie Angabe von Marktdaten erfolgt durch die Verknüpfung von heutigen und vorangegangenen Indikatoren.
Es gibt so viele Hinweise aufFisher Transformationauf Baidu und Zhihu, was hier nicht ausführlich erklärt wird.
Indikator-Algorithmus:
-
Mittlerer Preis heute:
mid=(low + high) / 2 -
Bestätigen Sie den Berechnungszeitraum; Sie können 10 Tage pro Zeitraum verwenden. Berechnen Sie den höchsten und den niedrigsten Preis im Zeitraum:
lowestLow = the lowest price in the period,highestHigh = the highest price in the period. -
Definition des Preisänderungsparameters (in dem
ratioist eine Konstante von 0 bis 1; zum Beispiel können Sie 0,5 oder 0,33 wählen):(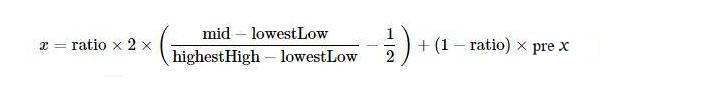
-
Anwendbar
FisherUmwandlung auf den Preisänderungsparameterx, und dieFisherDer Indikator kann erhalten werden: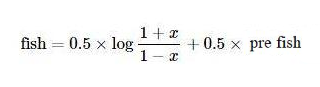
Verwenden Sie JavaScript, um den Algorithmus zu erkennen
Nach dem Indikator-Algorithmus, realisieren Sie es Schritt für Schritt.preX, preFish, werden sie zunächst auf 0 gesetzt.Math.logist der Logarithmus basierend auf der natürlichen Konstante e Außerdem wird die Modifikation von x nicht im obigen Algorithmus erwähnt, und ich habe dieses Problem beim Schreiben fast ignoriert:
Der Wert von x wird geändert; wenn der Wert größer als 0,99 ist, wird er zwangsweise auf 0,999 gesetzt; wenn er kleiner als -0,99 ist, wird er auf -0,999 gesetzt.
if (x > 0.99) {
x = 0.999
} else if (x < -0.99) {
x = -0.999
}
Dies ist das erste Mal, dass ich den Algorithmus und den Indikator sehe, nachdem ich ihn nach dem Algorithmus portiert habe. Ich habe die Implementierung nicht überprüft, und Studenten, die an Forschung interessiert sind, können überprüfen, ob es Fehler gibt. Vielen Dank für die Hinweisung auf Fehler, wenn es welche gibt.
Quellcode vonFisher TransformIndikatoralgorithmus:
function getHighest(arr, period) {
if (arr.length == 0 || arr.length - period < 0) {
return null
}
var beginIndex = arr.length - period
var ret = arr[beginIndex].High
for (var i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i++) {
if (arr[i + 1].High > ret) {
ret = arr[i + 1].High
}
}
return ret
}
function getLowest(arr, period) {
if (arr.length == 0 || arr.length - period < 0) {
return null
}
var beginIndex = arr.length - period
var ret = arr[beginIndex].Low
for (var i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i++) {
if (arr[i + 1].Low < ret) {
ret = arr[i + 1].Low
}
}
return ret
}
function calcFisher(records, ratio, period) {
var preFish = 0
var preX = 0
var arrFish = []
// when the K-line length is not long enough to meet the K-line period
if (records.length < period) {
for (var i = 0 ; i < records.length ; i++) {
arrFish.push(0)
}
return arrFish
}
// traverse K-lines
for (var i = 0 ; i < records.length ; i++) {
var fish = 0
var x = 0
var bar = records[i]
var mid = (bar.High + bar.Low) / 2
// when the current BAR is not enough for period to calculate
if (i < period - 1) {
fish = 0
preFish = 0
arrFish.push(fish)
continue
}
// calculate the highest price and the lowest price in the period
var bars = []
for (var j = 0 ; j <= i ; j++) {
bars.push(records[j])
}
var lowestLow = getLowest(bars, period)
var highestHigh = getHighest(bars, period)
// price change parameter x
x = ratio * 2 * ((mid - lowestLow) / (highestHigh - lowestLow) - 0.5) + (1 - ratio) * preX
if (x > 0.99) {
x = 0.999
} else if (x < -0.99) {
x = -0.999
}
preX = x
fish = 0.5 * Math.log((1 + x) / (1 - x)) + 0.5 * preFish
preFish = fish
arrFish.push(fish)
}
return arrFish
}
Komplott
Es ist sehr einfach, auf FMZ zu zeichnen; Sie können sich auf viele Beispiele im Strategie-Quadrat beziehen:https://www.fmz.com/square, und Sie können auch nach den Strategien suchen, die Sie brauchen.
