Gauss-Kanal-Trend nach Strategie
Schriftsteller:ChaoZhang, Datum: 2024-03-29 16:26:26Tags:
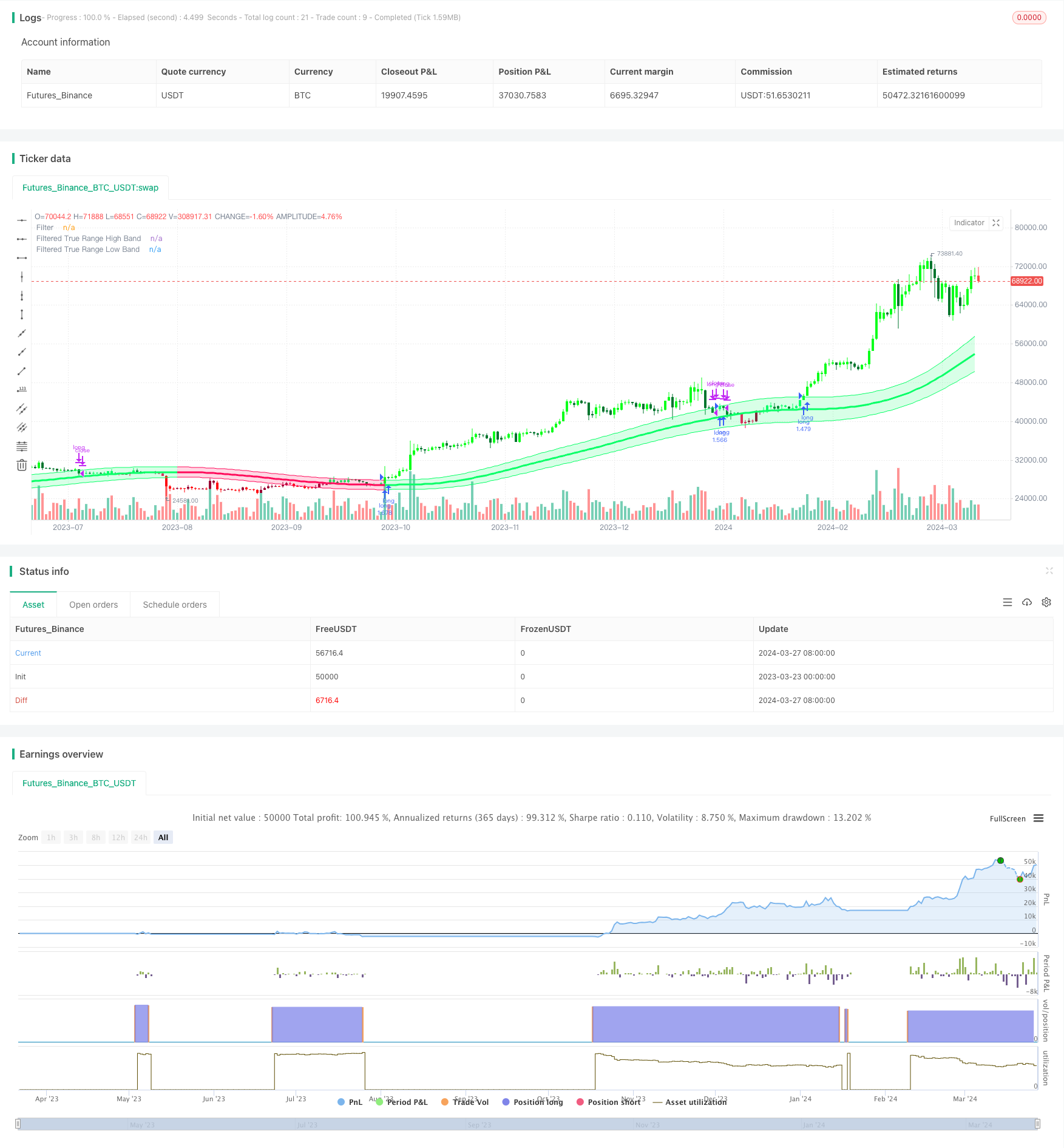
Übersicht
Die Gaussian Channel Trend Following Strategie ist eine Trend-following Handelsstrategie, die auf dem Gaussian Channel-Indikator basiert. Die Strategie zielt darauf ab, die wichtigsten Trends auf dem Markt zu erfassen, während Aufwärtstrends und Schließtrends Positionen zu kaufen und zu halten. Sie verwendet den Gaussian Channel-Indikator, um die Richtung und Stärke des Trends zu identifizieren, indem die Beziehung zwischen Preis und den oberen und unteren Bands des Kanals analysiert wird. Das Hauptziel der Strategie ist es, die Gewinne während anhaltender Trends zu maximieren und gleichzeitig die Frequenz während der Range-Bond-Handelsmärkte zu minimieren.
