Estratégia de negociação de poder de "bull bear" com sistema dinâmico de captação de lucros baseado em percentual de volume
Autora:ChaoZhang, Data: 2025-01-06 16:16:04Tags:PIBEMAATRTP
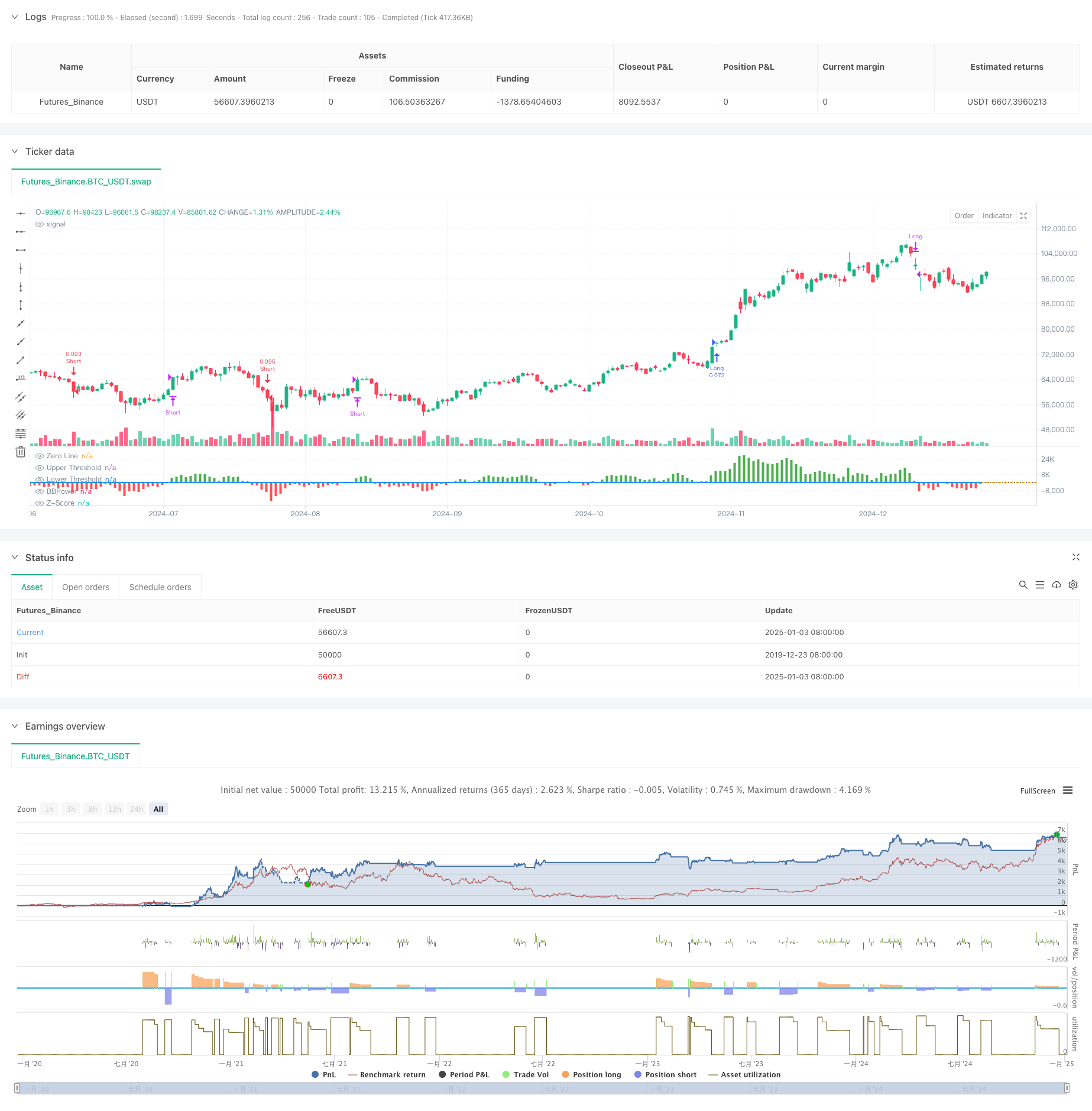
Resumo
Esta estratégia combina o indicador Bull Bear Power (BBP) com um sistema de take-profit dinâmico de vários níveis baseado em percentiles de volume. Ele cria um sistema de negociação adaptável e controlado pelo risco através de análise multidimensional de dados de preço, volume e momento.