var cfg = { // used to initially configure the chart objects (namely chart settings)
plotOptions: {
candlestick: {
color: '#d75442', // color value
upColor: '#6ba583' // color vlaue
}
},
title: { text: 'Fisher Transform'}, //title
subtitle: {text: ''}, //subtitle
plotOptions: {
candlestick: {
tooltip: {
pointFormat:
'<span style="color:{point.color}">\u25CF</span> <b> {series.name}</b><br/>' +
'open: {point.open}<br/>' +
'highest: {point.high}<br/>' +
'lowest: {point.low}<br/>' +
'close: {point.close}<br/>'
}
}
},
yAxis: [{
title: {
text: 'K-line market quote'
},
height: '70%',
lineWidth: 1
}, {
title: {
text: 'Fisher Transform'
},
top: '75%',
height: '30%',
offset: 0,
lineWidth: 1
}],
series: [//series
{
type: 'candlestick',
yAxis: 0,
name: 'K-line',
id: 'KLine',
// control the candlestick color of fall
color: 'green',
lineColor: 'green',
// control the candlestick color of rise
upColor: 'red',
upLineColor: 'red',
data: []
},{
type: 'line', // set the type of the current data series as: line
yAxis: 1, // the y axis for use is the y axis with index 0 (in highcharts, there can be multiple y axis, and here it indicates the y axis with index 0)
showInLegend: true, //
name: 'fish', // set according the parameter label passed by the function
lineWidth: 1,
data: [], // data item of the data series
tooltip: { // tip for tool
valueDecimals: 2 // the decimals of the value reserve 5
}
},{
type: 'line', // set the type of the current data series as: line
yAxis: 1, // the y axis for use is the y axis with index 0 (in highcharts, there can be multiple y axis, and here it indicates the y axis with index 0)
showInLegend: true, //
name: 'preFish', // set according the parameter label passed by the function
lineWidth: 1,
data: [], // data item of the data series
tooltip: { // tip for tool
valueDecimals: 2 // the decimals of the value reserve 5
}
}
]
}
var chart = Chart(cfg)
function main() {
var ts = 0
chart.reset()
while (true) {
var r = exchange.GetRecords()
var fisher = calcFisher(r, 0.33, 10)
if (!r || !fisher) {
Sleep(500)
continue