Strategieprinzip
Der Kern der Gaussian Channel Trend Following Strategie ist der Gaussian Channel Indikator, der von Ehlers vorgeschlagen wurde. Er kombiniert Gaussian Filtertechniken mit True Range, um die Trendaktivität zu analysieren. Der Indikator berechnet zuerst Beta- und Alpha-Werte basierend auf dem Probenzeitraum und der Anzahl der Pole, wendet dann einen Filter auf die Daten an, um eine glättete Kurve (Mitte) zu erhalten. Als nächstes multipliziert die Strategie die glättete True Range um einen Multiplikator, um die oberen und unteren Kanäle zu generieren. Wenn der Preis über/unter den oberen/unteren Kanal kreuzt, generiert er ein Kauf/Verkaufsignal. Zusätzlich bietet die Strategie Funktionen zur Verringerung der Indikatorverzögerung und einen schnellen Reaktionsmodus.
Strategische Vorteile
- Trendverfolgung: Die Strategie ist hervorragend darin, die wichtigsten Trends auf dem Markt zu erfassen und in die Richtung des Trends zu investieren, was dazu beiträgt, langfristige stabile Renditen zu erzielen.
- Verringerte Handelsfrequenz: Die Strategie tritt nur dann in Positionen ein, wenn ein Trend bestätigt wird, und hält während des Trends Positionen bei, wodurch unnötige Handels- und Transaktionskosten verringert werden.
- Verringerung der Verzögerung: Durch den reduzierten Verzögerungsmodus und den schnellen Reaktionsmodus kann die Strategie schneller auf Marktveränderungen reagieren.
- Flexible Parameter: Benutzer können die Strategieparameter entsprechend ihren Bedürfnissen anpassen, z. B. Probenzeit, Anzahl der Pole, Multiplikator für den wahren Bereich usw., um die Strategieleistung zu optimieren.
Strategische Risiken
- Parameteroptimierungsrisiko: Falsche Parameter-Einstellungen können zu schlechter Strategieleistung führen. Es wird empfohlen, Parameteroptimierung und Backtesting in verschiedenen Marktumgebungen durchzuführen, um die optimale Parameterkombination zu finden.
- Trendumkehrrisiko: Wenn sich die Markttrends plötzlich umkehren, kann die Strategie erhebliche Rückgänge erleben.
- Range-bound Marktrisiko: In Range-bound Märkten kann die Strategie häufige Handelssignale erzeugen, was zu verringerten Renditen führt. Dies kann durch Optimierung von Parametern oder Kombination mit anderen technischen Indikatoren zur Filterung von Signalen angegangen werden.
Strategieoptimierungsrichtlinien
- Einbeziehung anderer technischer Indikatoren: Kombination mit anderen Trend- oder Oszillatorindikatoren wie MACD, RSI usw. zur Verbesserung der Signalgenauigkeit und -zuverlässigkeit.
- Dynamische Parameteroptimierung: Dynamische Anpassung der Strategieparameter basierend auf Veränderungen der Marktbedingungen, um sich an verschiedene Marktumgebungen anzupassen.
- Hinzufügen eines Risikokontrollmoduls: Festlegen von angemessenen Stop-Loss- und Take-Profit-Regeln zur Kontrolle des individuellen Handelsrisikos und der Gesamtmenge der Zuwendungen.
- Multi-Timeframe-Analyse: Kombination von Signalen aus verschiedenen Zeitrahmen, z. B. Tages- und 4-Stunden-Charts, um umfassendere Marktinformationen zu erhalten.
Zusammenfassung
Die Gaussian Channel Trend Following Strategie ist eine Trend-Following-Handelsstrategie, die auf Gaussian-Filtertechniken basiert und darauf abzielt, die wichtigsten Markttrends für langfristige stabile Renditen zu erfassen. Die Strategie verwendet den Gaussian Channel-Indikator, um die Trendrichtung und -stärke zu identifizieren und bietet gleichzeitig Funktionen zur Verringerung der Verzögerung und schnellen Reaktion. Die Vorteile der Strategie liegen in ihrer starken Trend-Following-Fähigkeit und der geringen Handelsfrequenz. Sie ist jedoch auch mit Risiken wie Parameteroptimierung, Trendumkehrungen und Bereichsmärkten konfrontiert. Zukünftige Optimierungen können die Einbeziehung anderer technischer Indikatoren, dynamische Parameteroptimierung, das Hinzufügen von Risikokontrollmodulen und Multi-Timeframe-Analyse umfassen, um die Robustheit und Rentabilität der Strategie weiter zu verbessern.
