이중 시간 프레임 추진 전략
저자:차오장, 날짜: 2024-04-25 17:33:02태그:SMA
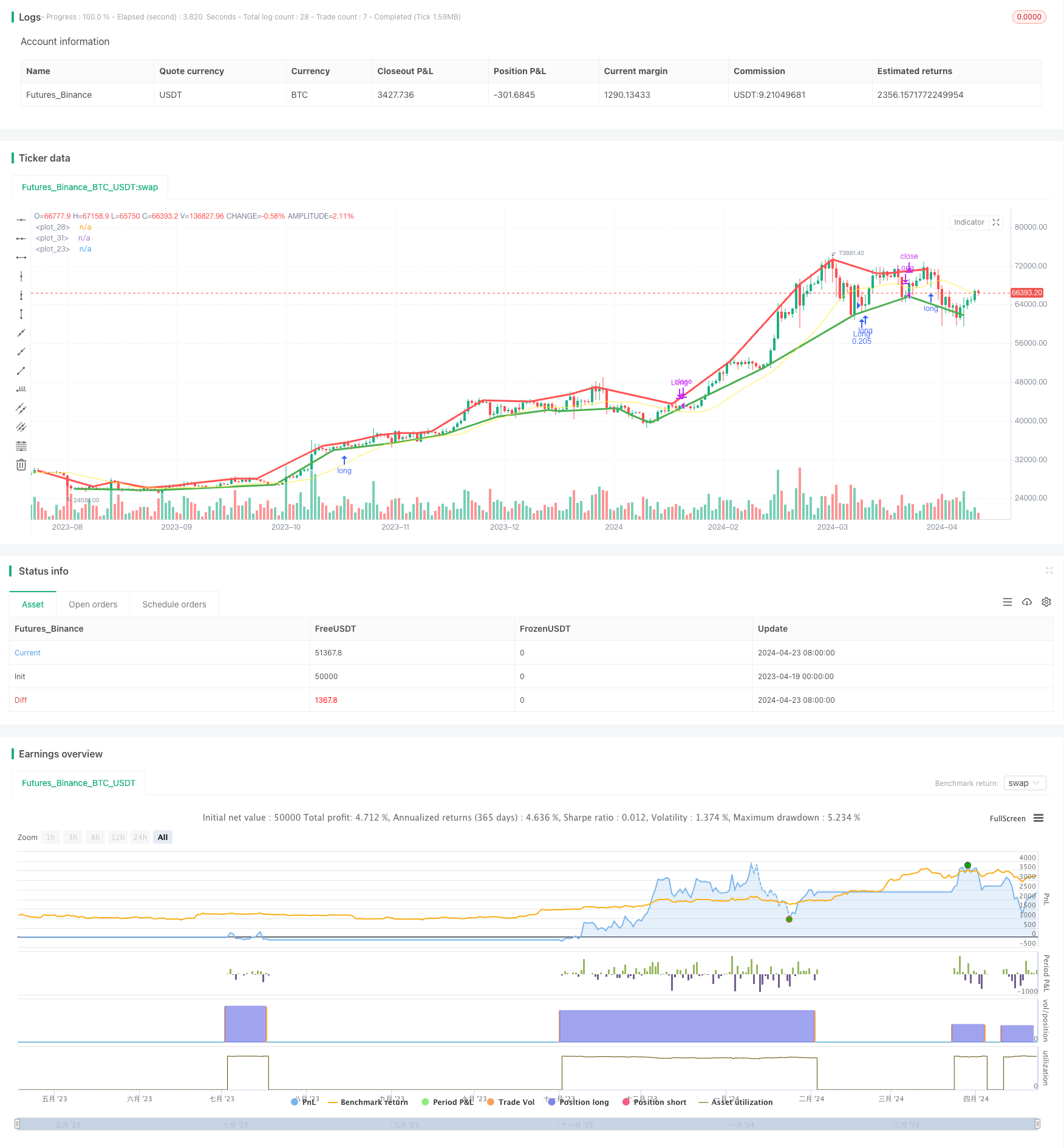
전반적인 설명
이 전략은 듀얼 타임프레임 모멘텀 전략이다. 단순 이동 평균 (SMA) 을 사용하여 더 높은 시간 프레임에서 트렌드 방향을 결정하고 피보트 포인트 (PivotLow 및 PivotHigh) 를 사용하여 더 낮은 시간 프레임에서 반전 지점을 식별합니다. 더 높은 시간 프레임에서 상승 추세가 나타나고 더 낮은 시간 프레임에서 상승 회전 지점이 나타나면 긴 시간으로 들어가고, 더 높은 시간 프레임에서 하락 추세가 나타나고 더 낮은 시간 프레임에서 하락 회전 지점이 나타나면 짧은 시간으로 들어갑니다.
