Chiến lược này là một hệ thống giao dịch định lượng dựa trên dao động động RSI. Bằng cách thực hiện phân tích chuỗi thời gian và hợp nhất đa phương thức của chỉ số RSI, tính toán tỷ lệ thay đổi của RSI để nắm bắt động lực thị trường. Chiến lược sử dụng các phương pháp toán học cao cấp như phân tích QR để xử lý tín hiệu và kết hợp với hệ thống thống nhất để đưa ra quyết định giao dịch.
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Trung tâm của chiến lược là dao động Delta-RSI, được thực hiện thông qua các bước sau:
- Đầu tiên, tính toán chỉ số RSI truyền thống như một dữ liệu cơ bản.
- RSI được xử lý trơn tru, giảm tiếng ồn bằng cách sử dụng sự phù hợp đa dạng
- Tính biến thời gian của RSI được lấy từ Delta-RSI, phản ánh tốc độ thay đổi của RSI
- So sánh Delta-RSI với đường trung bình di chuyển của nó để tạo ra tín hiệu giao dịch
- Đánh giá và lọc chất lượng phù hợp bằng cách sử dụng sai sót gốc đồng phương ((RMSE)
Các tín hiệu giao dịch có thể được tạo ra theo ba cách:
- Đi ngang 0: Delta-RSI tăng khi chuyển từ giá trị âm, giảm khi chuyển từ giá trị dương
- Giao lộ tín hiệu: Delta-RSI tăng/giảm khi vượt qua đường trung bình di chuyển của nó
- Thay đổi hướng: Delta-RSI làm nhiều khi vùng giá âm bắt đầu tăng, làm trống khi vùng giá dương bắt đầu giảm
Lợi thế chiến lược
- Cơ sở toán học vững chắc: sử dụng phương pháp toán học cao cấp như phân giải QR để xử lý tín hiệu, cơ sở lý thuyết đáng tin cậy
- Tín hiệu mượt mà: Kết hợp đa dạng có thể lọc hiệu quả tiếng ồn thị trường, cải thiện chất lượng tín hiệu
- Tính linh hoạt: cung cấp nhiều phương thức tạo tín hiệu và tùy chọn tham số để thích ứng với các môi trường thị trường khác nhau
- Kiểm soát rủi ro: Bao gồm cơ chế lọc RMSE, có thể lọc các tín hiệu có độ tin cậy cao hơn
- Hiệu quả tính toán: Máy tính toán ma trận sử dụng các thuật toán tối ưu hóa, hoạt động hiệu quả hơn
Rủi ro chiến lược
- Nhận định tham số: Nhiều tham số quan trọng cần được điều chỉnh kỹ lưỡng, lựa chọn tham số không đúng cách có thể ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến hiệu suất của chiến lược
- Sự chậm trễ: xử lý tín hiệu trơn tru sẽ dẫn đến sự chậm trễ, có thể bỏ lỡ tốc độ nhanh
- Phá vỡ giả: có thể tạo ra tín hiệu giả trong thị trường biến động, làm tăng chi phí giao dịch
- Tính toán phức tạp: liên quan đến nhiều hoạt động ma trận, có thể có sự tắc nghẽn về hiệu suất trong giao dịch tần số cao
- Quá phù hợp: Chú ý tránh quá phù hợp với dữ liệu lịch sử khi tối ưu hóa tham số
Hướng tối ưu hóa chiến lược
- Các tham số tự điều chỉnh: có thể điều chỉnh chu kỳ RSI và số bậc phù hợp theo biến động của thị trường
- Nhiều chu kỳ thời gian: tín hiệu kết hợp nhiều chu kỳ thời gian được kiểm tra chéo
- Bộ lọc tỷ lệ dao động: thêm các chỉ số tỷ lệ dao động như ATR để lọc tín hiệu
- Phân loại thị trường: sử dụng các quy tắc tạo tín hiệu khác nhau cho các tình trạng thị trường khác nhau (trend / oscillation)
- Tối ưu hóa dừng lỗ: thêm các cơ chế dừng lỗ thông minh hơn, chẳng hạn như dừng động dựa trên điểm kháng cự hỗ trợ
Tóm tắt
Đây là một chiến lược giao dịch định lượng có cấu trúc đầy đủ, nền tảng lý thuyết vững chắc. Bằng cách phân tích tính năng động của RSI, kết hợp với phương pháp toán học hiện đại để xử lý tín hiệu, có thể nắm bắt được xu hướng thị trường tốt hơn. Mặc dù có một số vấn đề về độ nhạy cảm và tính toán phức tạp, nhưng chiến lược này có giá trị ứng dụng tốt thông qua lựa chọn và tối ưu hóa tham số hợp lý.
