Système de suivi dynamique de tendance à plusieurs niveaux
Auteur:ChaoZhang est là., Date: 2024-07-29 17:19:43 Je vous en prie.Les étiquettes:ATR- Je vous en prie.Indice de résistance
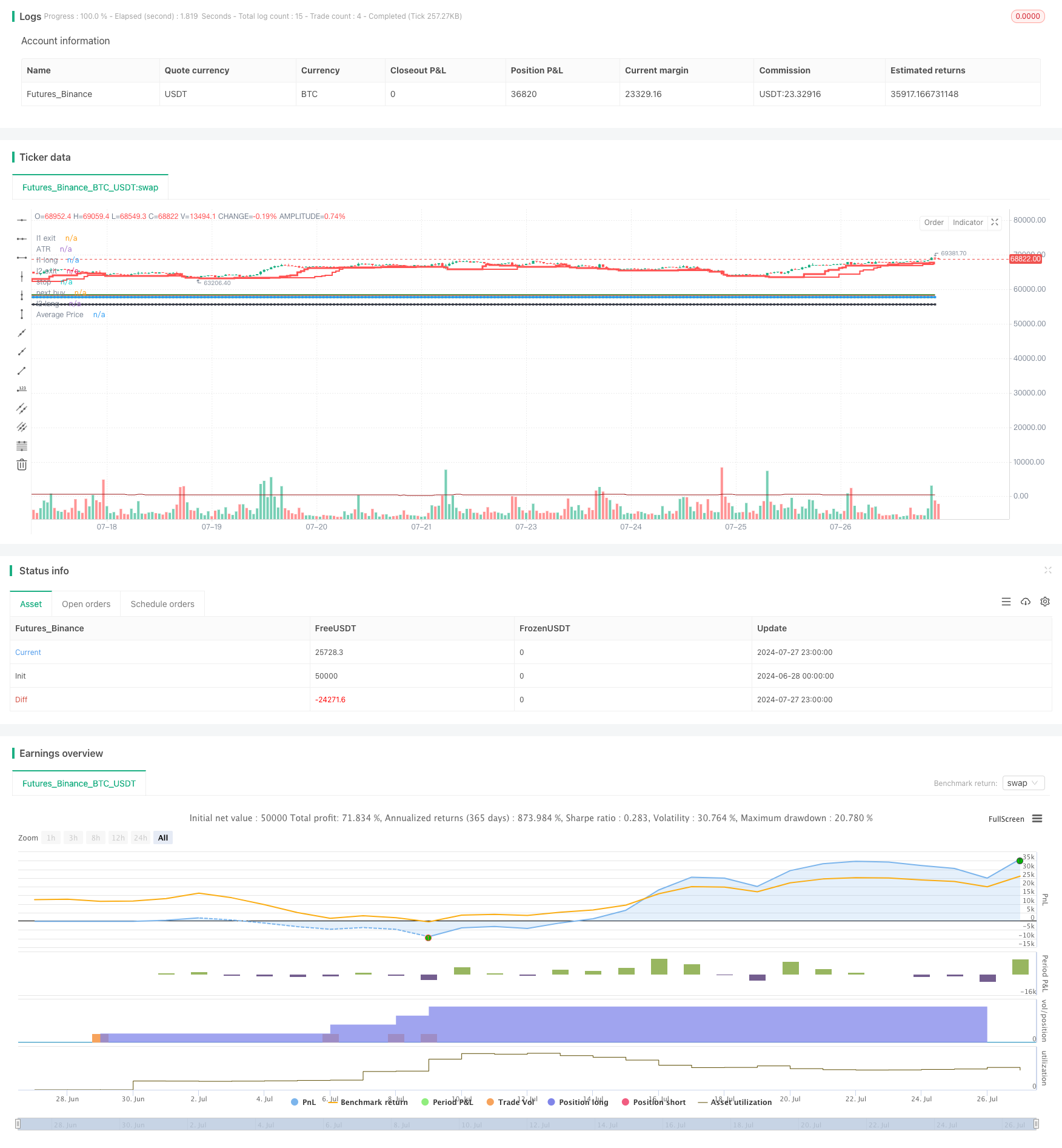
Résumé
Le système de suivi de tendance dynamique à plusieurs niveaux est une stratégie améliorée basée sur les règles de trading de la tortue. Cette stratégie utilise des signaux de tendance de plusieurs périodes de temps, combinés à un stop-loss dynamique et à la construction de positions pyramidales, pour capturer les tendances à moyen et long terme. Le système établit deux périodes de suivi de tendance (L1 et L2) pour capturer les tendances à différentes vitesses et utilise un indicateur ATR adaptatif pour ajuster dynamiquement les points d'entrée, de construction de position et de stop-loss. Cette conception à plusieurs niveaux permet à la stratégie de maintenir la stabilité dans différents environnements de marché tout en maximisant le profit potentiel grâce à la construction de positions pyramidales.
