Dynamic RSI Oscillator Polynomial Fitting Indicator Trend Quantitative Trading Strategy
Author: ChaoZhang, Date: 2024-12-11 15:32:23Tags: RSIDRSIQREMARMSEMSE
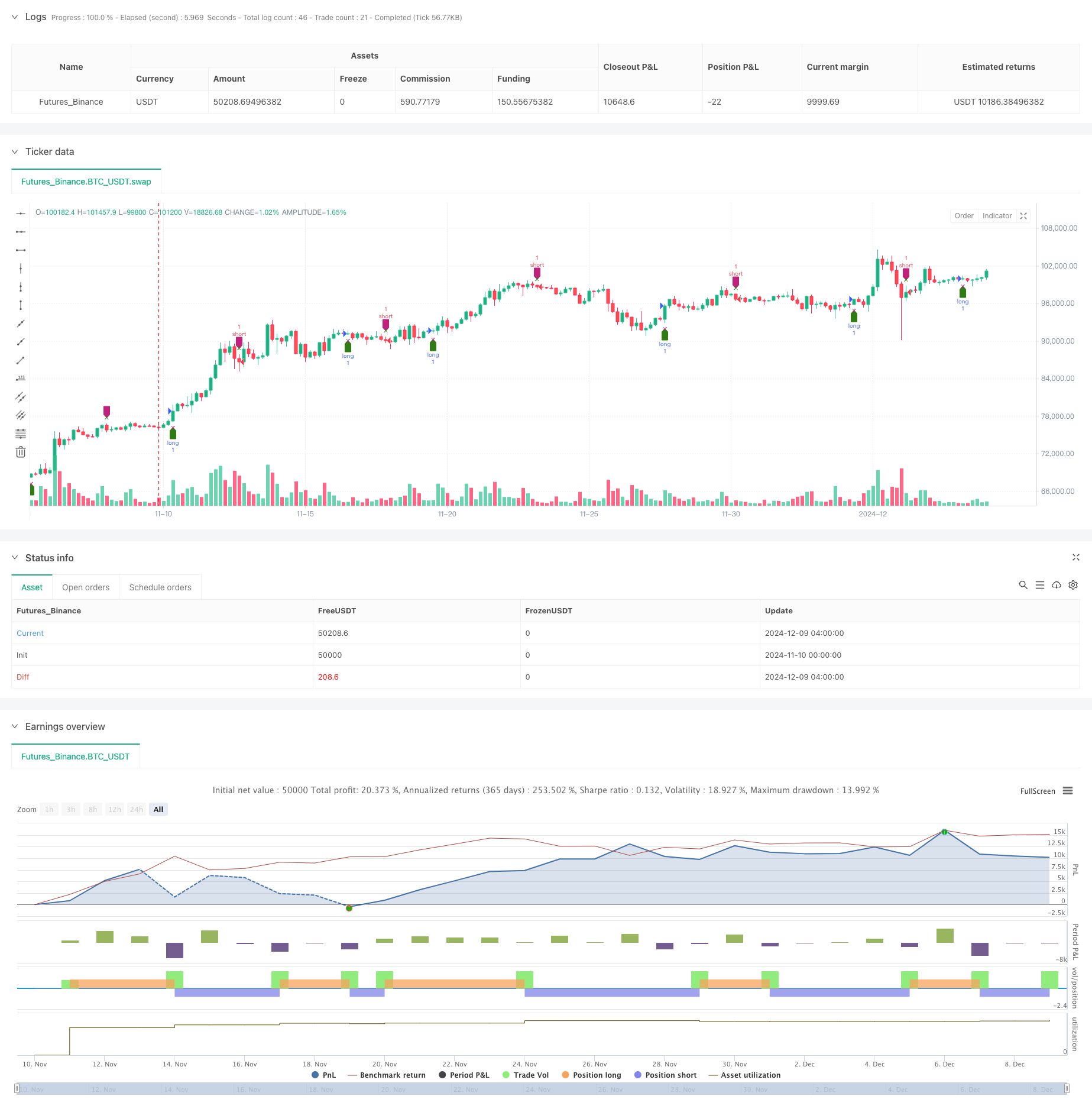
This strategy is a quantitative trading system based on RSI dynamic oscillator. By performing polynomial fitting and time series analysis on the RSI indicator, it calculates the rate of change of RSI to capture market momentum. The strategy uses advanced mathematical methods such as QR decomposition for signal processing and combines with moving average system for trading decisions.