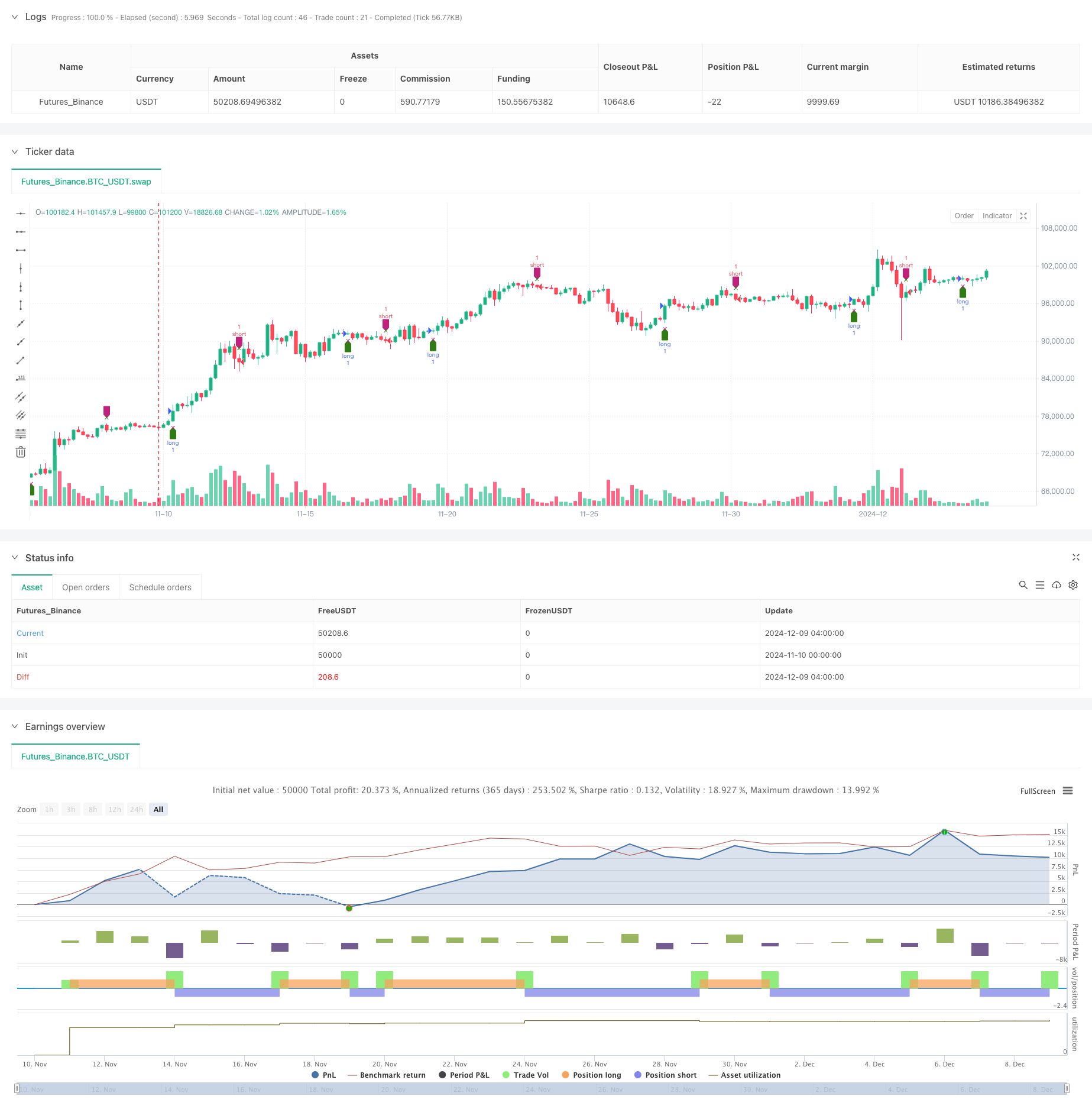
/*backtest
start: 2024-11-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-12-09 08:00:00
period: 4h
basePeriod: 4h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy
//
// A strategy that uses Delta-RSI Oscillator (© tbiktag) as a stand-alone indicator:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// Delta-RSI is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI, plotted as a histogram
// and serving as a momentum indicator.
//
// Input parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate the RSI.