Principes de stratégie
-
Identification des tendances: Deux périodes moyennes mobiles (L1 et L2) sont utilisées pour identifier les tendances à des vitesses différentes.
-
Signals d'entrée: Les signaux longs sont générés lorsque le prix dépasse le plus haut de L1 ou L2. Si le précédent commerce L1 était rentable, le signal L1 suivant est sauté jusqu'à ce qu'un signal L2 apparaisse.
-
Stop-Loss dynamique: un multiple de l'ATR (défaut 3x) est utilisé comme distance de stop-loss initiale, qui augmente progressivement au fur et à mesure que la position est maintenue.
-
Construction de positions pyramidales: pendant la continuation de la tendance, des positions supplémentaires sont ajoutées à chaque fois que le prix augmente de 0,5 ATR, jusqu'à un maximum de 5 fois.
-
Contrôle des risques: chaque transaction ne risque pas plus de 2% du capital du compte, ce qui est réalisé grâce à une dimensionnement dynamique des positions.
-
Mécanisme de sortie: les positions sont fermées lorsque le prix tombe en dessous du plus bas de 10 jours (L1) ou du plus bas de 20 jours (L2), ou lorsque le stop-loss de suivi est déclenché.
Les avantages de la stratégie
-
Capture des tendances à plusieurs niveaux: Les périodes L1 et L2 permettent de capturer les tendances à la fois rapides et à long terme, améliorant ainsi l'adaptabilité et la stabilité de la stratégie.
-
Gestion dynamique du risque: l'utilisation de l'ATR comme indicateur de volatilité permet un ajustement dynamique des points d'entrée, de stop-loss et de construction de position, en s'adaptant mieux aux changements du marché.
-
Construction de positions pyramidales: l'augmentation progressive des positions pendant la continuation de la tendance permet à la fois de contrôler le risque et de maximiser le potentiel de profit.
-
Réglage des paramètres flexible: plusieurs paramètres réglables permettent à la stratégie de s'adapter à différents marchés et styles de négociation.
-
Exécution automatisée: la stratégie peut être entièrement automatisée, réduisant l'intervention humaine et l'influence émotionnelle.
Risques stratégiques
-
Risque d'inversion de tendance: fonctionne bien sur les marchés à forte tendance, mais peut entraîner des pertes fréquentes sur les marchés à fourchette.
-
Les coûts de glissement et de transaction: la formation fréquente de positions et les mouvements de stop-loss peuvent entraîner des coûts de transaction élevés.
-
Risque d'optimisation excessive: de nombreux paramètres peuvent entraîner une suradaptation des données historiques.
-
Risque de gestion des capitaux: un capital initial plus faible peut ne pas permettre d'exécuter efficacement plusieurs constructions de positions.
-
Risque de liquidité du marché: dans les marchés moins liquides, il peut être difficile d'exécuter des transactions à des prix idéaux.
Directions d'optimisation de la stratégie
-
Incorporer le filtrage de l'environnement du marché: ajouter des indicateurs de force de tendance (par exemple, ADX) pour évaluer les conditions du marché et réduire la fréquence des transactions sur les marchés à fourchette.
-
Optimiser la stratégie de construction de position: envisager d'ajuster dynamiquement l'intervalle et le nombre de constructions de position en fonction de la force de la tendance, plutôt que de fixer 0,5 ATR et 5 fois.
-
Introduire un mécanisme de prise de bénéfices: dans les tendances à long terme, définissez une prise de bénéfices partielle pour verrouiller les gains, comme la fermeture de la moitié de la position lorsque vous atteignez un bénéfice ATR de 3 fois.
