가우스 채널 트렌드 전략
저자:차오장, 날짜: 2024-03-29 16:26:26태그:
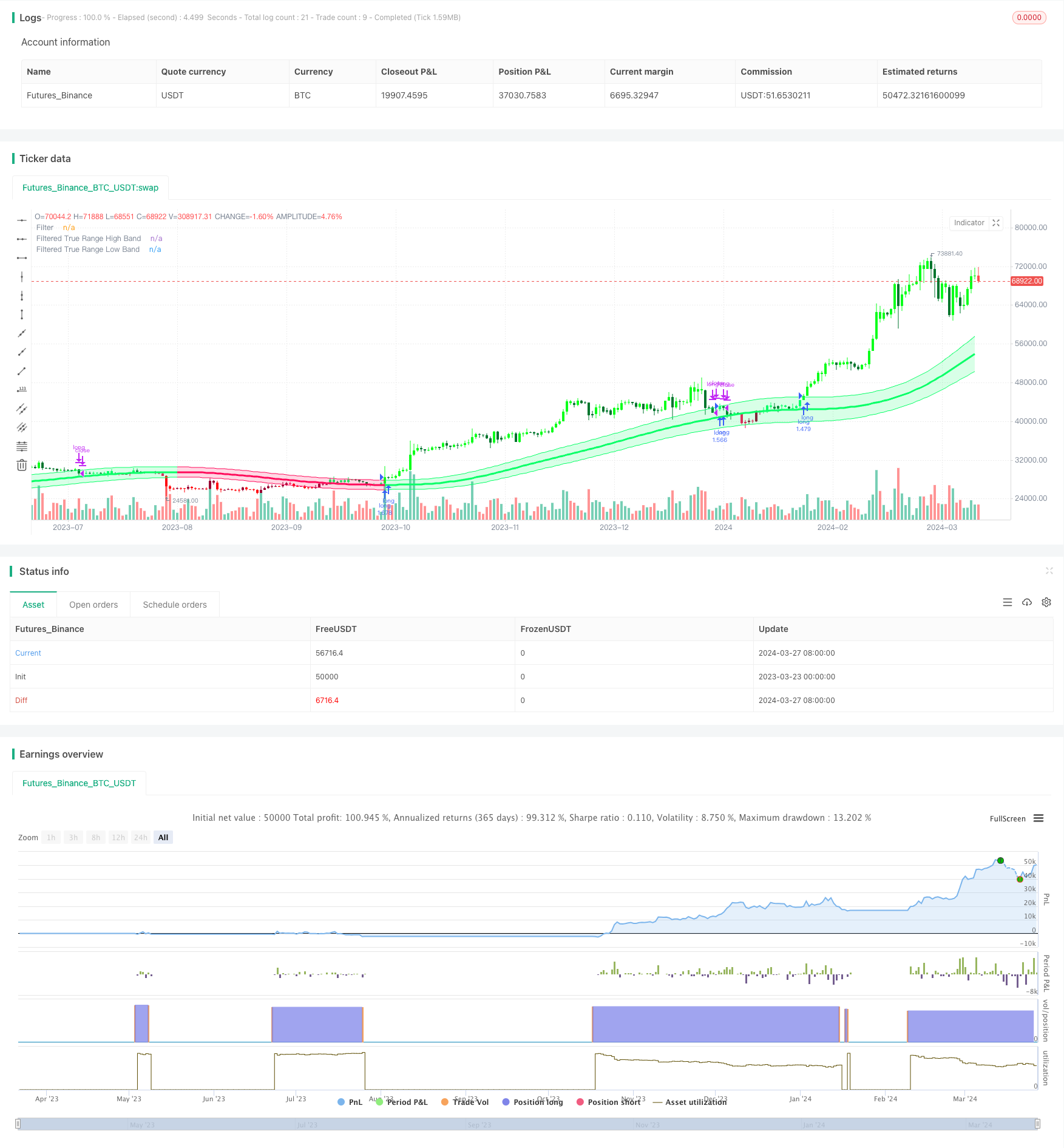
전반적인 설명
가우스 채널 트렌드 다음 전략 (Gaussian Channel Trend Following Strategy) 은 가우스 채널 지표에 기반을 둔 트렌드 다음 전략이다. 이 전략은 시장의 주요 트렌드를 포착하고, 상승 추세 중 구매 및 보유 포지션과 하락 추세 중 포지션을 닫는 것을 목표로 한다. 이 전략은 가우스 채널 지표를 사용하여 가격과 채널의 상부 및 하부 밴드 사이의 관계를 분석하여 트렌드의 방향과 강도를 파악한다. 전략의 주요 목표는 지속적인 트렌드 중 이익을 극대화하는 동시에 범위 제한 거래 시장에서 주파수를 최소화하는 것이다.