}
for (var i = 0; i < r.length; i++){
if (ts == r[i].Time) {
chart.add([0,[r[i].Time, r[i].Open, r[i].High, r[i].Low, r[i].Close], -1])
chart.add([1,[r[i].Time, fisher[i]], -1])
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
chart.add([2,[r[i].Time, fisher[i - 1]], -1])
}
}else if (ts < r[i].Time) {
chart.add([0,[r[i].Time, r[i].Open, r[i].High, r[i].Low, r[i].Close]])
chart.add([1,[r[i].Time, fisher[i]]])
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
chart.add([2,[r[i].Time, fisher[i - 1]]])
}
ts = r[i].Time
}
}
}
}
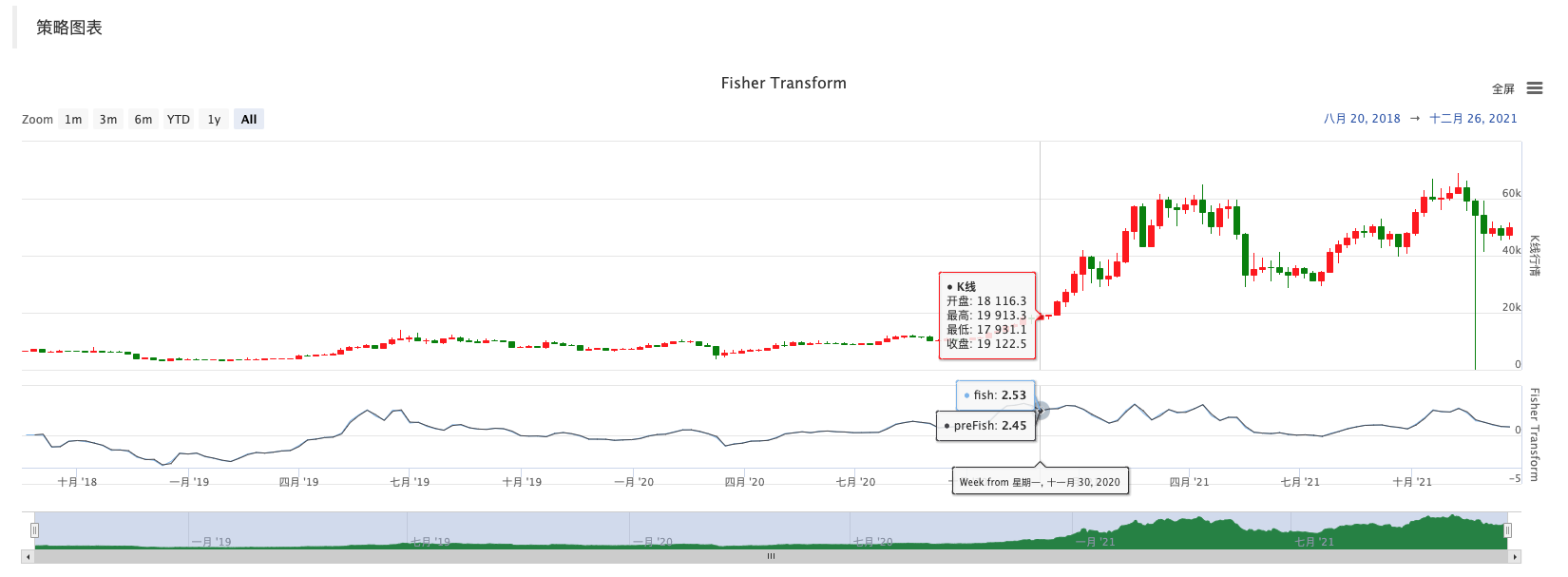
Daher ist es sehr praktisch, Daten, Diagrammdarstellung und Strategieentwurf auf FMZ zu studieren. Hier beginne ich die Diskussion für weitere Ideen, also begrüßen Sie Lehrer und Schüler hier, um Kommentare zu hinterlassen.
- Kryptowährungs-Kontrakt einfacher Auftragsüberwachungsbot
- Wenn Sie mit getdepth die entsprechende Zeitschrift erhalten möchten
- Ignoriert, gelöst
- Die Frage nach dem Gesichtswert
- dYdX-Strategie-Entwurfsbeispiel
- Erste Erforschung der Anwendung von Python Crawler auf FMZ
Crawling Binance Ankündigungsinhalt - Hedge-Strategie-Design-Forschung & Beispiel für offene Spot- und Futures-Orders
- Aktuelle Situation und empfohlene Anwendung der Finanzierungsrate-Strategie
- Strategie für einen doppelten gleitenden Durchschnitts-Brechpunkt von Kryptowährungs-Futures (Teaching)
- Strategie für einen doppelten gleitenden Durchschnitt mit mehreren Symbolen (Teaching)
- Treuhänder
- 2021 Kryptowährungs-TAQ-Überprüfung & Einfachste verpasste Strategie der 10-fachen Erhöhung
- Kryptowährungs-Futures Multi-Symbol ART-Strategie (Lehre)
- Aktualisieren! Kryptowährungs Futures Martingale Strategie
- Die Getrecords-Funktion kann keine K-Stringkarte in Sekunden erhalten
- Konstruktion eines FMZ-basierten Auftragsmanagementsystems (2)
- Die Volumen-Daten, die Getticker zurückgegeben hat, sind falsch.
- Gestaltung eines FMZ-basierten Auftragssynchronmanagementsystems (1)
- Entwerfen Sie eine Bibliothek mit mehreren Diagrammen
- Analogische Umgebung