전략 원칙
이 전략의 주요 원리는 더 높은 시간 프레임의 트렌드 방향이 더 낮은 시간 프레임의 움직임에 영향을 미칠 것이라는 것입니다. 더 높은 시간 프레임이 상승 추세를 보이는 경우, 더 낮은 시간 프레임에서 인회하는 것이 구매 기회일 가능성이 높습니다. 더 높은 시간 프레임이 하락 추세를 보이는 경우, 더 낮은 시간 프레임에서 리바운드하는 것이 단축 기회일 가능성이 높습니다. 이 전략은 더 높은 시간 프레임의 트렌드 방향을 결정하기 위해 간단한 이동 평균 (SMA) 을 사용하고, 낮은 시간 프레임에서 반전 지점을 식별하기 위해 피보트 로우 및 피보트 하이 (PivotLow 및 PivotHigh) 를 사용합니다.
전략적 장점
- 더 높은 시간 프레임의 영향을 더 낮은 시간 프레임에 활용하는 이중 시간 프레임 분석은 성공적인 거래의 확률을 증가시킵니다.
- 트렌드 방향을 결정하기 위해 SMA를 사용하는 것은 비교적 신뢰할 수 있으며, 반전 지점을 캡처하기 위해 피보트 포인트를 사용하는 것은 비교적 정확합니다.
- 매개 변수는 조절이 가능하여 전략이 매우 적응력이 있습니다. 사용자는 자신의 필요에 따라 더 높은 및 낮은 시간 프레임, SMA 기간 및 피보트 포인트의 매개 변수를 조정할 수 있습니다.
- 이 논리는 명확하고 이해하기 쉽고 적용하기 쉽습니다.
전략 위험
- 트렌드 변화의 위험: 더 높은 시간 프레임의 트렌드가 갑자기 변경되면, 더 낮은 시간 프레임은 아직 반응하지 않았을 수 있습니다.
- 매개 변수 설정의 위험. 부적절한 매개 변수 설정은 나쁜 전략 성과를 초래할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 너무 짧은 SMA 기간을 선택하는 것은 빈번한 거래로 이어질 수 있으며, 너무 긴 기간을 선택하는 것은 추세 판단에 차질을 초래할 수 있습니다.
- 극한 시장 조건의 위험: 극한 시장 조건 (비약 급격한 상승 또는 하락) 에서, 이 전략은 더 낮은 시간 프레임이 더 높은 시간 프레임의 추세를 따르지 않을 수 있기 때문에 실패할 수 있습니다.
전략 최적화 방향
- 트렌드 변화 검출을 추가합니다. 더 낮은 시간 프레임에서 거래를 더 빠르게 조정하기 위해 더 높은 시간 프레임의 트렌드가 변경되었는지 여부를 결정하기 위해 논리를 추가 할 수 있습니다.
- 매개 변수 선택 최적화 매개 변수 최적화 방법 (유전 알고리즘, 그리드 검색 등) 을 사용하여 최적의 매개 변수 조합을 찾을 수 있습니다.
- 리스크 통제를 추가합니다. 극단적인 시장 조건에서 손실을 줄이기 위해 리스크 제어 조치 (정지 손실, 위치 관리 등) 를 추가 할 수 있습니다.
- 다중 요인 융합: 다른 지표 또는 요인 (변동성, 부피 등) 을 전략의 안정성 향상을 위해 통합 할 수 있다고 간주 할 수 있습니다.