전략 원칙
가우스 채널 트렌드 추적 전략의 핵심은 에일러스가 제안한 가우스 채널 지표이다. 트렌드 활동을 분석하기 위해 가우스 필터링 기술과 트루 레인지를 결합한다. 지표는 먼저 샘플링 기간과 극의 수에 따라 베타와 알파 값을 계산하고, 그 다음
전략적 장점
- 트렌드 추적: 전략은 시장의 주요 트렌드를 포착하는 데 탁월하며, 트렌드 방향으로 투자하여 장기적으로 안정적인 수익을 얻는 데 도움이됩니다.
- 거래 빈도 감소: 전략은 트렌드가 확인되었을 때만 포지션을 입력하고 트렌드 동안 포지션을 유지하여 불필요한 거래 및 거래 비용을 줄입니다.
- 지연 감소: 감소된 지연 모드와 빠른 응답 모드를 통해 전략은 시장 변화에 더 신속하게 반응 할 수 있습니다.
- 유연한 매개 변수: 사용자는 샘플링 기간, 폴 수, 참 범위 곱기 등 전략 성능을 최적화하기 위해 필요에 따라 전략 매개 변수를 조정할 수 있습니다.
전략 위험
- 매개 변수 최적화 위험: 잘못된 매개 변수 설정으로 인해 전략 성능이 떨어질 수 있습니다. 최적의 매개 변수 조합을 찾기 위해 다른 시장 환경에서 매개 변수 최적화 및 백테스팅을 수행하는 것이 좋습니다.
- 트렌드 역전 위험: 시장 트렌드가 갑자기 역전되면 전략은 상당한 마감률을 경험할 수 있습니다. 이것은 스톱 로스를 설정하거나 위험을 제어하기 위해 다른 지표를 도입함으로써 완화 될 수 있습니다.
- 범위 제한 시장 위험: 범위 제한 시장에서 전략은 빈번한 거래 신호를 생성하여 수익률을 감소시킬 수 있습니다. 이는 매개 변수를 최적화하거나 신호를 필터하기 위해 다른 기술 지표와 결합하여 해결할 수 있습니다.
전략 최적화 방향
- 다른 기술 지표를 포함: 신호 정확성 및 신뢰성을 향상시키기 위해 MACD, RSI 등과 같은 다른 트렌드 추적 또는 오시레이터 지표와 결합합니다.
- 동적 매개 변수 최적화: 다른 시장 환경에 적응하기 위해 시장 조건의 변화에 따라 전략 매개 변수를 동적으로 조정합니다.
- 리스크 제어 모듈을 추가합니다. 개별 거래 리스크와 전체 마감 수치를 제어하기 위해 합리적인 스톱 로스 및 리프트 취리 규칙을 설정합니다.
- 멀티 타임프레임 분석: 더 포괄적인 시장 정보를 얻기 위해 일일 및 4 시간 차트와 같은 다른 시간 프레임의 신호를 결합합니다.
요약
가우스 채널 트렌드 추적 전략 (Gaussian Channel Trend Following Strategy) 은 가우스 채널 필터링 기법에 기반한 트렌드 추적 전략으로, 장기적인 안정적인 수익을 위해 주요 시장 트렌드를 파악하는 것을 목표로 한다. 이 전략은 트렌드 방향과 강도를 파악하기 위해 가우스 채널 지표를 사용하면서 지연을 줄이고 빠른 반응을 제공하는 기능을 제공한다. 이 전략의 장점은 강한 트렌드 추적 능력과 낮은 거래 빈도에 있다. 그러나, 또한 매개 변수 최적화, 트렌드 역전, 범위에 제한된 시장과 같은 위험에 직면한다. 미래 최적화는 다른 기술적 지표, 동적 매개 변수 최적화, 위험 제어 모듈 추가, 그리고 전략의 안정성과 수익성을 더욱 향상시키기 위해 다중 시간 프레임 분석을 포함할 수 있다.
/*backtest
start: 2023-03-23 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-28 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy(title="Gaussian Channel Strategy v2.0", overlay=true, calc_on_every_tick=false, initial_capital=1000, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.1, slippage=3)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Gaussian Channel Indicaor - courtesy of @DonovanWall
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Date condition inputs
startDate = input(timestamp("1 January 2018 00:00 +0000"), "Date Start", group="Main Algo Settings")
endDate = input(timestamp("1 January 2060 00:00 +0000"), "Date Start", group="Main Algo Settings")
timeCondition = true
// This study is an experiment utilizing the Ehlers Gaussian Filter technique combined with lag reduction techniques and true range to analyze trend activity.