Princípios de estratégia
Os cálculos essenciais incluem vários componentes-chave:
- Indicador BBP: mede o equilíbrio das forças de mercado somando a diferença entre o preço elevado e a EMA (poder de touro) e o preço baixo e a EMA (poder de baixa).
- Normalização do Z-Score: Normaliza os valores do BBP para avaliar os níveis de desvio da força de mercado.
- Análise de volume: Calcula o volume atual em relação à média móvel para avaliar a atividade do mercado.
- Análise percentil: Computa percentil históricos de preço e volume para a distribuição de probabilidade do estado do mercado.
- Dinâmico Take-Profit: Ajusta os níveis de take-profit com base na pontuação composta de ATR, percentil de volume e percentil de preço.
Vantagens da estratégia
- Análise multidimensional: fornece uma perspectiva abrangente do mercado através do ímpeto dos preços, volume e posicionamento do mercado.
- Alta adaptabilidade: adapta-se a diferentes ambientes de mercado através de um mecanismo dinâmico de lucro.
- Diversificação do risco: Implementa uma estratégia multi-nível de captação de lucros para a realização de lucros em diferentes níveis de preços.
- Avanço estatístico: obtém vantagem significativa através da análise do Z-Score e percentil.
- Extensibilidade: O quadro permite a adição fácil de novas dimensões de análise.
Riscos estratégicos
- Sensibilidade dos parâmetros: múltiplos parâmetros exigem otimização para diferentes ambientes de mercado.
- Dependência do ambiente de mercado: Pode apresentar um desempenho inferior durante períodos voláteis ou transições de tendência.
- Deslizamento de execução: as ordens de take-profit de vários níveis podem sofrer deslizamento de execução.
- Complexidade computacional: o cálculo em tempo real de múltiplos indicadores pode causar carga no sistema.
- Risco de sinal falso: pode gerar sinais de negociação incorretos em mercados variados.
Orientações de otimização
- Adaptação de parâmetros: introduzir métodos de aprendizagem de máquina para otimização automática de parâmetros.
- Previsão do mercado: adicionar o módulo de classificação do ambiente de mercado para a identificação precoce de condições adversas.
- Optimização do stop-loss: Implementar um mecanismo dinâmico de stop-loss para melhorar o controlo do risco.
- Filtragem de sinal: adicionar filtros de força de tendência para reduzir os falsos sinais.
- Gestão de posições: Otimização do algoritmo de alocação de posições para melhorar a eficiência do capital.
Resumo
Esta estratégia combina o indicador tradicional do BBP com métodos de análise quantitativa moderna para criar um sistema de negociação com base teórica sólida e forte praticidade. Atinge um bom equilíbrio entre retornos e risco através de mecanismos de lucro e ajuste dinâmico de vários níveis. Embora a otimização de parâmetros apresente alguns desafios, a extensão do quadro de estratégia fornece amplo espaço para melhorias futuras. Na aplicação prática, os comerciantes devem fazer ajustes específicos com base nas características do mercado e nas preferências individuais de risco.
/*backtest
start: 2019-12-23 08:00:00
end: 2025-01-04 08:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This Pine Script™ code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © PresentTrading
// The BBP Strategy with Volume-Percentile TP by PresentTrading emerges as a sophisticated approach that integrates multiple analytical layers to enhance trading precision and profitability.