Strategy Principle
The core of the strategy is the Delta-RSI oscillator, which is implemented through the following steps: 1. First calculate traditional RSI indicator as basic data 2. Use polynomial fitting to smooth RSI and reduce noise 3. Calculate time derivative of RSI to get Delta-RSI, reflecting rate of change of RSI 4. Compare Delta-RSI with its moving average to generate trading signals 5. Use root mean square error (RMSE) to evaluate and filter fitting quality
Trading signals can be generated in three ways: - Zero-line crossing: Long when Delta-RSI turns positive from negative, short when turns negative from positive - Signal line crossing: Long/short when Delta-RSI crosses above/below its moving average - Direction change: Long when Delta-RSI starts rising in negative territory, short when starts falling in positive territory
Strategy Advantages
- Solid mathematical foundation: Uses advanced mathematical methods like QR decomposition for signal processing
- Signal smoothing: Polynomial fitting can effectively filter market noise and improve signal quality
- High flexibility: Provides multiple signal generation methods and parameter choices to adapt to different market conditions
- Controllable risk: Includes RMSE filtering mechanism to screen out more reliable signals
- Computational efficiency: Matrix operations use optimized algorithms for high running efficiency
Strategy Risks
- Parameter sensitivity: Multiple key parameters need careful adjustment, poor parameter selection seriously affects strategy performance
- Lag: Signal smoothing introduces some delay, may miss rapid market moves
- False breakouts: May generate false signals in oscillating markets, increasing trading costs
- Computational complexity: Involves many matrix operations, may have performance bottlenecks in high-frequency trading
- Overfitting: Need to avoid overfitting historical data when optimizing parameters
Strategy Optimization Directions
- Adaptive parameters: Dynamically adjust RSI period and fitting order based on market volatility
- Multiple timeframes: Incorporate signals from more timeframes for cross-validation
- Volatility filtering: Add volatility indicators like ATR for signal filtering
- Market classification: Use different signal generation rules for different market states (trend/oscillation)
- Stop-loss optimization: Add smarter stop-loss mechanisms, like dynamic stops based on support/resistance levels
Summary
This is a complete quantitative trading strategy with solid theoretical foundation. Through analysis of RSI’s dynamic characteristics combined with modern mathematical methods for signal processing, it can effectively capture market trends. While there are some issues with parameter sensitivity and computational complexity, the strategy has good practical value through proper parameter selection and optimization improvements. When applying to live trading, it’s recommended to pay attention to risk control, set reasonable position sizes, and continuously monitor strategy performance.
/*backtest
start: 2024-11-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-12-09 08:00:00
period: 4h
basePeriod: 4h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy
//
// A strategy that uses Delta-RSI Oscillator (© tbiktag) as a stand-alone indicator:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// Delta-RSI is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI, plotted as a histogram
// and serving as a momentum indicator.
//
// Input parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate the RSI.
// Signal Length: The length of a EMA of the D-RSI series that is used as a signal line.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending (bearish otherwise)
//
// Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option
// to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
//
//@version=5
strategy(title='Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy-QuangVersion', shorttitle='D-RSI-Q', overlay=true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A, _i + _nrows * _j)
matrix_set(_A, _value, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A, _i + _nrows * _j, _value)
transpose(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A, i, j, _nrows), j, i, _ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A, _B, _nrowsA, _ncolumnsA, _ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA * _ncolumnsB, 0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC = 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB - 1 by 1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA - 1 by 1
elementC += matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrowsA) * matrix_get(_B, k, j, _nrowsB)
elementC
matrix_set(_C, elementC, i, j, _nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X, _n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n - 1 by 1
_norm += math.pow(array.get(_X, i), 2)
_norm
math.sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, 0, _nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R, _r, 0, 0, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, 0, _nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrows))
for j = 0 to k - 1 by 1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows) * array.get(_a, i)
_r
matrix_set(_R, _r, j, k, _ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_aux := array.get(_a, i) - _r * matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows)
array.set(_a, i, _aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
matrix_set(_R, _r, k, k, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, k, _nrows)
[_Q, _R]
pinv(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q, _R] = qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q, _nrows, _ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, 0, 0, _ncolumns), 0, 0, _ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to j - 1 by 1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Rinv, i, k, _ncolumns) * matrix_get(_R, k, j, _ncolumns)
_r
matrix_set(_Rinv, _r, i, j, _ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Rinv, -matrix_get(_Rinv, k, j, _ncolumns) / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), k, j, _ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), j, j, _ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv, _QT, _ncolumns, _ncolumns, _nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
_nrmse
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N - 1 by 1
_mse += math.pow(array.get(_x, i) - array.get(_xhat, i), 2) / _N
_mse
_xmean = array.sum(_x) / _N
_nrmse := math.sqrt(_mse) / _xmean
_nrmse
_nrmse
diff(_src, _window, _degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree], with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window * (_degree + 1), 0)
for i = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _degree by 1
matrix_set(_J, math.pow(i, j), i, j, _window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window, na)
for j = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
array.set(_Y_raw, j, _src[_window - 1 - j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J, _window, _degree + 1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C, _Y_raw, _degree + 1, _window, 1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree by 1
_diff += i * array.get(_a_coef, i) * math.pow(_window - 1, i - 1)
_diff
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J, _a_coef, _window, _degree + 1, 1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw, _Y_hat)
[_diff, _nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input.int(title='Polynomial Order', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=2, minval=1)
rsi_l = input.int(title='RSI Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=21, minval=1, tooltip='The period length of RSI that is used as input.')