/*backtest
start: 2023-03-23 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-28 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy(title="Gaussian Channel Strategy v2.0", overlay=true, calc_on_every_tick=false, initial_capital=1000, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.1, slippage=3)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Gaussian Channel Indicaor - courtesy of @DonovanWall
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Date condition inputs
startDate = input(timestamp("1 January 2018 00:00 +0000"), "Date Start", group="Main Algo Settings")
endDate = input(timestamp("1 January 2060 00:00 +0000"), "Date Start", group="Main Algo Settings")
timeCondition = true
// This study is an experiment utilizing the Ehlers Gaussian Filter technique combined with lag reduction techniques and true range to analyze trend activity.
// Gaussian filters, as Ehlers explains it, are simply exponential moving averages applied multiple times.
// First, beta and alpha are calculated based on the sampling period and number of poles specified. The maximum number of poles available in this script is 9.
// Next, the data being analyzed is given a truncation option for reduced lag, which can be enabled with "Reduced Lag Mode".
// Then the alpha and source values are used to calculate the filter and filtered true range of the dataset.
// Filtered true range with a specified multiplier is then added to and subtracted from the filter, generating a channel.
// Lastly, a one pole filter with a N pole alpha is averaged with the filter to generate a faster filter, which can be enabled with "Fast Response Mode".
// Custom bar colors are included.
// Note: Both the sampling period and number of poles directly affect how much lag the indicator has, and how smooth the output is.
// Larger inputs will result in smoother outputs with increased lag, and smaller inputs will have noisier outputs with reduced lag.
// For the best results, I recommend not setting the sampling period any lower than the number of poles + 1. Going lower truncates the equation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Updates:
// Huge shoutout to @e2e4mfck for taking the time to improve the calculation method!
// -> migrated to v4
// -> pi is now calculated using trig identities rather than being explicitly defined.
// -> The filter calculations are now organized into functions rather than being individually defined.
// -> Revamped color scheme.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Functions - courtesy of @e2e4mfck
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Filter function
f_filt9x (_a, _s, _i) =>
int _m2 = 0, int _m3 = 0, int _m4 = 0, int _m5 = 0, int _m6 = 0,
int _m7 = 0, int _m8 = 0, int _m9 = 0, float _f = .0, _x = (1 - _a)
// Weights.
// Initial weight _m1 is a pole number and equal to _i
_m2 := _i == 9 ? 36 : _i == 8 ? 28 : _i == 7 ? 21 : _i == 6 ? 15 : _i == 5 ? 10 : _i == 4 ? 6 : _i == 3 ? 3 : _i == 2 ? 1 : 0
_m3 := _i == 9 ? 84 : _i == 8 ? 56 : _i == 7 ? 35 : _i == 6 ? 20 : _i == 5 ? 10 : _i == 4 ? 4 : _i == 3 ? 1 : 0
_m4 := _i == 9 ? 126 : _i == 8 ? 70 : _i == 7 ? 35 : _i == 6 ? 15 : _i == 5 ? 5 : _i == 4 ? 1 : 0
_m5 := _i == 9 ? 126 : _i == 8 ? 56 : _i == 7 ? 21 : _i == 6 ? 6 : _i == 5 ? 1 : 0
_m6 := _i == 9 ? 84 : _i == 8 ? 28 : _i == 7 ? 7 : _i == 6 ? 1 : 0
_m7 := _i == 9 ? 36 : _i == 8 ? 8 : _i == 7 ? 1 : 0
_m8 := _i == 9 ? 9 : _i == 8 ? 1 : 0
_m9 := _i == 9 ? 1 : 0
// filter
_f := math.pow(_a, _i) * nz(_s) +
_i * _x * nz(_f[1]) - (_i >= 2 ?
_m2 * math.pow(_x, 2) * nz(_f[2]) : 0) + (_i >= 3 ?
_m3 * math.pow(_x, 3) * nz(_f[3]) : 0) - (_i >= 4 ?
_m4 * math.pow(_x, 4) * nz(_f[4]) : 0) + (_i >= 5 ?
_m5 * math.pow(_x, 5) * nz(_f[5]) : 0) - (_i >= 6 ?
_m6 * math.pow(_x, 6) * nz(_f[6]) : 0) + (_i >= 7 ?
_m7 * math.pow(_x, 7) * nz(_f[7]) : 0) - (_i >= 8 ?
_m8 * math.pow(_x, 8) * nz(_f[8]) : 0) + (_i == 9 ?