// Unlike traditional strategies that rely solely on price movements or volume indicators, this strategy synergizes Bollinger Bands Power (BBP) with volume percentile analysis to determine optimal entry and exit points. Additionally, it employs a dynamic take-profit mechanism based on ATR (Average True Range) multipliers adjusted by volume and percentile factors, ensuring adaptability to varying market conditions.
// This multi-faceted approach not only enhances signal accuracy but also optimizes risk management, setting it apart from conventional trading methodologies.
//@version=5
strategy("BBP Strategy with Volume-Percentile TP - Strategy [presentTrading] ", overlay=false, precision=3, commission_value= 0.1, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, slippage= 1, currency=currency.USD, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 10, initial_capital=10000)
// ————————
// Bull Bear Power Strategy Settings
// ————————
lengthInput = input.int(21, "EMA Length")
zLength = input.int(252, "Z-Score Length")
zThreshold = input.float(1.618, "Z-Score Threshold")
// ————————
// Take Profit Settings
// ————————
tp_group = "Take Profit Settings"
// Enable/disable take profit function
useTP = input.bool(true, "Use Take Profit", group=tp_group)
// === ATR Base Settings ===
// ATR calculation period for determining base price movement range
baseAtrLength = input.int(20, "ATR Period", minval=1, group=tp_group, tooltip="ATR period for calculating base price movement range. Shorter periods are more sensitive to recent volatility")
// === Take Profit Multiplier Settings ===
// First take profit ATR multiplier, usually the most conservative target
atrMult1 = input.float(1.618, "TP1 ATR Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=tp_group, tooltip="First take profit level ATR multiplier, recommended 1.5-2.0")
// Second take profit ATR multiplier, medium profit target
atrMult2 = input.float(2.382, "TP2 ATR Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=tp_group, tooltip="Second take profit level ATR multiplier, recommended 2.5-3.0")
// Third take profit ATR multiplier, most aggressive target
atrMult3 = input.float(3.618, "TP3 ATR Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=tp_group, tooltip="Third take profit level ATR multiplier, recommended 4.0-5.0")
// === Position Size Allocation ===
// First take profit position size, usually larger for securing basic profits
tp1_size = input.float(13, "TP1 Position %", minval=1, maxval=100, group=tp_group, tooltip="Position size percentage for first take profit, recommended 30-40%")
// Second take profit position size, medium allocation
tp2_size = input.float(13, "TP2 Position %", minval=1, maxval=100, group=tp_group, tooltip="Position size percentage for second take profit, recommended 30-40%")
// Third take profit position size, usually smaller for catching larger moves
tp3_size = input.float(13, "TP3 Position %", minval=1, maxval=100, group=tp_group, tooltip="Position size percentage for third take profit, recommended 20-30%")
// ————————
// Volume Analysis Settings
// ————————
vol_group = "Volume Analysis Settings"
// Volume MA period for determining relative volume levels
vol_period = input.int(100, "Volume MA Period", minval=1, group=vol_group, tooltip="Period for calculating volume moving average, recommended 20-30")
// === Volume Level Thresholds ===
// High volume threshold relative to MA
vol_high = input.float(2.0, "High Volume Multiplier", minval=1.0, step=0.1, group=vol_group, tooltip="High volume threshold multiplier, typically 2x MA or above")
// Medium volume threshold
vol_med = input.float(1.5, "Medium Volume Multiplier", minval=1.0, step=0.1, group=vol_group, tooltip="Medium volume threshold multiplier, typically around 1.5x MA")
// Low volume threshold
vol_low = input.float(1.0, "Low Volume Multiplier", minval=0.5, step=0.1, group=vol_group, tooltip="Low volume threshold multiplier, typically around 1x MA")
// === Volume Adjustment Factors ===
