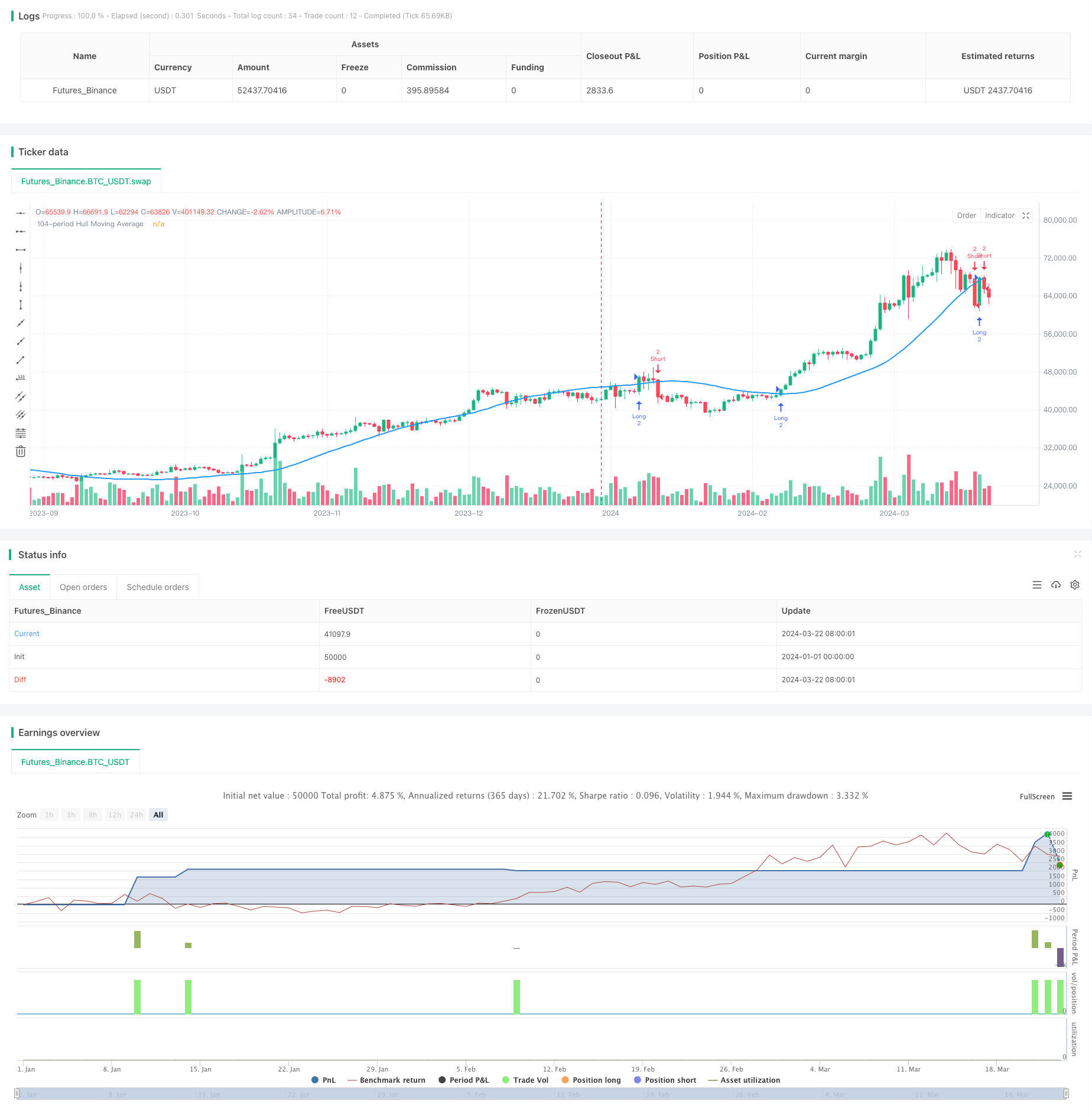
概述
自适应价格交叉均线交易策略是一种基于Hull移动平均线(HMA)的量化交易方法。该策略利用价格与HMA的交叉来生成买入和卖出信号,同时设置固定的止损和止盈水平来管理风险和收益。策略采用了104周期的HMA作为主要指标,结合价格交叉来触发交易。
策略原理
该策略的核心是使用Hull移动平均线(HMA)作为主要指标。HMA是一种先进的移动平均线,它能够快速响应价格变化,同时减少滞后。策略逻辑如下:
- 计算104周期的HMA。
- 当价格向上穿过HMA时,开仓做多。
- 当价格向下穿过HMA时,开仓做空。
- 对每个交易设置固定的止损(\(1.25)和止盈(\)37.5)水平。
- 每次交易使用2个合约。
策略通过跟踪开放头寸来确保不会在已有头寸的情况下重复开仓。当一个交易被平仓后,系统重置标志,允许新的交易信号生效。
策略优势
- 适应性强:HMA能够快速适应市场变化,减少假信号。
- 风险管理:使用固定的止损和止盈水平,有效控制每笔交易的风险。
- 简单明确:交易规则清晰,易于理解和执行。
- 双向交易:同时捕捉上涨和下跌机会,增加盈利潜力。
- 自动化:策略可以完全自动化,减少人为干预和情绪影响。
策略风险
- 频繁交易:在波动剧烈的市场中可能产生过多的交易信号,增加交易成本。
- 固定止损/止盈:可能不适合所有市场条件,在某些情况下可能过早出场或错过大趋势。
- 依赖单一指标:仅依赖HMA可能在某些市场环境下表现不佳。
- 滞后性:尽管HMA减少了滞后,但仍可能在急剧转折点反应不足。
- 缺乏市场环境过滤:没有考虑整体市场趋势或波动率,可能在不适合的市场条件下交易。
策略优化方向
- 引入额外指标:结合其他技术指标(如RSI或MACD)来确认信号,提高准确性。
- 动态止损/止盈:根据市场波动性调整止损和止盈水平,以适应不同市场环境。
- 增加市场过滤器:加入趋势强度或波动率过滤器,避免在不利市场条件下交易。
- 优化HMA参数:测试不同的HMA周期,找到最适合特定市场的参数。
- 引入仓位管理:根据市场风险和账户规模动态调整交易规模。
- 添加时间过滤:避免在市场波动性较大的时间段交易,如重要经济数据发布期间。
总结
自适应价格交叉均线交易策略是一种简单而有效的量化交易方法。通过利用Hull移动平均线的优势,该策略能够捕捉市场趋势,同时通过固定的风险管理措施来保护资金。虽然策略存在一些潜在风险,但通过持续优化和改进,可以进一步提高其性能和适应性。对于寻求自动化交易解决方案的交易者来说,这是一个值得考虑的基础策略框架。
策略源码
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-23 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("SHIESTD", overlay=true)
// Function to calculate Hull Moving Average (HMA)
hma(src, length) =>
wma1 = ta.wma(src, length)
wma2 = ta.wma(src, length / 2)
hma = ta.wma(2 * wma2 - wma1, math.round(math.sqrt(length)))
hma
// Parameters
hma_length = 104
// Calculate Hull Moving Average
hma_value = hma(close, hma_length)
// Plot HMA