// Gaussian filters, as Ehlers explains it, are simply exponential moving averages applied multiple times.
// First, beta and alpha are calculated based on the sampling period and number of poles specified. The maximum number of poles available in this script is 9.
// Next, the data being analyzed is given a truncation option for reduced lag, which can be enabled with "Reduced Lag Mode".
// Then the alpha and source values are used to calculate the filter and filtered true range of the dataset.
// Filtered true range with a specified multiplier is then added to and subtracted from the filter, generating a channel.
// Lastly, a one pole filter with a N pole alpha is averaged with the filter to generate a faster filter, which can be enabled with "Fast Response Mode".
// Custom bar colors are included.
// Note: Both the sampling period and number of poles directly affect how much lag the indicator has, and how smooth the output is.
// Larger inputs will result in smoother outputs with increased lag, and smaller inputs will have noisier outputs with reduced lag.
// For the best results, I recommend not setting the sampling period any lower than the number of poles + 1. Going lower truncates the equation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Updates:
// Huge shoutout to @e2e4mfck for taking the time to improve the calculation method!
// -> migrated to v4
// -> pi is now calculated using trig identities rather than being explicitly defined.
// -> The filter calculations are now organized into functions rather than being individually defined.
// -> Revamped color scheme.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Functions - courtesy of @e2e4mfck
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Filter function
f_filt9x (_a, _s, _i) =>
int _m2 = 0, int _m3 = 0, int _m4 = 0, int _m5 = 0, int _m6 = 0,
int _m7 = 0, int _m8 = 0, int _m9 = 0, float _f = .0, _x = (1 - _a)
// Weights.
// Initial weight _m1 is a pole number and equal to _i
_m2 := _i == 9 ? 36 : _i == 8 ? 28 : _i == 7 ? 21 : _i == 6 ? 15 : _i == 5 ? 10 : _i == 4 ? 6 : _i == 3 ? 3 : _i == 2 ? 1 : 0
_m3 := _i == 9 ? 84 : _i == 8 ? 56 : _i == 7 ? 35 : _i == 6 ? 20 : _i == 5 ? 10 : _i == 4 ? 4 : _i == 3 ? 1 : 0
_m4 := _i == 9 ? 126 : _i == 8 ? 70 : _i == 7 ? 35 : _i == 6 ? 15 : _i == 5 ? 5 : _i == 4 ? 1 : 0
_m5 := _i == 9 ? 126 : _i == 8 ? 56 : _i == 7 ? 21 : _i == 6 ? 6 : _i == 5 ? 1 : 0
_m6 := _i == 9 ? 84 : _i == 8 ? 28 : _i == 7 ? 7 : _i == 6 ? 1 : 0
_m7 := _i == 9 ? 36 : _i == 8 ? 8 : _i == 7 ? 1 : 0
_m8 := _i == 9 ? 9 : _i == 8 ? 1 : 0
_m9 := _i == 9 ? 1 : 0
// filter
_f := math.pow(_a, _i) * nz(_s) +
_i * _x * nz(_f[1]) - (_i >= 2 ?
_m2 * math.pow(_x, 2) * nz(_f[2]) : 0) + (_i >= 3 ?
_m3 * math.pow(_x, 3) * nz(_f[3]) : 0) - (_i >= 4 ?
_m4 * math.pow(_x, 4) * nz(_f[4]) : 0) + (_i >= 5 ?
_m5 * math.pow(_x, 5) * nz(_f[5]) : 0) - (_i >= 6 ?
_m6 * math.pow(_x, 6) * nz(_f[6]) : 0) + (_i >= 7 ?
_m7 * math.pow(_x, 7) * nz(_f[7]) : 0) - (_i >= 8 ?
_m8 * math.pow(_x, 8) * nz(_f[8]) : 0) + (_i == 9 ?