// High volume adjustment factor, usually extends take profit targets
vol_high_mult = input.float(1.5, "High Volume Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=vol_group, tooltip="Take profit adjustment factor for high volume")
// Medium volume adjustment factor
vol_med_mult = input.float(1.3, "Medium Volume Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=vol_group, tooltip="Take profit adjustment factor for medium volume")
// Low volume adjustment factor
vol_low_mult = input.float(1.0, "Low Volume Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=vol_group, tooltip="Take profit adjustment factor for low volume")
// ————————
// Percentile Analysis Settings
// ————————
perc_group = "Percentile Analysis Settings"
// Percentile calculation period for evaluating price position
perc_period = input.int(100, "Percentile Period", minval=20, group=perc_group, tooltip="Historical period for percentile calculations, recommended 100-200")
// === Percentile Thresholds ===
// High percentile threshold, typically indicates relative high levels
perc_high = input.float(90, "High Percentile", minval=50, maxval=100, group=perc_group, tooltip="High level percentile threshold, typically above 90")
// Medium percentile threshold
perc_med = input.float(80, "Medium Percentile", minval=50, maxval=100, group=perc_group, tooltip="Medium level percentile threshold, typically around 80")
// Low percentile threshold
perc_low = input.float(70, "Low Percentile", minval=0, maxval=100, group=perc_group, tooltip="Low level percentile threshold, typically around 70")
// === Percentile Adjustment Factors ===
// High percentile adjustment factor
perc_high_mult = input.float(1.5, "High Percentile Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=perc_group, tooltip="Take profit adjustment factor for high percentile levels")
// Medium percentile adjustment factor
perc_med_mult = input.float(1.3, "Medium Percentile Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=perc_group, tooltip="Take profit adjustment factor for medium percentile levels")
// Low percentile adjustment factor
perc_low_mult = input.float(1.0, "Low Percentile Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=perc_group, tooltip="Take profit adjustment factor for low percentile levels")
// ————————
// Core Bull Bear Power Calculations
// ————————
emaClose = ta.ema(close, lengthInput)
bullPower = high - emaClose
bearPower = low - emaClose
bbp = bullPower + bearPower
bbp_mean = ta.sma(bbp, zLength)
bbp_std = ta.stdev(bbp, zLength)
zscore = (bbp - bbp_mean) / bbp_std
// ————————
// Volume & Percentile Analysis
// ————————
// 成交量分析
vol_sma = ta.sma(volume, vol_period)
vol_mult = volume / vol_sma
// 百分位數計算
calcPercentile(src) =>
var values = array.new_float(0)
array.unshift(values, src)
if array.size(values) > perc_period
array.pop(values)
array.size(values) > 0 ? array.percentrank(values, array.size(values)-1) * 100 : 50
price_perc = calcPercentile(close)
vol_perc = calcPercentile(volume)
// 止盈動態調整系數計算
getTpFactor() =>
vol_score = vol_mult > vol_high ? vol_high_mult : vol_mult > vol_med ? vol_med_mult : vol_mult > vol_low ? vol_low_mult : 0.8
price_score = price_perc > perc_high ? perc_high_mult :price_perc > perc_med ? perc_med_mult :price_perc > perc_low ? perc_low_mult : 0.8
math.avg(vol_score, price_score)
// ————————
// Entry/Exit Logic
// ————————
longCondition = ta.crossover(zscore, zThreshold)
shortCondition = ta.crossunder(zscore, -zThreshold)
exitLongCondition = ta.crossunder(zscore, 0)
exitShortCondition = ta.crossover(zscore, 0)
if (barstate.isconfirmed)
if longCondition
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if shortCondition
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
if exitLongCondition
strategy.close("Long")
if exitShortCondition
strategy.close("Short")
// ————————
// Take Profit Execution
// ————————
if useTP and strategy.position_size != 0
base_move = ta.atr(baseAtrLength)
tp_factor = getTpFactor()