window = input.int(title='Length ( > Order)', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=21, minval=2)
signalLength = input.int(title='Signal Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=9, tooltip='The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.')
islong = input.bool(title='Buy', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
isshort = input.bool(title='Sell', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
showendlabels = input.bool(title='Exit', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
buycond = input.string(title='Buy', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
sellcond = input.string(title='Sell', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
endcond = input.string(title='Exit', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
usenrmse = input.bool(title='', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=false)
rmse_thrs = input.float(title='RSI fitting Error Threshold, %', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=10, minval=0.0) / 100
src = ta.rsi(close, rsi_l)
[drsi, nrmse] = diff(src, window, degree)
signalline = ta.ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions and filters
filter_rmse = usenrmse ? nrmse < rmse_thrs : true
dirchangeup = drsi > drsi[1] and drsi[1] < drsi[2] and drsi[1] < 0.0
dirchangedw = drsi < drsi[1] and drsi[1] > drsi[2] and drsi[1] > 0.0
crossup = ta.crossover(drsi, 0.0)
crossdw = ta.crossunder(drsi, 0.0)
crosssignalup = ta.crossover(drsi, signalline)
crosssignaldw = ta.crossunder(drsi, signalline)
//Signals
golong = (buycond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : buycond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
goshort = (sellcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : sellcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endlong = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endshort = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
plotshape(golong and islong ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.small, title='Buy')
plotshape(goshort and isshort ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.small, title='Sell')
plotshape(showendlabels and endlong and islong ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Long')
plotshape(showendlabels and endshort and isshort ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Short')
alertcondition(golong, title='Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Long Signal')
alertcondition(goshort, title='Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Short Signal')
alertcondition(endlong, title='Exit Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Long')
alertcondition(endshort, title='Exit Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Short')
strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, when=golong and islong)
strategy.entry('short', strategy.short, when=goshort and isshort)
strategy.close('long', when=endlong and islong)
strategy.close('short', when=endshort and isshort)
- Multi-Period RSI Momentum and Triple EMA Trend Following Composite Strategy
- Dual EMA-RSI Divergence Strategy: A Trend Capture System Based on Exponential Moving Average and Relative Strength
- Low finder
- RSI and Dual EMA Crossover Signal Quantitative Strategy
- Dual EMA RSI Momentum Trend Reversal Trading System - A Momentum Breakthrough Strategy Based on EMA and RSI Crossover
- EMA, RSI, Volume-Price Trend, Engulfing Pattern
- EMA Bullish Crossover Strategy
- Dual Exponential Moving Average and Relative Strength Index Crossover Strategy
- Dynamic Moving Average Trend Following with RSI Confirmation Trading Strategy
- Dynamic Multi-Period Quantitative Trading Strategy Combining RSI and EMA
- Multi-Indicator Trend Following Strategy with Profit Optimization
- Fractal Breakout Momentum Trading Strategy with Take Profit Optimization
- Adaptive Mean-Reversion Trading Strategy Based on Chande Momentum Oscillator
- MACD-Supertrend Dual Confirmation Trend Following Trading Strategy
- Multi-Period SuperTrend Dynamic Trading Strategy
- Multi-Timeframe EMA with Fibonacci Retracement and Pivot Points Trading Strategy
- Multi-Timeframe Dynamic Stop-Loss EMA-Squeeze Trading Strategy
- MACD and Linear Regression Dual Signal Intelligent Trading Strategy
- Multi-EMA Trend Following Trading Strategy
- Multi-Timeframe Smoothed Heikin Ashi Trend Following Quantitative Trading System
- Daily Range Breakout Single-Direction Trading Strategy
- SMA-RSI-MACD Multi-Indicator Dynamic Limit Order Trading Strategy
- EMA/SMA Trend Following with Swing Trading Strategy Combined Volume Filter and Percentage Take-Profit/Stop-Loss System
- VWAP Standard Deviation Mean Reversion Trading Strategy
- Dynamic Price Zone Breakout Trading Strategy Based on Support and Resistance Quantitative System
- Multi-Indicator Trend Momentum Crossover Quantitative Strategy
- Advanced Dynamic Trailing Stop with Risk-Reward Targeting Strategy
- Advanced Long-Only Dynamic Trendline Breakout Strategy
- Multi-Level Intelligent Dynamic Trailing Stop Strategy Based on Bollinger Bands and ATR
- Dynamic Dual EMA Crossover Strategy with Adaptive Profit/Loss Control