_m9 * math.pow(_x, 9) * nz(_f[9]) : 0)
// 9 var declaration fun
f_pole (_a, _s, _i) =>
_f1 = f_filt9x(_a, _s, 1), _f2 = (_i >= 2 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 2) : 0), _f3 = (_i >= 3 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 3) : 0)
_f4 = (_i >= 4 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 4) : 0), _f5 = (_i >= 5 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 5) : 0), _f6 = (_i >= 6 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 6) : 0)
_f7 = (_i >= 2 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 7) : 0), _f8 = (_i >= 8 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 8) : 0), _f9 = (_i == 9 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 9) : 0)
_fn = _i == 1 ? _f1 : _i == 2 ? _f2 : _i == 3 ? _f3 :
_i == 4 ? _f4 : _i == 5 ? _f5 : _i == 6 ? _f6 :
_i == 7 ? _f7 : _i == 8 ? _f8 : _i == 9 ? _f9 : na
[_fn, _f1]
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Inputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Source
src = input(defval=hlc3, title="Source")
// Poles
int N = input.int(defval=4, title="Poles", minval=1, maxval=9)
// Period
int per = input.int(defval=144, title="Sampling Period", minval=2)
// True Range Multiplier
float mult = input.float(defval=1.414, title="Filtered True Range Multiplier", minval=0)
// Lag Reduction
bool modeLag = input.bool(defval=false, title="Reduced Lag Mode")
bool modeFast = input.bool(defval=false, title="Fast Response Mode")
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Definitions
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Beta and Alpha Components
beta = (1 - math.cos(4*math.asin(1)/per)) / (math.pow(1.414, 2/N) - 1)
alpha = - beta + math.sqrt(math.pow(beta, 2) + 2*beta)
// Lag
lag = (per - 1)/(2*N)
// Data
srcdata = modeLag ? src + (src - src[lag]) : src
trdata = modeLag ? ta.tr(true) + (ta.tr(true) - ta.tr(true)[lag]) : ta.tr(true)
// Filtered Values
[filtn, filt1] = f_pole(alpha, srcdata, N)
[filtntr, filt1tr] = f_pole(alpha, trdata, N)
// Lag Reduction
filt = modeFast ? (filtn + filt1)/2 : filtn
filttr = modeFast ? (filtntr + filt1tr)/2 : filtntr
// Bands
hband = filt + filttr*mult
lband = filt - filttr*mult
// Colors
color1 = #0aff68
color2 = #00752d
color3 = #ff0a5a
color4 = #990032
fcolor = filt > filt[1] ? #0aff68 : filt < filt[1] ? #ff0a5a : #cccccc
barcolor = (src > src[1]) and (src > filt) and (src < hband) ? #0aff68 : (src > src[1]) and (src >= hband) ? #0aff1b : (src <= src[1]) and (src > filt) ? #00752d :
(src < src[1]) and (src < filt) and (src > lband) ? #ff0a5a : (src < src[1]) and (src <= lband) ? #ff0a11 : (src >= src[1]) and (src < filt) ? #990032 : #cccccc
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Outputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Filter Plot
filtplot = plot(filt, title="Filter", color=fcolor, linewidth=3)
// Band Plots
hbandplot = plot(hband, title="Filtered True Range High Band", color=fcolor)
lbandplot = plot(lband, title="Filtered True Range Low Band", color=fcolor)
// Channel Fill
fill(hbandplot, lbandplot, title="Channel Fill", color=color.new(fcolor, 80))
// Bar Color
barcolor(barcolor)
longCondition = ta.crossover(close, hband) and timeCondition
closeAllCondition = ta.crossunder(close, hband) and timeCondition
if longCondition
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long)
if closeAllCondition
strategy.close("long")
- 이중 이동 평균 및 RSI 기반 단기 확장 트렌드 전략
- 듀얼 레인지 필터 모멘텀 거래 전략
- VWAP 이동 평균 크로스오버와 동적 ATR 스톱 로스 및 영업 전략
- 자금 데이터에 기초한 시간 계열 적응적 동적 기준 전략
- 아시아 세션 높은 낮은 브레이크업 전략
- 화살표와 경고 전략으로 마커스의 트렌드 트레이더
- 전략에 따른 EMA의 이중 이동평균 크로스오버 트렌드
- 이동 평균 크로스오버 전략
- 수동 TP와 SL로 RSI 모멘텀 전략
- EMA RSI 트렌드 추적 및 모멘텀 전략
- 볼링거 밴드와 DCA를 결합한 고주파 거래 전략
- 전략에 따라 상대적 강도 지표의 변화 추세
- 내일 상승성 브레이크업 전략
- EMA-MACD-SuperTrend-ADX-ATR 다중 지표 거래 신호 전략
- 트렌드를 따르는 변수 위치 그리드 전략
- 슈퍼트렌드와 볼린거 밴드 조합 전략
- MACD 트렌드 전략
- EMA의 이중 이동 평균 크로스오버 전략
- XAUUSD 1분 스칼핑 전략
- 벡터 촛불 기반 채널 브레이크오웃 및 사용자 지정 ChoCH 전략