// Signal Length: The length of a EMA of the D-RSI series that is used as a signal line.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending (bearish otherwise)
//
// Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option
// to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
//
//@version=5
strategy(title='Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy-QuangVersion', shorttitle='D-RSI-Q', overlay=true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A, _i + _nrows * _j)
matrix_set(_A, _value, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A, _i + _nrows * _j, _value)
transpose(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A, i, j, _nrows), j, i, _ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A, _B, _nrowsA, _ncolumnsA, _ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA * _ncolumnsB, 0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC = 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB - 1 by 1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA - 1 by 1
elementC += matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrowsA) * matrix_get(_B, k, j, _nrowsB)
elementC
matrix_set(_C, elementC, i, j, _nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X, _n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n - 1 by 1
_norm += math.pow(array.get(_X, i), 2)
_norm
math.sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, 0, _nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R, _r, 0, 0, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, 0, _nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrows))
for j = 0 to k - 1 by 1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows) * array.get(_a, i)
_r
matrix_set(_R, _r, j, k, _ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_aux := array.get(_a, i) - _r * matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows)
array.set(_a, i, _aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
matrix_set(_R, _r, k, k, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, k, _nrows)
[_Q, _R]
pinv(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q, _R] = qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q, _nrows, _ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, 0, 0, _ncolumns), 0, 0, _ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to j - 1 by 1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Rinv, i, k, _ncolumns) * matrix_get(_R, k, j, _ncolumns)
_r
matrix_set(_Rinv, _r, i, j, _ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Rinv, -matrix_get(_Rinv, k, j, _ncolumns) / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), k, j, _ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), j, j, _ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv, _QT, _ncolumns, _ncolumns, _nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
_nrmse
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N - 1 by 1
_mse += math.pow(array.get(_x, i) - array.get(_xhat, i), 2) / _N
_mse
_xmean = array.sum(_x) / _N
_nrmse := math.sqrt(_mse) / _xmean
_nrmse
_nrmse
diff(_src, _window, _degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree], with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window * (_degree + 1), 0)
for i = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _degree by 1
matrix_set(_J, math.pow(i, j), i, j, _window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window, na)
for j = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
array.set(_Y_raw, j, _src[_window - 1 - j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J, _window, _degree + 1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C, _Y_raw, _degree + 1, _window, 1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree by 1
_diff += i * array.get(_a_coef, i) * math.pow(_window - 1, i - 1)
_diff
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J, _a_coef, _window, _degree + 1, 1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw, _Y_hat)
[_diff, _nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input.int(title='Polynomial Order', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=2, minval=1)
rsi_l = input.int(title='RSI Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=21, minval=1, tooltip='The period length of RSI that is used as input.')
window = input.int(title='Length ( > Order)', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=21, minval=2)
signalLength = input.int(title='Signal Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=9, tooltip='The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.')
islong = input.bool(title='Buy', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
isshort = input.bool(title='Sell', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
showendlabels = input.bool(title='Exit', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
buycond = input.string(title='Buy', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
sellcond = input.string(title='Sell', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
endcond = input.string(title='Exit', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
usenrmse = input.bool(title='', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=false)
rmse_thrs = input.float(title='RSI fitting Error Threshold, %', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=10, minval=0.0) / 100
src = ta.rsi(close, rsi_l)
[drsi, nrmse] = diff(src, window, degree)
signalline = ta.ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions and filters
filter_rmse = usenrmse ? nrmse < rmse_thrs : true
dirchangeup = drsi > drsi[1] and drsi[1] < drsi[2] and drsi[1] < 0.0
dirchangedw = drsi < drsi[1] and drsi[1] > drsi[2] and drsi[1] > 0.0
crossup = ta.crossover(drsi, 0.0)
crossdw = ta.crossunder(drsi, 0.0)
crosssignalup = ta.crossover(drsi, signalline)
crosssignaldw = ta.crossunder(drsi, signalline)
//Signals
golong = (buycond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : buycond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
goshort = (sellcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : sellcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endlong = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endshort = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
plotshape(golong and islong ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.small, title='Buy')
plotshape(goshort and isshort ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.small, title='Sell')
plotshape(showendlabels and endlong and islong ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Long')
plotshape(showendlabels and endshort and isshort ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Short')
alertcondition(golong, title='Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Long Signal')
alertcondition(goshort, title='Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Short Signal')
alertcondition(endlong, title='Exit Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Long')
alertcondition(endshort, title='Exit Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Short')
strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, when=golong and islong)
strategy.entry('short', strategy.short, when=goshort and isshort)
strategy.close('long', when=endlong and islong)
strategy.close('short', when=endshort and isshort)