_m9 * math.pow(_x, 9) * nz(_f[9]) : 0)
// 9 var declaration fun
f_pole (_a, _s, _i) =>
_f1 = f_filt9x(_a, _s, 1), _f2 = (_i >= 2 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 2) : 0), _f3 = (_i >= 3 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 3) : 0)
_f4 = (_i >= 4 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 4) : 0), _f5 = (_i >= 5 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 5) : 0), _f6 = (_i >= 6 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 6) : 0)
_f7 = (_i >= 2 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 7) : 0), _f8 = (_i >= 8 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 8) : 0), _f9 = (_i == 9 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 9) : 0)
_fn = _i == 1 ? _f1 : _i == 2 ? _f2 : _i == 3 ? _f3 :
_i == 4 ? _f4 : _i == 5 ? _f5 : _i == 6 ? _f6 :
_i == 7 ? _f7 : _i == 8 ? _f8 : _i == 9 ? _f9 : na
[_fn, _f1]
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Inputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Source
src = input(defval=hlc3, title="Source")
// Poles
int N = input.int(defval=4, title="Poles", minval=1, maxval=9)
// Period
int per = input.int(defval=144, title="Sampling Period", minval=2)
// True Range Multiplier
float mult = input.float(defval=1.414, title="Filtered True Range Multiplier", minval=0)
// Lag Reduction
bool modeLag = input.bool(defval=false, title="Reduced Lag Mode")
bool modeFast = input.bool(defval=false, title="Fast Response Mode")
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Definitions
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Beta and Alpha Components
beta = (1 - math.cos(4*math.asin(1)/per)) / (math.pow(1.414, 2/N) - 1)
alpha = - beta + math.sqrt(math.pow(beta, 2) + 2*beta)
// Lag
lag = (per - 1)/(2*N)
// Data
srcdata = modeLag ? src + (src - src[lag]) : src
trdata = modeLag ? ta.tr(true) + (ta.tr(true) - ta.tr(true)[lag]) : ta.tr(true)
// Filtered Values
[filtn, filt1] = f_pole(alpha, srcdata, N)
[filtntr, filt1tr] = f_pole(alpha, trdata, N)
// Lag Reduction
filt = modeFast ? (filtn + filt1)/2 : filtn
filttr = modeFast ? (filtntr + filt1tr)/2 : filtntr
// Bands
hband = filt + filttr*mult
lband = filt - filttr*mult
// Colors
color1 = #0aff68
color2 = #00752d
color3 = #ff0a5a
color4 = #990032
fcolor = filt > filt[1] ? #0aff68 : filt < filt[1] ? #ff0a5a : #cccccc
barcolor = (src > src[1]) and (src > filt) and (src < hband) ? #0aff68 : (src > src[1]) and (src >= hband) ? #0aff1b : (src <= src[1]) and (src > filt) ? #00752d :
(src < src[1]) and (src < filt) and (src > lband) ? #ff0a5a : (src < src[1]) and (src <= lband) ? #ff0a11 : (src >= src[1]) and (src < filt) ? #990032 : #cccccc
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Outputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Filter Plot
filtplot = plot(filt, title="Filter", color=fcolor, linewidth=3)
// Band Plots
hbandplot = plot(hband, title="Filtered True Range High Band", color=fcolor)
lbandplot = plot(lband, title="Filtered True Range Low Band", color=fcolor)
// Channel Fill
fill(hbandplot, lbandplot, title="Channel Fill", color=color.new(fcolor, 80))
// Bar Color
barcolor(barcolor)
longCondition = ta.crossover(close, hband) and timeCondition
closeAllCondition = ta.crossunder(close, hband) and timeCondition
if longCondition
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long)
if closeAllCondition
strategy.close("long")
- Kurzfristige, auf einem doppelten gleitenden Durchschnitt und einem RSI basierenden, skalierbaren Trend nach Strategie
- Handelsstrategie für den Dual-Range-Filter-Impuls
- VWAP Moving Average Crossover mit dynamischer ATR Stop Loss und Take Profit Strategie
- Zeitreihe Adaptive dynamische Schwellenstrategie auf Basis von Eigenkapitaldaten
- Asiatische Sitzung hohe Niedrige Breakout-Strategie
- Marcus' Trend Trader mit Pfeilen und Warnungen Strategie
- Doppel gleitender Durchschnittsverlauf der EMA nach der Strategie
- Strategie für die Verlagerung des gleitenden Durchschnitts
- RSI-Momentumsstrategie mit manuellem TP und SL
- EMA-RSI-Trend-Folge- und Momentumstrategie
- Hochfrequenzhandelsstrategie, die Bollinger-Bänder und DCA kombiniert
- Geänderter Trend des Relative Strength Index nach Strategie
- Innertägige Bullish-Breakout-Strategie
- EMA-MACD-SuperTrend-ADX-ATR Multi-Indikator-Handelssignalstrategie
- Strategie für das Trendverfolgungsnetz der variablen Positionen
- Strategie zur Kombination von Supertrend und Bollinger Bands
- MACD-Trend nach Strategie
- Strategie der EMA für die Übertragung von Doppel gleitenden Durchschnitten
- XAUUSD 1-Minuten-Scalping-Strategie
- Vektor-Candle-basierte Channel Breakout und benutzerdefinierte ChoCH-Strategie