Tendencia cruzada de promedio móvil siguiendo la estrategia
El autor:¿ Qué pasa?, Fecha: 2024-02-05 14:12:27Las etiquetas:
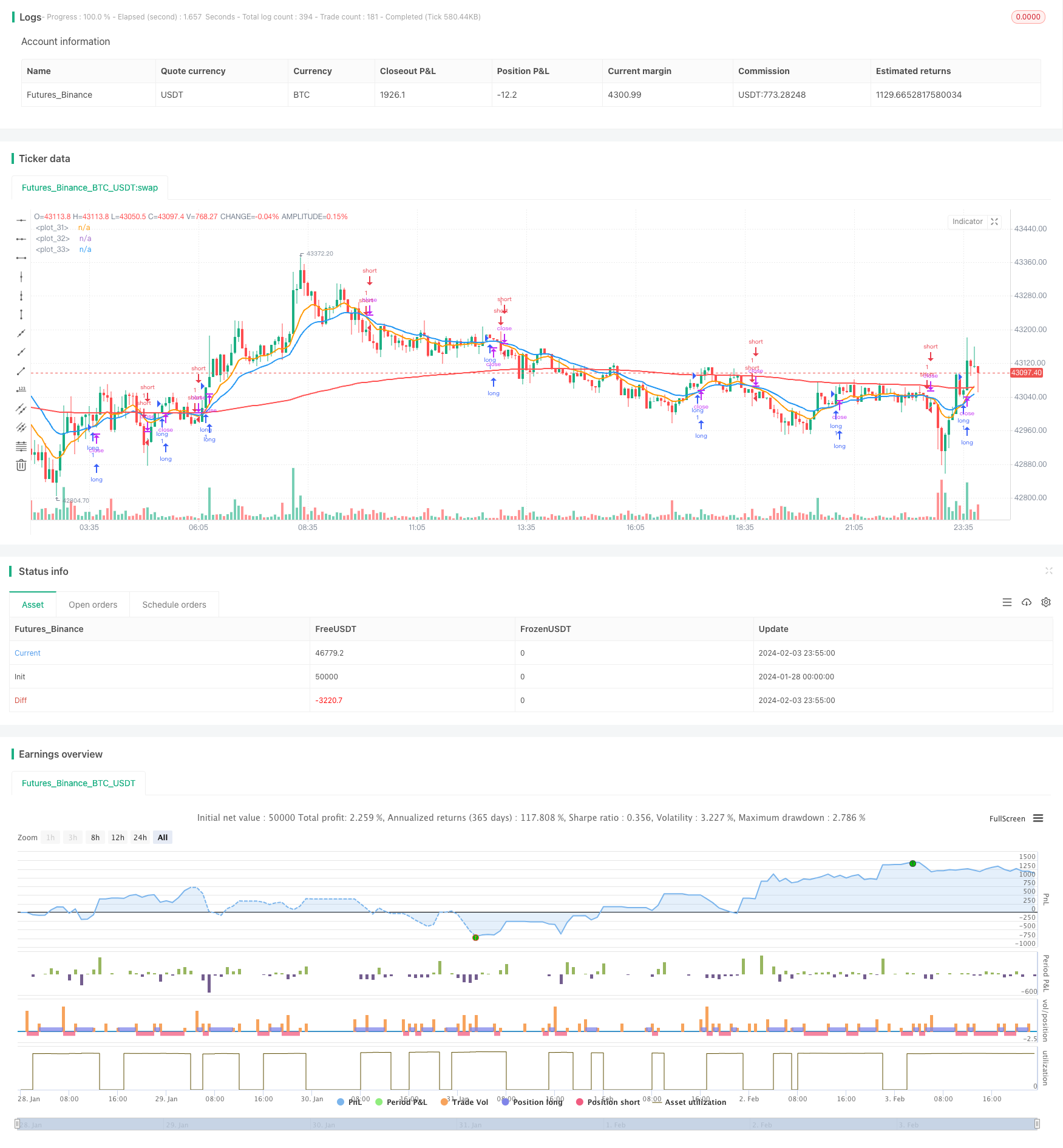
Resumen general
La estrategia de seguimiento de tendencias de cruce de promedios móviles es una estrategia comercial cuantitativa que rastrea las tendencias del mercado.
Estrategia lógica
El principio básico de esta estrategia es juzgar las tendencias del mercado utilizando promedios móviles exponenciales (EMA) con diferentes parámetros. La estrategia define una EMA rápida y una EMA lenta. Cuando la EMA rápida cruza por encima de la EMA lenta, indica una inversión de tendencia alcista en el mercado. Cuando la EMA rápida cruza por debajo de la EMA lenta, indica una inversión de tendencia bajista.
En los cruces ascendentes, la estrategia abrirá posiciones largas. En los cruces descendentes, la estrategia abrirá posiciones cortas. La estrategia mantendrá su posición hasta que se active el take profit o el stop loss, o se produzca nuevamente un cruce en la dirección opuesta.
Análisis de ventajas
La estrategia tiene las siguientes ventajas:
- La lógica de la estrategia es simple y clara, fácil de entender e implementar, adecuada para principiantes;
- El uso de EMA para suavizar los precios puede filtrar eficazmente el ruido del mercado e identificar tendencias;
- Los parámetros pueden ajustarse de forma flexible para adaptarse a mercados con diferentes ciclos.
- La estrategia puede ampliarse a versiones de varios marcos de tiempo para mejorar la estabilidad.