요약
이 이중 타임프레임 모멘텀 전략은 높은 시간 프레임과 낮은 시간 프레임 사이의 연결을 활용하여 높은 시간 프레임의 트렌드 방향을 결정하고 낮은 시간 프레임의 반전 지점을 캡처하여 트렌드 추적 및 반전 거래를 달성합니다. 전략은 명확한 논리와 명백한 장점을 가지고 있지만 또한 몇 가지 위험을 가지고 있습니다. 미래에 전략은 트렌드 변화 탐지, 매개 변수 최적화, 위험 제어 및 다중 요인 융합과 같은 측면에서 최적화되어 적응력과 탄력성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
/*backtest
start: 2023-04-19 00:00:00
end: 2024-04-24 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This Pine Script™ code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © Riester
//@version=5
strategy("Dual Timeframe Momentum", overlay=true, precision=6, pyramiding=0, initial_capital=1000, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=25.0, commission_value=0.05)
n = input.int(20, "Moving Average Period", minval=1)
src = input.source(close, "Source")
high_tf = input.timeframe("240", "Resolution")
pivot_l = input.int(5, "Pivot Let Bars")
pivot_r = input.int(2, "Pivot Right Bars")
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Calculations
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 1. Define low and high timeframe prices
low_src = src
high_src = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, high_tf, src)
// 2. Use simple moving average to determine trend of higher timeframe (up or down)
high_tf_ma = ta.sma(high_src, n)
plot(high_tf_ma, color=color.yellow)
high_tf_trend = high_tf_ma > high_tf_ma[1] ? 1 : -1
// 3. Use pivots to identify reversals on the low timeframe
low_tf_pl = ta.pivotlow(high_src, pivot_l, pivot_r)
plot(low_tf_pl, style=plot.style_line, linewidth=3, color= color.green, offset=-pivot_r)
low_tf_ph = ta.pivothigh(high_src, pivot_l, pivot_r)
plot(low_tf_ph, style=plot.style_line, linewidth=3, color= color.red, offset=-pivot_r)
bool long = low_tf_pl and high_tf_trend == 1
bool short = low_tf_ph and high_tf_trend == -1
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Plots
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// this message is an alert that can be sent to a webhook, which allows for simple automation if you have a server that listens to alerts and trades programmatically.
enter_long_alert = '{"side": "Long", "order": "Enter", "price": ' + str.tostring(open) + ', "timestamp": ' + str.tostring(timenow) + '}'
exit_long_alert = '{"side": "Long", "order": "Exit", "price": ' + str.tostring(open) + ', "timestamp": ' + str.tostring(timenow) + '}'
if long
strategy.entry(id="Long", direction=strategy.long, limit=open, alert_message=enter_long_alert)
if short
strategy.close(id="Long", comment="Close Long", alert_message=exit_long_alert)
- 보린저 밴드 및 RSI 통합을 통해 향상된 평균 역전 전략
- 멀티테크니컬 인디케이터 크로스 트렌드 추적 전략: RSI와 스토카스틱 RSI 시너지 거래 시스템
- 지능형 파동 트렌드 달러 비용 평균화 주기적 거래 전략
- MACD-RSI 크로스오버 트렌드
- 다중 SMA 구역의 파업과 동적 수익 잠금 양적 거래 전략
- 동적 파동 트렌드 추적 전략
- 부피 확증과 함께 구조의 해체 다 조건 지능형 거래 전략
- 다중 지표 동적 스톱 로스 동력 트렌드 거래 전략
- 거래 전략에 따른 다중 이동 평균 트렌드
- 멀티 필터 트렌드 돌파구 스마트 이동 평균 거래 전략
- 다중 지표 추세 옵션 거래 EMA 크로스 전략
- KRK aDa AI 향상과 함께 스토카스틱 느린 평균 반전 전략
- 피보트 포인트 및 기울기 기반의 실시간 트렌드 라인 거래
- EMA23/EMA50 이중 이동 평균 크로스오버 양적 거래 전략
- 수평선 파열과 함께 트렌드 포착 전략
- 다중 취득 전략의 이동 평균 크로스오버
- MACD 골든 크로스와 데스 크로스 전략
- MACD-V 및 피보나치 다중 시간 프레임 동적 영업 전략
- 트렌드 포착 전략
- 이동 평균과 볼린거 대역에 기초한 양적 거래 전략
- 볼링거 밴드 브레이크업 전략
- MACD BB 브레이크업 전략
- 웨이브트렌드 대폭 과판 리바운드 그리드 거래 전략
- MACD 크로스오버 전략
- ATR 기반의 리스크 관리로 최적화된 MACD 트렌드 추적 전략
- 제로래그 MACD 긴 짧은 전략
- BBSR 극단적 전략
- 모멘텀 RSI 인디케이터에 기초한 고주파 반전 거래 전략
- RSI 상대적 강도 지수 전략
- 볼링거 밴드 브레이크업 전략
- 돈치안 채널과 래리 윌리엄스 대형 무역 지수 전략