-
Analyse de la corrélation entre plusieurs instruments: lors de l'application d'un portefeuille, ajoutez une analyse de la corrélation entre les instruments pour optimiser le ratio risque/rendement global.
-
Ajouter un filtre de volatilité: interrompre la négociation ou ajuster les paramètres de risque pendant les périodes de volatilité extrême pour gérer les conditions anormales du marché.
-
Optimiser le mécanisme de sortie: envisager l'utilisation d'indicateurs de sortie plus flexibles tels que SAR parabolique ou sortie chandelier.
Résumé
Le système de suivi des tendances dynamiques à plusieurs niveaux est une stratégie complète combinant des règles de trading de tortue classiques avec des techniques quantitatives modernes. Grâce à l'identification des tendances à plusieurs niveaux, à la gestion dynamique des risques et à la construction de positions pyramidales, cette stratégie améliore la capacité de capture des tendances et le potentiel de profit tout en maintenant la robustesse. Bien qu'elle soit confrontée à des défis sur les marchés à plage, avec une optimisation appropriée des paramètres et un contrôle des risques, la stratégie a le potentiel de maintenir des performances stables dans différents environnements de marché. Les améliorations futures peuvent se concentrer sur l'introduction d'une évaluation de l'environnement du marché, l'optimisation des mécanismes de construction de position et de sortie pour améliorer la robustesse et la rentabilité de la stratégie.
/*backtest
start: 2024-06-28 00:00:00
end: 2024-07-28 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
// This is a strategy based on the famous turtle system.
// https://www.tradingblox.com/originalturtles/originalturtlerules.htm
//
// In a nutshell, it a trend trading system where you are buying on strength, selling on weakness.
// positions should be entered when the price crosses over the 20-day high (L1 high) or 55-day high (L2 high).
// positions should be exited when the prices crosses below the 10-day low (L1 low) or 20-day low (L2 low)
// you can add positions at every unit (measured by multiple of n, where n=1 ATR)
// stops should be placed at 2*n below every position entered, when the stop is hit exit your entire position.
// positions should be entered everytime price crosses over L1 or L2, with one exception:
// if the last trade was an L1 trade and it was a winning trade, skip the next trade unless the price crosses
// over L2, if that is the case, you should take it.
// L1 and L2 levels are also configurable for high and lows.
// N multiple for stops and pyramid are also configurable
// To change this from a strategy to a study:
// 1) uncomment the next line and comment out the strategy line.
// 2) at the end of the file comment out the last 2 lines
// study(title="Turtle Study", overlay=true)
strategy(title='kTF-VNI', overlay=true, initial_capital=100000000, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.0, pyramiding=100, process_orders_on_close=true, calc_on_every_tick=true)
stopInput = input.float(3, 'Stop N', step=.05)
riskPercent = input.float(.01, 'Risk % of capital', step=.005)
pyramidInput = input.float(0.5, 'Pyramid N', step=.05)
maxUnits = input.int(5, 'Max Pyramid Units', step=1)
atrPeriod = input(20, 'ATR period')
l1LongInput = 10
l2LongInput = 20
l1LongExitInput = 20
l2LongExitInput = 40
l1LongInput := input.int(20, 'L1 Long', minval=2)
l2LongInput := input.int(60, 'L2 Long', minval=2)
l1LongExitInput := input.int(10, 'L1 Long Exit', minval=2)
l2LongExitInput := input.int(20, 'L2 Long Exit', minval=2)
FromYear = input.int(1970, 'From Year', minval=1900)
FromMonth = input.int(1, 'From Month', minval=1, maxval=12)
FromDay = input.int(1, 'From Day', minval=1, maxval=31)
ToYear = input.int(9999, 'To Year', minval=1900)
ToMonth = input.int(1, 'To Month', minval=1, maxval=12)
ToDay = input.int(1, 'To Day', minval=1, maxval=31)
FromDate = timestamp(FromYear, FromMonth, FromDay, 00, 00)
ToDate = timestamp(ToYear, ToMonth, ToDay, 23, 59)
TradeDateIsAllowed() =>
time >= FromDate and time <= ToDate
l1Long = ta.highest(l1LongInput)
l1LongExit = ta.lowest(l1LongExitInput)
l2Long = ta.highest(l2LongInput)
l2LongExit = ta.lowest(l2LongExitInput)
bool win = false // tracks if last trade was winning trade of losing trade.