is_long = strategy.position_size > 0
entry_price = strategy.position_avg_price
if is_long
tp1_price = entry_price + (base_move * atrMult1 * tp_factor)
tp2_price = entry_price + (base_move * atrMult2 * tp_factor)
tp3_price = entry_price + (base_move * atrMult3 * tp_factor)
strategy.exit("TP1", "Long", qty_percent=tp1_size, limit=tp1_price)
strategy.exit("TP2", "Long", qty_percent=tp2_size, limit=tp2_price)
strategy.exit("TP3", "Long", qty_percent=tp3_size, limit=tp3_price)
else
tp1_price = entry_price - (base_move * atrMult1 * tp_factor)
tp2_price = entry_price - (base_move * atrMult2 * tp_factor)
tp3_price = entry_price - (base_move * atrMult3 * tp_factor)
strategy.exit("TP1", "Short", qty_percent=tp1_size, limit=tp1_price)
strategy.exit("TP2", "Short", qty_percent=tp2_size, limit=tp2_price)
strategy.exit("TP3", "Short", qty_percent=tp3_size, limit=tp3_price)
// ————————
// Plotting
// ————————
plot(bbp, color=bbp >= 0 ? color.new(color.green, 0) : color.new(color.red, 0),
title="BBPower", style=plot.style_columns)
hline(0, "Zero Line", color=color.gray, linestyle=hline.style_dotted)
plot(zscore, title="Z-Score", color=color.blue, linewidth=2)
hline(zThreshold, "Upper Threshold", color=color.orange, linestyle=hline.style_dashed)
hline(-zThreshold, "Lower Threshold", color=color.orange, linestyle=hline.style_dashed)
- Segue-se uma tendência dinâmica com uma estratégia precisa de captação de lucro e de stop-loss
- Tendência dinâmica seguindo uma estratégia que combina a supertendência e a EMA
- Estratégia de cruzamento de média móvel exponencial dinâmica gerida pelo risco
- Estratégia de negociação de tendência de média móvel tripla exponencial
- Tendência de cruzamento avançada da EMA após a estratégia com sistema de gestão de paradas dinâmicas baseado no ATR
- Sistema de Estratégia Dinâmica Crossover Multi-Indicator: Um Modelo de Negociação Quantitativo Baseado na EMA, RVI e nos Sinais de Negociação
- MACD Crossover Momentum Strategy com Dynamic Take Profit e Stop Loss Optimization
- Sistema de Gestão de Capital Baseado na Força da Tendência do RSI e do ADX
- A taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação.
- Estratégia dinâmica de negociação de swing longo/curto com sistema de sinalização cruzada de média móvel
- Estratégia de negociação de padrões de velas de vários prazos
- Algoritmo de negociação de tendências dinâmicas de supertendências de vários prazos
- Estratégia avançada de negociação MACD crossover com gestão de risco adaptativa
- Estratégia quantitativa de captura de tendências baseada na análise do comprimento do candelabro
- Estratégia estatística de negociação de desvio padrão duplo VWAP
- Estratégia de rede longa baseada na utilização e no lucro-alvo
- Tendência cruzada de média móvel dinâmica de acordo com a estratégia com o sistema de gestão de riscos ATR
- Estratégia de cruzamento de tendências KDJ com múltiplos indicadores optimizada baseada no sistema de negociação de padrões estocásticos dinâmicos
- Método de negociação de média móvel de Heikin-Ashi
- A taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa de variação da taxa
- Estratégia de negociação quantitativa de sinal linear normalizado Z-Score
- Estratégia de negociação de tendências estocásticas inteligentes com vários parâmetros
- Método de negociação multi-EMA cruzado com estratégia de volume-preço
- Sistema de negociação de tendências de ruptura de níveis de preços de vários períodos baseado em níveis de preços fundamentais
- Estratégia de negociação de retrocesso de Fibonacci avançado
- Tendência de cruzamento avançada da EMA após a estratégia com sistema de gestão de paradas dinâmicas baseado no ATR
- Estratégia de negociação de bandas de Bollinger com sinal de retorno racional
- Tendência da média móvel de vários períodos seguindo a estratégia cruzada VWAP
- Opções de sinergia de média móvel dupla-RSI Estratégia quantitativa de negociação
- Avançada WaveTrend e Estratégia de Negociação de Fusão da EMA