plot(hma_value, title="104-period Hull Moving Average", color=color.blue, linewidth=2)
// Define SL and TP values in dollars
long_sl_amount = 1.25
long_tp_amount = 37.5
short_sl_amount = 1.25
short_tp_amount = 37.5
// Number of contracts
contracts = 2
// Function to calculate SL and TP prices based on entry price and dollar amounts
long_sl_price(entry_price) =>
entry_price - long_sl_amount
long_tp_price(entry_price) =>
entry_price + long_tp_amount
short_sl_price(entry_price) =>
entry_price + short_sl_amount
short_tp_price(entry_price) =>
entry_price - short_tp_amount
// Trading conditions
price_intersects_hma = ta.crossover(close, hma_value) or ta.crossunder(close, hma_value)
// Long and Short Conditions based on price intersecting HMA
long_condition = ta.crossover(close, hma_value)
short_condition = ta.crossunder(close, hma_value)
// Track open positions
var bool long_open = false
var bool short_open = false
// Handle Long Positions
if (long_condition and not long_open)
entry_price = close
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, qty=contracts)
strategy.exit("Exit Long", from_entry="Long", stop=long_sl_price(entry_price), limit=long_tp_price(entry_price))
long_open := true
// Handle Short Positions
if (short_condition and not short_open)
entry_price = close
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, qty=contracts)
strategy.exit("Exit Short", from_entry="Short", stop=short_sl_price(entry_price), limit=short_tp_price(entry_price))
short_open := true
// Reset flags when the position is closed
if (strategy.opentrades == 0)
long_open := false
short_open := false
相关推荐