float buyPrice = 0.0 // tracks the buy price of the last long position.
float nextBuyPrice = 0.0 // tracks the next buy price
float stopPrice = na // tracks the stop price
int totalBuys = 0 // tracks the total # of pyramid buys
bool inBuy = false // tracks if we are in a long position or not.
float l1LongPlot = ta.highest(l1LongInput) // tracks the L1 price to display
float l2LongPlot = ta.highest(l2LongInput) // tracks the L2 price to display
float n = ta.atr(atrPeriod) // tracks the n used to calculate stops and pyramid buys
string mode = 'L1' // tracks whether we are in a L1 position or L2 position.
bool fake = na // tracks if this is a fake trade, see comments below.
string longLevel = na // tracks where long positions, stops, pyramid buys occur.
float capitalLeft = strategy.initial_capital
var shares = 0
float fakeBuyPrice = 0.0
// by default use the last value from the previous bar.
buyPrice := buyPrice[1]
totalBuys := totalBuys[1]
nextBuyPrice := nextBuyPrice[1]
stopPrice := stopPrice[1]
win := win[1]
capitalLeft := capitalLeft[1]
inBuy := inBuy[1]
n := ta.atr(atrPeriod)
fakeBuyPrice := fakeBuyPrice[1]
// State to track if we are in a long positon or not.
if not inBuy[1] and (high > l1Long[1] or high > l2Long[1])
inBuy := true
inBuy
else
inBuy := inBuy[1] and low < stopPrice[1] ? false : inBuy
inBuy := inBuy[1] and mode[1] == 'L1' and low < l1LongExit[1] ? false : inBuy
inBuy := inBuy[1] and mode[1] == 'L2' and low < l2LongExit[1] ? false : inBuy
inBuy
// State to track if we are ia a fake trade. If the last trade was a winning, we need to skip the next trade.
// We still track it though as a fake trade (not counted against us). as the outcome determines if we can
// can take the next trade.
if not inBuy[1] and high > l1Long[1] and win[1]
fake := true
fakeBuyPrice := close
fakeBuyPrice
else
fake := fake[1]
fake
if fake[1] and inBuy[1] and not inBuy
fake := false
win := close >= fakeBuyPrice
win
fake := high > l2Long[1] ? false : fake
// Series representing the l1 and l2 levels. If we break out above the l1 or l2 level, we want the
// line to stay at the breakout level, not follow it up.
l1LongPlot := not inBuy[1] or inBuy[1] and mode == 'L1' and fake[1] ? l1Long[1] : l1LongPlot[1]
l2LongPlot := not inBuy[1] or inBuy[1] and mode == 'L1' and fake[1] ? l2Long[1] : l2LongPlot[1]
// Variable in the series is only set when it happens. Possible values is L1, L2, SR
// (stopped out with a loss), SG (exited with a gain), and 'P' for pyramid buy.
longLevel := not inBuy[1] and high > l1Long[1] ? 'L1' : na
longLevel := (not inBuy[1] or inBuy[1] and fake[1]) and high > l2Long[1] ? 'L2' : longLevel
// Either 'L1' or 'L2' depending on what breakout level we are in.
mode := longLevel == na ? mode[1] : longLevel
// Variables to track calculating nextBuyPrice for pyramiding.