Análisis de riesgos
La estrategia también tiene algunos riesgos:
- En los mercados variados, pueden producirse múltiples pérdidas de parada, lo que afecta a la rentabilidad;
- No puede identificar eficazmente los tipos de tendencia (bullish o bearish), que pueden conducir a pérdidas graves;
- Los parámetros de EMA que se ajusten incorrectamente pueden provocar un exceso de negociación o retrasos en la detección.
Para mitigar los riesgos, considere combinar otros indicadores para determinar los tipos de tendencia o establecer coeficientes de stop loss más amplios.
Direcciones de optimización
La estrategia también puede optimizarse en los siguientes aspectos:
- Aumentar el juicio de los tipos de tendencia para evitar la apertura de posiciones en contra de la tendencia;
- Añadir juicios de varios marcos de tiempo para mejorar la calidad de la señal;
- Ajustar dinámicamente las tasas de stop loss y take profit para optimizar los puntos de salida;
- Combine otros indicadores para filtrar las operaciones erróneas.
Conclusión
En resumen, la Moving Average Crossover Trend Following Strategy es una estrategia de trading de tendencias simple y práctica. Las ideas centrales de la estrategia son claras y fáciles de implementar, y también hay espacio para la optimización. Al ajustar los parámetros, agregar análisis de marcos de tiempo múltiples, paradas dinámicas, etc., la estabilidad y rentabilidad de la estrategia se pueden mejorar continuamente.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-28 00:00:00
end: 2024-02-04 00:00:00
period: 5m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy('Zhukov trade', overlay=true, calc_on_every_tick=true, currency=currency.USD)
// INPUT:
// Options to enter fast and slow Exponential Moving Average (EMA) values
emaFast = input.int(title='Fast EMA', defval=10, minval=1, maxval=9999)
emaSlow = input.int(title='Slow EMA', defval=20, minval=1, maxval=9999)
// Option to select trade directions
tradeDirection = input.string(title='Trade Direction', options=['Long', 'Short', 'Both'], defval='Both')
// Options that configure the backtest date range
startDate = input(title='Start Date', defval=timestamp('01 Jan 2023 00:00'))
endDate = input(title='End Date', defval=timestamp('31 Dec 2030 23:59'))
// Set take profit and stop loss percentages
take_profit_percent = input(1.0, title ="Take Profit Percent") / 100.0
stop_loss_percent = input(1.0, title ="Stop Loss Percent") / 100.0
// CALCULATIONS:
// Use the built-in function to calculate two EMA lines
fastEMA = ta.ema(close, emaFast)
slowEMA = ta.ema(close, emaSlow)
emapos = ta.ema(close, 200)
// PLOT:
// Draw the EMA lines on the chart
plot(series=fastEMA, color=color.new(color.orange, 0), linewidth=2)
plot(series=slowEMA, color=color.new(color.blue, 0), linewidth=2)
plot(series=emapos, color=color.new(color.red, 0), linewidth=2)
// CONDITIONS:
// Check if the close time of the current bar falls inside the date range
inDateRange = true
// Translate input into trading conditions
longOK = tradeDirection == 'Long' or tradeDirection == 'Both'
shortOK = tradeDirection == 'Short' or tradeDirection == 'Both'
// Decide if we should go long or short using the built-in functions
longCondition = ta.crossover(fastEMA, slowEMA) and inDateRange
shortCondition = ta.crossunder(fastEMA, slowEMA) and inDateRange
// ORDERS:
// Submit entry (or reverse) orders
if longCondition and longOK
strategy.entry(id='long', direction=strategy.long)
if shortCondition and shortOK
strategy.entry(id='short', direction=strategy.short)
// Exit orders
if strategy.position_size > 0 and longOK
strategy.exit(id='exit long', from_entry='long', limit=strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + take_profit_percent), stop=strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - stop_loss_percent))
if strategy.position_size < 0 and shortOK
strategy.exit(id='exit short', from_entry='short', limit=strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - take_profit_percent), stop=strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + stop_loss_percent))
- Tendencia de seguimiento de la estrategia de stop loss basada en el indicador de alerta de tendencia
- Estrategia de Bressert estocástica doblemente suavizada
- Tendencia cruzada de la media estocástica y de la media móvil siguiendo una estrategia cuantitativa
- Estrategia de ruptura del canal de la media móvil de 5 días combinada con el concepto de kilometraje
- Estrategia de reversión de ruptura con stop loss
- Impulso de la estrategia de EMA
- Estrategia de negociación de impulso de compresión basada en el indicador LazyBear
- Estrategia de puntos de pivote de Camarilla basada en bandas de Bollinger
- Tendencia siguiendo la estrategia basada en las líneas de la EMA
- Estrategia de promedio móvil dinámico
- Estrategia de ruptura de promedio móvil de pirámide paso a paso
- Estrategia de despliegue de bandas de Bollinger de doble vía
- Las líneas futuras de la estrategia de demarcación
- Estrategia de negociación cuántica basada en el canal SuperTrend
- Teoría de la tasa de ganancia Estrategia de cuantificación del índice de volatilidad
- Estrategia de suspensión de pérdidas de seguimiento de la media móvil doble
- Estrategia de intercambio entre los indicadores de crecimiento y la AMM
- Estrategia de tendencia cruzada de la SMA dinámica
- Estrategia de seguimiento de precios oscilantes con doble indicador MA