if longLevel == 'L1' or longLevel == 'L2'
buyPrice := close
totalBuys := 1
stopPrice := close - stopInput * n
nextBuyPrice := close + pyramidInput * n
nextBuyPrice
// Marks if we hit our next buy price, if so mark it with a 'P'
longLevel := longLevel == na and inBuy[1] and high > nextBuyPrice and TradeDateIsAllowed() and totalBuys < maxUnits ? 'P' : longLevel
if longLevel == 'P'
buyPrice := close
totalBuys := totalBuys[1] + 1
stopPrice := close - stopInput * n
nextBuyPrice := close + pyramidInput * n
nextBuyPrice
// Tracks stops and exits, marking them with SG or SR
longLevel := longLevel == na and inBuy[1] and low < stopPrice and close >= strategy.position_avg_price ? 'SG' : longLevel
longLevel := longLevel == na and inBuy[1] and low < stopPrice and close < strategy.position_avg_price ? 'SR' : longLevel
longLevel := longLevel == na and mode[1] == 'L1' and inBuy[1] and low < l1LongExit[1] and close >= strategy.position_avg_price ? 'SG' : longLevel
longLevel := longLevel == na and mode[1] == 'L2' and inBuy[1] and low < l2LongExit[1] and close >= strategy.position_avg_price ? 'SG' : longLevel
longLevel := longLevel == na and mode[1] == 'L1' and inBuy[1] and low < l1LongExit[1] and close < strategy.position_avg_price ? 'SR' : longLevel
longLevel := longLevel == na and mode[1] == 'L2' and inBuy[1] and low < l2LongExit[1] and close < strategy.position_avg_price ? 'SR' : longLevel
// Tracks if the trade was a win or loss.
win := longLevel == 'SG' ? true : win
win := longLevel == 'SR' ? false : win
// Variables used to tell strategy when to enter/exit trade.
//plotarrow(fake ? 1 : 0, colordown=color.red, colorup=color.purple, transp=40) // down arrow for winning trade
enterLong = (longLevel == 'L1' or longLevel == 'L2' or longLevel == 'P') and not fake and TradeDateIsAllowed()
exitLong = (longLevel == 'SG' or longLevel == 'SR') and not fake and TradeDateIsAllowed()
p1 = plot(l1LongPlot, title='l1 long', linewidth=3, style=plot.style_stepline, color=color.new(color.green, 0))
p2 = plot(l1LongExit[1], title='l1 exit', linewidth=3, style=plot.style_stepline, color=color.new(color.red, 0))
p3 = plot(l2LongPlot, title='l2 long', linewidth=2, style=plot.style_stepline, color=color.new(color.green, 0))
p4 = plot(l2LongExit[1], title='l2 exit', linewidth=2, style=plot.style_stepline, color=color.new(color.red, 0))
color1 = color.new(color.black, 0)
color2 = color.new(color.black, 100)
col = inBuy ? color1 : color2
p5 = plot(stopPrice, title='stop', linewidth=2, style=plot.style_circles, join=true, color=color.new(color.black, 0))
p6 = plot(nextBuyPrice, title='next buy', linewidth=2, style=plot.style_circles, join=true, color=color.new(color.blue, 0))
fill(p1, p3, color=color.new(color.green, 90))
fill(p2, p4, color=color.new(color.red, 90))
risk = (strategy.initial_capital + strategy.netprofit) * riskPercent
shares := math.floor(risk / (stopInput * n))
capitalLeft := strategy.initial_capital + strategy.netprofit - strategy.position_size * strategy.position_avg_price
if shares * close > capitalLeft
shares := math.max(0, math.floor(capitalLeft / close))
shares
shares := math.max(0, shares)
plotshape(longLevel == 'L1' and not fake and strategy.position_size == 0 ? true : false, color=color.new(color.green, 40), style=shape.triangleup, text='L1 ') // up arrow for entering L1 trade
plotshape(not fake[1] and fake and longLevel == 'L1' and strategy.position_size == 0 ? true : false, color=color.new(color.gray, 40), style=shape.triangleup, text='L1') // up arrow for entering L1 trade
plotshape(longLevel == 'L2' and strategy.position_size == 0 ? true : false, color=color.new(color.green, 40), style=shape.triangleup, text='L2') // up arrow for entering L2 trade
plotshape((mode == 'L1' or mode == 'L2') and shares > 0 and enterLong and strategy.position_size > 0 ? true : false, color=color.new(color.green, 40), style=shape.triangleup, text='P')
plotarrow(strategy.position_size == 0 and longLevel == 'L1' and enterLong ? 1 : 0, colordown=color.new(color.black, 40), colorup=color.new(color.green, 40)) // up arrow for entering L1 trade
plotarrow(strategy.position_size == 0 and longLevel == 'L2' and enterLong ? 1 : 0, colordown=color.new(color.black, 40), colorup=color.new(color.green, 40)) // up arrow for entering L2 trade
plotarrow(strategy.position_size > 0 and longLevel == 'SR' and exitLong ? -1 : 0, colordown=color.new(color.red, 40), colorup=color.new(color.purple, 40)) // down arrow for losing trade
plotarrow(strategy.position_size > 0 and longLevel == 'SG' and exitLong ? -1 : 0, colordown=color.new(color.green, 40), colorup=color.new(color.purple, 40)) // down arrow for winning trade
plotshape(longLevel == na and inBuy[1] and not inBuy, color=color.new(color.gray, 40), style=shape.triangleup, text='Exit') // up arrow for entering L1 trade
plot(ta.atr(atrPeriod), title='ATR', color=color.new(#991515, 0))
plot(strategy.position_avg_price, title='Average Price', color=color.new(#991515, 0))
alertcondition(low < stopPrice, title='crosses under stop price', message='price crossed under stop price')
alertcondition(high > l1Long, title='crosses over L1 price', message='price crossed over L1 price')
alertcondition(high > l2Long, title='crosses over L2 price', message='price crossed over L2 price')
alertcondition(low < l1LongExit, title='crosses under L1 exit price', message='price crossed under L1 exit price')
alertcondition(low < l2LongExit, title='crosses under L2 exit price', message='price crossed under L2 exit price')
strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, qty=shares, comment='long', when=enterLong)
strategy.close('long', when=exitLong)
// simulate_amount = 100000
// simulate_risk = simulate_amount*0.005
// simulate_shares = floor(simulate_risk/(n*stopInput))
// plot(simulate_shares, "Shares", color=#991515, transp=0)
// if (enterLong)
// label.new(bar_index, high, text=tostring(simulate), style=label.style_none)
- Stratégie de redressement du mardi (filtre du week-end)
- RSI-ATR Momentum Volatilité Stratégie de négociation combinée
- Stratégie de pyramide intelligente à indicateurs multiples
- Stratégie de rupture améliorée avec cibles et optimisation de la perte d'arrêt
- Stratégie de négociation AlphaTradingBot
- Tendance multi-indicateurs à la suite de la stratégie
- L'éclatement de la bougie du matin et la stratégie d'inversion
- Stratégie de négociation basée sur la tendance avec filtrage de l'élan
- Système de négociation adaptatif stop-loss optimisé par l'IA avec intégration d'indicateurs techniques multiples
- Stratégie de négociation équilibrée basée sur le temps et sur la rotation à court terme
- Stratégie de croisement des moyennes mobiles exponentielles sur plusieurs périodes
- Stratégie de croisement dynamique de canaux à plusieurs périodes
- Stratégie globale de capture des tendances à court terme liées à l'écart de prix
- Système d'analyse de l'oscillation et du moment multi-stochastique
- Stratégie de négociation des moyennes mobiles sur plusieurs délais et des indicateurs de tendance RSI
- Tendance croisée moyenne mobile à plusieurs périodes suivant la stratégie
- Stratégie de négociation à forte dynamique à faible dynamique de trois semaines
- Stratégie de croisement de moyenne mobile adaptative
- Stratégie d'indicateur technique, stratégie de gestion des risques, tendance d'adaptation à la suite de la stratégie
- Stratégie d'optimisation de l'élan des bandes de Bollinger
- Stratégie de négociation avancée de réversion moyenne: Système de rupture dynamique de la fourchette basé sur l'écart type
- Crossover de l' EMA avec la stratégie de double entrée des bandes de Bollinger: un système de négociation quantitatif combinant suivi de tendance et rupture de volatilité
- Stratégie de négociation adaptative en fonction de la tendance: 200 EMA Breakout avec système de gestion dynamique des risques
- Stratégie croisée de dynamique du marché sur plusieurs délais
- Tendance multi-indicateurs à la suite de la stratégie
- L'échange de titres de titres est effectué en fonction de l'évolution de la valeur de l'échange.
- Stratégie de négociation de divergence multi-indicateur avec prise de profit et stop-loss adaptatif
- Stratégie de négociation de la dynamique de la zone de rupture
- Stratégie de négociation de précision et système de gestion des risques basé sur l'indicateur SuperTrend
- EMA, RSI, Tendance du volume des prix, modèle d'engouement